
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal frame to which the organs and soft tissues attach; and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal structure supported by the hydrostatic pressure of body fluids.

The larynx, commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word 'larynx' comes from the Ancient Greek word lárunx ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ

The rib cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrate animals that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels. The circumferential enclosure formed by left and right rib cages, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi-rigid bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdles to form the core part of the axial skeleton.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The rima glottidis is the opening between the two true vocal cords anteriorly, and the two arytenoid cartilages posteriorly. It is part of the larynx.
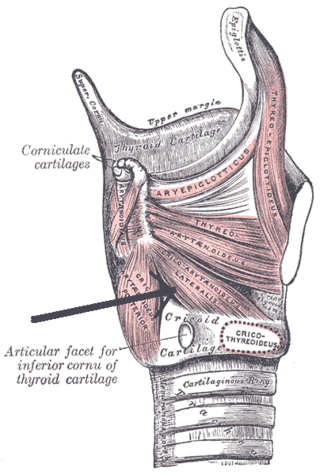
The lateral cricoarytenoid is an intrinsic muscle of the larynx. It attaches at the cricoid cartilage anteriorly, and at the arytenoid cartilage of the same side posteriorly. It is innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. It acts to close the rima glottidis, thus closing the airway.

The posterior cricoarytenoid muscle is a intrinsic muscle of the larynx. It arises from the cricoid cartilage; it inserts onto the arytenoid cartilage of the same side. It is innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Each acts to open the vocal folds by pulling the vocal fold of the same side laterally. It participates in the production of sounds.

The cricoid cartilage, or simply cricoid or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment site for muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in producing speech.

The cricothyroid muscle is the only tensor muscle of the larynx aiding with phonation. It is innervated by the superior laryngeal nerve. Its action tilts the thyroid forward to help tense the vocal cords, thus increasing the pitch of the voice.

The arytenoid cartilages are a pair of small three-sided pyramids which form part of the larynx. They are the site of attachment of the vocal cords. Each is pyramidal or ladle-shaped and has three surfaces, a base, and an apex. The arytenoid cartilages allow for movement of the vocal cords by articulating with the cricoid cartilage. They may be affected by arthritis, dislocations, or sclerosis.

The inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a skeletal muscle of the neck. It is the thickest of the three outer pharyngeal muscles. It arises from the sides of the cricoid cartilage and the thyroid cartilage. It is supplied by the vagus nerve. It is active during swallowing, and partially during breathing and speech. It may be affected by Zenker's diverticulum.

The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches, are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches.

The thyroarytenoid muscle is a broad, thin muscle that forms the body of the vocal fold and that supports the wall of the ventricle and its appendix. It functions to shorten the vocal folds.

The oblique arytenoid is bilaterally paired intrinsic muscle of the larynx. It is superficial to the transverse arytenoid; the oblique and transverse arytenoids are often considered two parts of a single muscle - the interarytenoid muscle.
The cricoarytenoid ligament extends from the lamina of the cricoid cartilage to the medial surface of the base and muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage.

The muscular process of arytenoid cartilage is the posterolateral projection of the lateral angle of the base of the arytenoid cartilage. The muscular process gives insertion to the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles behind, and to the lateral cricoarytenoid muscles in front.

In the human larynx, the vocal process is the anterior angle of the base of the arytenoid cartilage, as it projects horizontally forward and gives attachment to the vocal ligament.
Thyroplasty is a phonosurgical technique designed to improve the voice by altering the thyroid cartilage of the larynx, which houses the vocal cords in order to change the position or the length of the vocal cords.
Arytenoid adduction is a surgical procedure used to treat vocal cord paralysis. A suture is used to emulate the action of the lateral cricoarytenoid muscle and position the paralyzed vocal cord closer to the midline. This allows the two vocal cords to meet and can improve speaking and swallowing ability for affected patients. Arytenoid adduction is often performed in conjunction with medialization thyroplasty.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.













