
The Yangtze, Yangzi, or officially Chang Jiang is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains and flows 6,300 km (3,900 mi) in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea. It is the seventh-largest river by discharge volume in the world. Its drainage basin comprises one-fifth of the land area of China, and is home to nearly one-third of the country's population.

The Indus is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The 3,180 km (1,980 mi) river rises in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, bends sharply to the left after the Nanga Parbat massif, and flows south-by-southwest through Pakistan, before emptying into the Arabian Sea near the port city of Karachi.

The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system on the North American continent, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for 2,340 miles (3,770 km) to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is 1,151,000 sq mi (2,980,000 km2), of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.

The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The longest river in Africa, it has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer. Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About 6,650 km (4,130 mi) long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Republic of the Sudan, and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt, Sudan and South Sudan. Additionally, the Nile is an important economic river, supporting agriculture and fishing.

The Ohio River is a 981-mile (1,579 km) long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from far-western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illinois. It is the third largest river by discharge volume in the United States and the largest tributary by volume of the north-south flowing Mississippi River that divides the eastern from western United States. It is also the 6th oldest river on the North American continent. The river flows through or along the border of six states, and its drainage basin includes parts of 14 states. Through its largest tributary, the Tennessee River, the basin includes several states of the southeastern U.S. It is the source of drinking water for three million people.

The Rhine is one of the major European rivers. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein, Swiss-Austrian, Swiss-German borders. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border, after which it flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally in Germany the Rhine turns into a predominantly westerly direction and flows into the Netherlands where it eventually empties into the North Sea.

The Tiber is the third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing 406 km (252 mi) through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the River Aniene, to the Tyrrhenian Sea, between Ostia and Fiumicino. It drains a basin estimated at 17,375 km2 (6,709 sq mi). The river has achieved lasting fame as the main watercourse of the city of Rome, which was founded on its eastern banks.

The Rio Grande, known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The length of the Rio Grande is 1,896 miles (3,051 km). It originates in south-central Colorado, in the United States, and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. The Rio Grande drainage basin (watershed) has an area of 182,200 square miles (472,000 km2); however, the endorheic basins that are adjacent to and within the greater drainage basin of the Rio Grande increase the total drainage-basin area to 336,000 square miles (870,000 km2).

The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge volume, following only the Amazon. It is also the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths around 219.5 m (720 ft). The Congo-Lualaba-Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,920 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,120 mi).

The Jordan River or River Jordan, also known as Nahr Al Sharieat, is a 251-kilometre-long (156 mi) river in the Middle East that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and on to the Dead Sea. Jordan and the Golan Heights border the river to the east, while the West Bank and Israel lie to its west. Both Jordan and the West Bank take their names from the river.

The Hudson River is a 315-mile (507 km) river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York in the United States. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the Upper New York Bay between New York City and Jersey City, eventually draining into the Atlantic Ocean at New York Harbor. The river serves as a political boundary between the states of New Jersey and New York at its southern end. Farther north, it marks local boundaries between several New York counties. The lower half of the river is a tidal estuary, deeper than the body of water into which it flows, occupying the Hudson Fjord, an inlet which formed during the most recent period of North American glaciation, estimated at 26,000 to 13,300 years ago. Even as far north as the city of Troy, the flow of the river changes direction with the tides.
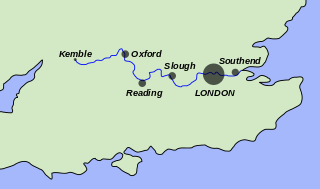
The River Thames, known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England, including London. At 215 mi (346 km), it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn.

The Río de la Plata, called River Plate in British English and the Commonwealth and La Plata River in other English-speaking countries, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and forms a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf, or a marginal sea. If considered a river, it is the widest in the world, with a maximum width of 220 kilometres (140 mi).

The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma and the extreme southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover a significant portion of northern Arkansas and most of the southern half of Missouri, extending from Interstate 40 in central Arkansas to Interstate 70 in central Missouri.

The headwaters of a river or stream is the farthest place in that river or stream from its estuary or downstream confluence with another river, as measured along the course of the river. It is also known as a river's source.

The Jhelum River is a river in the northern Indian subcontinent. It originates at Verinag and flows through the Indian administered territory of Jammu and Kashmir, to the Pakistani-administered territory of Azad Kashmir, and then into the Pakistani province of Punjab. It is the westernmost of the five rivers of the Punjab region, and flows through the Kashmir Valley. It is a tributary of the Chenab River and has a total length of about 725 kilometres (450 mi).

A stream is a continuous body of surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long large streams are usually called rivers, while smaller, less voluminous and more intermittent streams are known as streamlets, brooks or creeks, etc.

A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as stream, creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague.

The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through much of Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest into the Black Sea. Its longest headstream Breg rises in Furtwangen im Schwarzwald, while the river carries its name from its source confluence in Donaueschingen onwards.

A river mouth is where a river flows into a larger body of water, such as another river, a lake/reservoir, a bay/gulf, a sea, or an ocean. At the river mouth, sediments are often deposited due to the slowing of the current reducing the carrying capacity of the water.






















