The Android Dev Phone (ADP) is a SIM-unlocked and bootloader unlocked Android device that is designed for advanced developers. While developers can use regular consumer devices purchased at retail to test and use their apps, some developers may choose not to use a retail device, preferring an unlocked or no-contract device.
Rooting is the process by which users of Android devices can attain privileged control over various subsystems of the device, usually smartphones and tablets. Because Android is based on a modified version of the Linux kernel, rooting an Android device gives similar access to administrative (superuser) permissions as on Linux or any other Unix-like operating system such as FreeBSD or macOS.
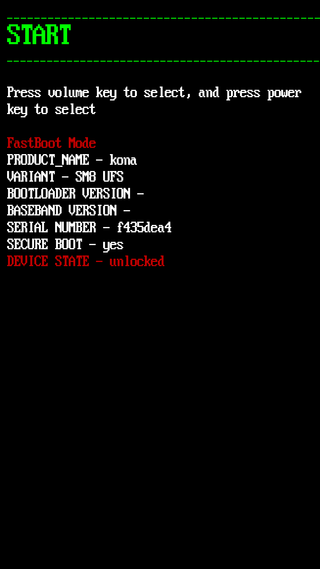
Fastboot is a communication protocol used primarily with Android devices. It is implemented in a command-line interface tool of the same name and as a mode of the bootloader of Android devices. The tool is included with the Android SDK package and used primarily to modify the flash filesystem via a USB connection from a host computer. It requires that the device be started in Fastboot mode. If the mode is enabled, it will accept a specific set of commands, sent through USB bulk transfers. Fastboot on some devices allows unlocking the bootloader, and subsequently, enables installing custom recovery image and custom ROM on the device. Fastboot does not require USB debugging to be enabled on the device. To use fastboot, a specific combination of keys must be held during boot.
The hacking of consumer electronics is a common practice that users perform to customize and modify their devices beyond what is typically possible. This activity has a long history, dating from the days of early computer, programming, and electronics hobbyists.
The Motorola Atrix 4G is an Android-based smartphone developed by Motorola, introduced at CES 2011 along with the Motorola Xoom, Motorola Droid Bionic, and Motorola Cliq 2 on January 5, 2011. It was made available in the first quarter of 2011.

The HTC Sensation is a smartphone designed and manufactured by HTC Corporation that runs the Android 2.3 Gingerbread software stock. Officially announced by HTC on April 12, 2011, the HTC Sensation was launched by Vodafone in key European markets including the United Kingdom on May 19, 2011 and by T-Mobile in the United States on June 12, 2011. It was HTC's fifth flagship Android phone and the first HTC phone to support the HTC Sense 3.0 user interface. At the time of its release, the Sensation XE was the world's fastest Android phone.

The Verizon Droid Razr is an Android-based, 4G LTE-capable smartphone designed by Motorola that launched on Verizon Wireless on November 11, 2011. It was announced on October 18, 2011 in New York City.

The Asus Eee Pad Transformer TF201 or Asus Eee Pad Transformer Prime is a 2-in-1 detachable tablet from the Asus Transformer Pad series. It is the world's first Android tablet computer with a quad-core processor, and a successor to the dual-core Asus Eee Pad Transformer. It runs Android 4.1. The Transformer Prime was announced by Asus on 9 November 2011. It was released in Taiwan on 1 December 2011, and in Canada and the United States during the week of 19 December 2011.

Wear OS is a version of Google's Android operating system designed for smartwatches and other wearables. By pairing with mobile phones running Android version 6.0 "Marshmallow" or newer, or iOS version 10.0 or newer with limited support from Google's pairing application, Wear OS integrates Google Assistant technology and mobile notifications into a smartwatch form factor. Wear OS is closed-source, in contrast to the free and open-source Android.

The Xiaomi Redmi 1S, code-named armani HM 1S, is a smartphone released in May 2014, developed by the Chinese company Xiaomi Inc. It is a part of the Redmi series of smartphones, and succeeded the Redmi 1. Visually similar to its predecessor, it comes with a 4.7-inch screen, a quad-core 1.6 GHz Cortex-A7 processor and runs Android version 4.3 (Jellybean), bundled with the proprietary MIUI v5 user interface, which can be upgraded to MIUI v9 based on Android 4.4.4 KTU84P.

Odin is a utility software program developed and used by Samsung internally which is used to communicate with Samsung devices in Odin mode. It can be used to flash a custom recovery firmware image to a Samsung Android device. Odin is also used for unbricking certain Android devices. Odin is the Samsung proprietary alternative to Fastboot.

Samsung Internet Browser is a desktop and mobile web browser developed by Samsung Electronics, based on the open-source Chromium project. It comes pre-installed on Samsung Galaxy devices and, since 2015, has been available for download from Google Play for all Android devices. It is also available for their Tizen-based smartwatch via the Galaxy Store.

postmarketOS is an operating system primarily for smartphones, based on the Alpine Linux distribution.

One UI is a user interface (UI) developed by Samsung Electronics for its Android devices running Android 9 "Pie" and later. Succeeding Samsung Experience and TouchWiz, it is designed to make using larger smartphones easier and be more visually appealing. To provide more clarity, some elements of the UI are tweaked to match colors that are based on the color of the user's phone. It was announced at Samsung Developer Conference in 2018, and was unveiled in Galaxy Unpacked in February 2019 alongside the Galaxy S10 series, Galaxy Buds and the Galaxy Fold.
HarmonyOS (HMOS) is a distributed operating system developed by Huawei for smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, smart watches, personal computers and other smart devices. It has a multikernel design with dual frameworks: the operating system selects suitable kernels from the abstraction layer in the case of devices that use diverse resources. The operating system was officially launched by Huawei in August 2019.
CalyxOS is an operating system for smartphones based on Android with mostly free and open-source software. It is produced by the Calyx Institute as part of its mission to "defend online privacy, security and accessibility."

The Android recovery mode is a mode of Android used for installing updates and wipe data. It consists of a Linux kernel with ramdisk on a separate partition from the main Android system.

Good Lock (Korean: 굿락) is a software suite to tweak and customize the user interface and experience on Samsung Galaxy devices. It is developed by Good Lock Labs in cooperation with Samsung, and can be downloaded from the Galaxy Store.

PixelExperience is a discontinued open-sourced custom ROM, or Android distribution, based on the stock Android AOSP that aimed to provide a bloat-free, stock-android, Pixel-like experience to a wide range of Android devices. The project, initiated by a community of developers in 2017, focused on delivering a clean, minimalistic, and visually appealing user interface reminiscent of Google's Pixel devices. Pixel Experience was designed to be as close to stock Android as possible, with a focus on reliability, security, stability, performance, battery life, and useful customizations.














