Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells, in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs as well as organism structure and function. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena.

In biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose the quaternary structure, tertiary structure, and secondary structure which is present in their native state, by application of some external stress or compound, such as a strong acid or base, a concentrated inorganic salt, an organic solvent, agitation and radiation, or heat. If proteins in a living cell are denatured, this results in disruption of cell activity and possibly cell death. Protein denaturation is also a consequence of cell death. Denatured proteins can exhibit a wide range of characteristics, from conformational change and loss of solubility or cofactors to aggregation due to the exposure of hydrophobic groups. The loss of solubility as a result of denaturation is called coagulation. Denatured proteins lose their 3D structure, and therefore, cannot function.
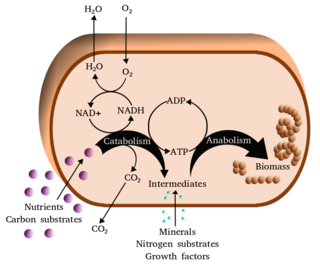
Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism.
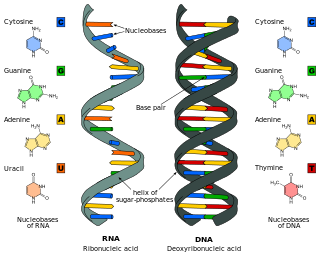
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is deoxyribose, a variant of ribose, the polymer is DNA.

Nucleotides are organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver.

Polysaccharides, or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin.

Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthesis is most commonly performed by ribosomes in cells. Peptides can also be synthesized in the laboratory. Protein primary structures can be directly sequenced, or inferred from DNA sequences.

Protein biosynthesis is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences.

The RNA world is a hypothetical stage in the evolutionary history of life on Earth, in which self-replicating RNA molecules proliferated before the evolution of DNA and proteins. The term also refers to the hypothesis that posits the existence of this stage.

A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biological processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. The most common macromolecules in biochemistry are biopolymers and large non-polymeric molecules such as lipids, nanogels and macrocycles. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes are also examples of macromolecules.

In polymer science, the polymer chain or simply backbone of a polymer is the main chain of a polymer. Polymers are often classified according to the elements in the main chains. The character of the backbone, i.e. its flexibility, determines the properties of the polymer. For example, in polysiloxanes (silicone), the backbone chain is very flexible, which results in a very low glass transition temperature of −123 °C. The polymers with rigid backbones are prone to crystallization in thin films and in solution. Crystallization in its turn affects the optical properties of the polymers, its optical band gap and electronic levels.

Biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes in living organisms. It deals with the structure and function of cellular components such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and other biomolecules.
The term amphibolic is used to describe a biochemical pathway that involves both catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism is a degradative phase of metabolism in which large molecules are converted into smaller and simpler molecules, which involves two types of reactions. First, hydrolysis reactions, in which catabolism is the breaking apart of molecules into smaller molecules to release energy. Examples of catabolic reactions are digestion and cellular respiration, where sugars and fats are broken down for energy. Breaking down a protein into amino acids, or a triglyceride into fatty acids, or a disaccharide into monosaccharides are all hydrolysis or catabolic reactions. Second, oxidation reactions involve the removal of hydrogens and electrons from an organic molecule. Anabolism is the biosynthesis phase of metabolism in which smaller simple precursors are converted to large and complex molecules of the cell. Anabolism has two classes of reactions. The first are dehydration synthesis reactions; these involve the joining of smaller molecules together to form larger, more complex molecules. These include the formation of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. The second are reduction reactions, in which hydrogens and electrons are added to a molecule. Whenever that is done, molecules gain energy.
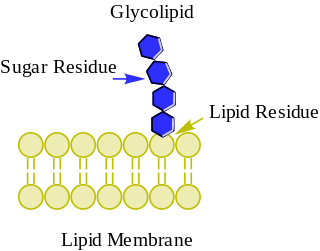
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment.
In molecular biology, biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.
Protein metabolism denotes the various biochemical processes responsible for the synthesis of proteins and amino acids (anabolism), and the breakdown of proteins by catabolism.
Biomolecular engineering is the application of engineering principles and practices to the purposeful manipulation of molecules of biological origin. Biomolecular engineers integrate knowledge of biological processes with the core knowledge of chemical engineering in order to focus on molecular level solutions to issues and problems in the life sciences related to the environment, agriculture, energy, industry, food production, biotechnology and medicine.
In biochemistry, two biopolymers are antiparallel if they run parallel to each other but with opposite directionality (alignments). An example is the two complementary strands of a DNA double helix, which run in opposite directions alongside each other.
This glossary of cellular and molecular biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts commonly used in the study of cell biology, molecular biology, and related disciplines, including genetics, biochemistry, and microbiology. It is split across two articles:
This glossary of cellular and molecular biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts commonly used in the study of cell biology, molecular biology, and related disciplines, including genetics, biochemistry, and microbiology. It is split across two articles: