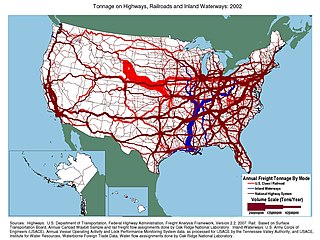
Transportation in the United States is facilitated by road, air, rail, and waterways. The vast majority of passenger travel occurs by automobile for shorter distances, and airplane for longer distances. In descending order, most cargoes travel by railroad, truck, pipeline, or boat; air shipping is typically used only for perishables and premium express shipments. Transportation is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions by the United States.

The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Construction of the system was authorized by the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956. The system extends throughout the contiguous United States and has routes in Hawaii, Alaska, and Puerto Rico.

The Historic Columbia River Highway is an approximately 75-mile-long (121 km) scenic highway in the U.S. state of Oregon between Troutdale and The Dalles, built through the Columbia River Gorge between 1913 and 1922. As the first planned scenic roadway in the United States, it has been recognized in numerous ways, including a listing on the National Register of Historic Places as a National Historic Landmark, designation as a National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark by the American Society of Civil Engineers, and considered a "destination unto itself" as an All-American Road by the U.S. Secretary of Transportation. The historic roadway was bypassed by the present Columbia River Highway No. 2 from the 1930s to the 1950s, leaving behind the old two-lane road. The road is now mostly owned and maintained by the state through the Oregon Department of Transportation as the Historic Columbia River Highway No. 100 or the Oregon Parks and Recreation Department as the Historic Columbia River Highway State Trail.
M-1, commonly known as Woodward Avenue, is a north–south state trunkline highway in the Metro Detroit area of the US state of Michigan. The highway, called "Detroit's Main Street", runs from Detroit north-northwesterly to Pontiac. It is one of the five principal avenues of Detroit, along with Michigan, Grand River, Gratiot, and Jefferson avenues. These streets were platted in 1805 by Judge Augustus B. Woodward, namesake to Woodward Avenue. The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) has listed the highway as the Automotive Heritage Trail, an All-American Road in the National Scenic Byways Program. It has also been designated a Pure Michigan Byway by the Michigan Department of Transportation (MDOT), and was also included in the MotorCities National Heritage Area designated by the US Congress in 1998.

The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program and the Federal Lands Highway Program. Its role had previously been performed by the Office of Road Inquiry, Office of Public Roads and the Bureau of Public Roads.
The Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (PennDOT) oversees transportation issues in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. The administrator of PennDOT is the Pennsylvania Secretary of Transportation, currently Yassmin Gramian. Presently, PennDOT supports over 40,500 miles (65,200 km) of state roads and highways, about 25,000 bridges, as well as new roadway construction, the exception being the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission, although they currently follow PennDOT policies and procedures. In addition, other modes of transportation are supervised or supported by PennDOT. These include aviation, rail traffic, mass transit, intrastate highway shipping traffic, motor vehicle safety & licensing, and driver licensing. PennDOT also supports the Ports of Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, and Erie. The current budget is approximately $3.8 billion in federal and state funds. The state budget is supported by the motor vehicle fuels tax which is dedicated solely to transportation issues.

Interstate 205 (I-205) is an east–west auxiliary Interstate Highway in the San Joaquin Valley in Northern California. It runs from I-5 west to I-580. Along with those highways, I-205 forms the north side of a triangle around the city of Tracy. The route provides access from the San Francisco Bay Area to the northern San Joaquin Valley.
The Tennessee Department of Transportation (TDOT) is a multimodal agency with statewide responsibilities in roadways, aviation, public transit, waterways, and railroads. The mission of TDOT is to provide a safe and reliable transportation system for people, goods, and services that supports economic prosperity in Tennessee.
Texas state highways are a network of highways owned and maintained by the U.S. state of Texas. The Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) is the state agency responsible for the day-to-day operations and maintenance of the system. Texas has the largest state highway system, followed closely by North Carolina's state highway system. In addition to the nationally numbered Interstate Highways and U.S. Highways, the highway system consists of a main network of state highways, loops, spurs, and beltways that provide local access to the other highways. The system also includes a large network of farm to market roads that connect rural areas of the state with urban areas and the rest of the state highway system. The state also owns and maintains some park and recreational roads located near and within state and national parks, as well as recreational areas. All state highways, regardless of classification, are paved roads. The Old San Antonio Road, also known as the El Camino Real, is the oldest highway in the United States, first being blazed in 1691. The length of the highways varies from US 83's 893.4 miles (1,437.8 km) inside the state borders to Spur 200 at just 0.05 miles long.

The Oklahoma Department of Transportation (ODOT) is an agency of the government of Oklahoma responsible for the construction and maintenance of the state's transportation infrastructure. Under the leadership of the Oklahoma Secretary of Transportation and ODOT Executive Director, the Department maintains public infrastructure that includes highways and state-owned railroads and administers programs for county roads, city streets, public transit, passenger rail, waterways and active transportation. Along with the Oklahoma Turnpike Authority, the Department is the primary infrastructure construction and maintenance agency of the State.

The Indiana Department of Transportation (INDOT) is a governmental agency of the U.S. state of Indiana charged with maintaining and regulating transportation and transportation related infrastructure such as state owned airports, state highways and state owned canals or railroads.

The Texas Department of Transportation is a government agency in the American state of Texas. Though the public face of the agency is generally associated with the construction and maintenance of the state's immense state highway system, the agency is also responsible for overseeing aviation, rail, and public transportation systems in the state.
The Nebraska Department of Transportation (NDOT) is the state government agency charged with building and maintaining the state and Federal highways in the U.S. State of Nebraska, as well as the state's airports. The main headquarters of the agency is located in Lincoln, the capital city. There are currently eight NDOT district offices located across the state.
The South Carolina Department of Transportation (SCDOT) is a government agency in the US state of South Carolina. Its mission is to build and maintain roads and bridges and administer mass transit services.

The Montana Department of Transportation (MDT) is a governmental agency in the U.S. state of Montana, responsible for numerous programs related to the construction, maintenance, and monitoring of Montana's transportation infrastructure and operations. While most of MDT's programs relate to the state's highway network, Montana's railroads and airports are also under the agency's purview.

The James Earl Rudder State Office Building is a historic office building in downtown Austin, Texas, USA. Built in 1918, the five-story structure features 18-foot ceilings and terrazzo and marble flooring.

The Board of Road Commissioners for Alaska, more commonly known as the Alaska Road Commission or ARC, was created in 1905 as a board of the U.S. War Department. It was responsible for the construction and improvement of many important Alaska highways, such as the Richardson Highway, Steese Highway, Elliot Highway and Edgerton Highway, among others.

The primary highway system makes up over 9,000 miles (14,000 km), a mere 8 percent of the U.S. state of Iowa's public road system. The Iowa Department of Transportation is responsible for the day-to-day maintenance of the primary highway system, which consists of Interstate Highways, United States Highways, and Iowa state highways. Currently, the longest primary highway is U.S. Route 30 at 332 miles (534 km). The shortest highway is Interstate 129 at 0.27 miles (0.43 km).

The Arkansas Highway System is made up of all the highways designated as Interstates, U.S. Highways and State Highways in the US state of Arkansas. The system is maintained by the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ArDOT), known as the Arkansas State Highway Department (AHD) until 1977 and the Arkansas State Highway and Transportation Department (AHTD) from 1977 to 2017. The system contains 16,442.90 miles (26,462.28 km) of Interstates, U.S. Routes, state highways, and special routes. The shortest members are unsigned state highways Arkansas Highway 806 and Arkansas Highway 885, both 0.09 miles (0.14 km) in length. The longest route is U.S. Route 67, which runs 296.95 miles (477.89 km) from Texarkana to Missouri.

The Wisconsin State Trunk Highway System is the state highway system of the U.S. state of Wisconsin, including Wisconsin's segments of the Interstate Highway System and the United States Numbered Highway System, in addition to its other state trunk highways. These separate types of highways are respectively designated with an I-, US, or STH- prefix. The system also includes minor roads designated as Scenic Byways, four routes intended to promote tourism to scenic and historic areas of the state; and as Rustic Roads, lightly-traveled and often unpaved local roads which the state has deemed worthy of preservation and protection. The state highway system, altogether totaling 11,753 miles (18,915 km) across all of Wisconsin's 72 counties, is maintained by the Wisconsin Department of Transportation (WisDOT).
















