Galba was the sixth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 68 to 69. After his adoption by his stepmother, and before becoming emperor, he was known as Livius Ocella Sulpicius Galba. He was the first emperor in the Year of the Four Emperors and assumed the throne following Emperor Nero's suicide.

Year 193 (CXCIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sosius and Ericius. The denomination 193 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Marcus Didius Julianus was Roman emperor from March to June 193, during the Year of the Five Emperors. Julianus had a promising political career, governing several provinces, including Dalmatia and Germania Inferior, and defeated the Chauci and Chatti, two invading Germanic tribes. He was even appointed to the consulship in 175 along with Pertinax as a reward, before being demoted by Commodus. After this demotion, his early, promising political career languished.

Lucius Aelius Sejanus, commonly known as Sejanus, was a Roman soldier, friend and confidant of the Roman Emperor Tiberius. Of the Equites class by birth, Sejanus rose to power as prefect of the Praetorian Guard, of which he was commander from AD 14 until his execution for treason in AD 31.

The Praetorian Guard was an elite unit of the Imperial Roman army that served as personal bodyguards and intelligence agents for the Roman emperors.

The Revolt of the Batavi took place in the Roman province of Germania Inferior between AD 69 and 70. It was an uprising against the Roman Empire started by the Batavi, a small but militarily powerful Germanic tribe that inhabited Batavia, on the delta of the river Rhine. They were soon joined by the Celtic tribes from Gallia Belgica and some Germanic tribes.

Tiberius Claudius Pompeianus was a politician and military commander during the 2nd century in the Roman Empire. A general under the Emperor Marcus Aurelius, Pompeianus distinguished himself during Rome's wars against the Parthians and the Marcomanni. He was a member of the imperial family due to his marriage to Lucilla, a daughter of Marcus Aurelius, and was a key figure during the emperor's reign. Pompeianus was offered the imperial throne three times, though he refused to claim the title for himself.

The Jovians and Herculians were the senior palatine imperial guard units under the rule of Roman Emperor Diocletian. They continued in existence thereafter as senior units in the field armies of the Western and Eastern Roman Empires.

A barracks emperor was a Roman emperor who seized power by virtue of his command of the army. Barracks emperors were especially common from 235 to 284 AD, during the Crisis of the Third Century, which began with the assassination of Severus Alexander. Beginning with Maximinus Thrax, there were approximately fourteen barracks emperors in 33 years, which produced an average reign of a little over two years apiece. The resulting instability in the imperial office and the nearly-constant state of civil war and insurrection threatened to destroy the Roman Empire from within and left it vulnerable to attack from external adversaries.

The Aurelian Walls are a line of city walls built between 271 AD and 275 AD in Rome, Italy, during the reign of the Roman Emperor Aurelian. They superseded the earlier Servian Wall built during the 4th century BC.

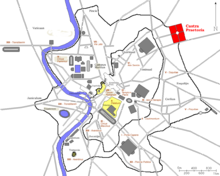
Castro Pretorio is the 18th rione of Rome (Italy), identified by the initials R. XVIII, and it is located within the Municipio I. The rione takes its name by the ruins of the Castrum Praetorium, the barracks of the Praetorian Guard, included in the Aurelian Walls.

The Year of the Five Emperors was AD 193, in which five men claimed the title of Roman emperor: Pertinax, Didius Julianus, Pescennius Niger, Clodius Albinus, and Septimius Severus. This year started a period of civil war when multiple rulers vied for the chance to become emperor.
Cornelius Repentinus was a Roman Senator who was active in the 2nd century AD. He held a number of positions during the reigns of emperors Marcus Aurelius, Commodus and Didius Julianus, which included suffect consul and Urban prefect of Rome.
The Classis Misenensis, later awarded the honorifics praetoria and Pia Vindex, was the senior fleet of the imperial Roman navy.

The history of the Roman Empire covers the history of ancient Rome from the fall of the Roman Republic in 27 BC until the abdication of Romulus Augustulus in AD 476 in the West, and the Fall of Constantinople in the East in AD 1453. Ancient Rome became a territorial empire while still a republic, but was then ruled by Roman emperors beginning with Augustus, becoming the Roman Empire following the death of the last republican dictator, the first emperor's adoptive father Julius Caesar.

Castro Pretorio is a station on Line B of the Rome Metro. It was opened on 8 December 1990 and is located on Viale Castro Pretorio, at its junction with Via San Martino della Battaglia, in the Castro Pretorio rione. Its exit overlooks the Castra Praetoria, now the site of the Biblioteca Nazionale Centrale.
Titus Flavius Claudius Sulpicianus was a Roman statesman who served as Senator and Consul suffectus. He unsuccessfully attempted to succeed his son-in-law Pertinax as Emperor in 193.

The Camp of Diocletian was a Roman military complex, or castra, built in the ancient city of Palmyra in the Syrian Desert. The complex was built under the Roman Emperor Diocletian in the late third-century CE and served as the military headquarters for the Legio I Illyricorum.

The castra of ancient Rome represent the complex of camps that housed the various military corps located in the city of Rome.
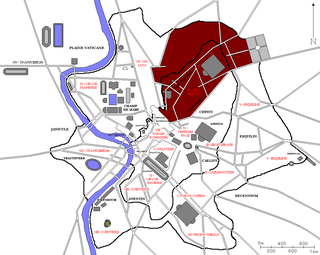
The Regio VI Alta Semita is the sixth regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio VI took its name from the street passing over the Quirinal Hill. It was a large regio that also encompassed the Viminal Hill, the lower slopes of the Pincian, and the valleys in-between.