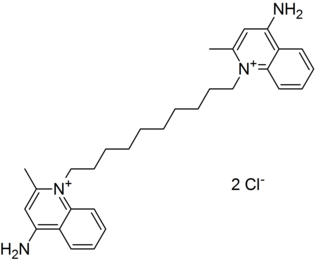A bactericide or bacteriocide, sometimes abbreviated Bcidal, is a substance which kills bacteria. Bactericides are disinfectants, antiseptics, or antibiotics. However, material surfaces can also have bactericidal properties based solely on their physical surface structure, as for example biomaterials like insect wings.
An antiseptic is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue to reduce the possibility of sepsis, infection or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from antibiotics by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from disinfectants, which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects.

A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than sterilization, which is an extreme physical or chemical process that kills all types of life. Disinfectants are generally distinguished from other antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics, which destroy microorganisms within the body, and antiseptics, which destroy microorganisms on living tissue. Disinfectants are also different from biocides—the latter are intended to destroy all forms of life, not just microorganisms. Disinfectants work by destroying the cell wall of microbes or interfering with their metabolism. It is also a form of decontamination, and can be defined as the process whereby physical or chemical methods are used to reduce the amount of pathogenic microorganisms on a surface.

Benzalkonium chloride, also known as alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride (ADBAC) and by the trade name Zephiran, is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. ADBACs have three main categories of use: as a biocide, a cationic surfactant, and a phase transfer agent. ADBACs are a mixture of alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chlorides, in which the alkyl group has various even-numbered alkyl chain lengths.
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms (microbicide) or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals are used against fungi. They can also be classified according to their function. The use of antimicrobial medicines to treat infection is known as antimicrobial chemotherapy, while the use of antimicrobial medicines to prevent infection is known as antimicrobial prophylaxis.

In organic chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively-charged polyatomic ions of the structure [NR4]+, where R is an alkyl group, an aryl group or organyl group. Unlike the ammonium ion and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule.

Cetrimonium bromide ([(C16H33)N(CH3)3]Br; cetyltrimethylammonium bromide; hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide; CTAB) is a quaternary ammonium surfactant.
Cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) is a cationic quaternary ammonium compound used in some types of mouthwashes, toothpastes, lozenges, throat sprays, breath sprays, and nasal sprays. It is an antiseptic that kills bacteria and other microorganisms. It has been shown to be effective in preventing dental plaque and reducing gingivitis. It has also been used as an ingredient in certain pesticides. Though one study seems to indicate cetylpyridinium chloride does not cause brown tooth stains, at least one mouthwash containing CPC as an active ingredient bears the warning label "In some cases, antimicrobial rinses may cause surface staining to teeth," following a failed class-action lawsuit brought by customers whose teeth were stained.

Benzethonium chloride, also known as hyamine is a synthetic quaternary ammonium salt. This compound is an odorless white solid, soluble in water. It has surfactant, antiseptic, and anti-infective properties, and it is used as a topical antimicrobial agent in first aid antiseptics. It is also found in cosmetics and toiletries such as soap, mouthwashes, anti-itch ointments, and antibacterial moist towelettes. Benzethonium chloride is also used in the food industry as a hard surface disinfectant.

Lysol is a brand of American cleaning and disinfecting products distributed by Reckitt, which markets the similar Dettol or Sagrotan in other markets. The line includes liquid solutions for hard and soft surfaces, air treatment, and hand washing. The active ingredient in many Lysol products is benzalkonium chloride, but the active ingredient in the Lysol "Power and Free" line is hydrogen peroxide. Lysol has been used since its invention in the late 19th century as a household and industrial cleaning agent, and previously as a medical disinfectant.

Mercuric amidochloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Hg(NH2)Cl.
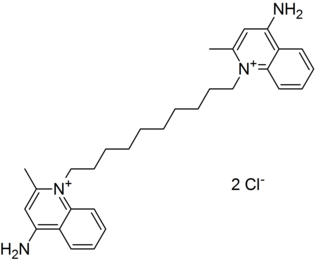
Dequalinium is a quaternary ammonium cation and bolaamphiphile commonly available as the dichloride salt. It is useful as an antiseptic and disinfectant. The bromide, iodide, acetate, and undecenoate salts are known as well. Dequalinium chloride is the active ingredient of several medications.
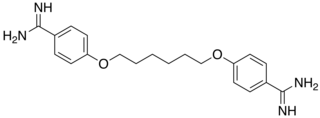
Hexamidine is an antiseptic and disinfectant. Hexomedine is the trade name of a diisethionate solution (1/1.000) of hexamidine. Hexamidine is used primarily as its diisethionate salt, which is more water-soluble than the dihydrochloride. The dihydrochloride was first synthesized and patented as a trypanocide for May & Baker in 1939. Its amoebicidal properties emerged in the 1990s. The exact mechanism of its biocidal action is unknown, but presumed similar to quaternary ammonium compounds, involving binding to the negatively charged lipid membranes of pathogens. Hexamidine and its shorter congener, propamidine, are used as antiseptics and preservatives in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. They are particularly used for the topical treatment of acanthamoebiasis.
Stearalkonium chloride is a type of benzalkonium chloride which is used as an anti-static agent, a surfactant and an antimicrobial. It is an ingredient in some cosmetics and hair care products, particularly conditioners. It was originally designed by the fabric industry for use as a fabric softener.
A virucide is any physical or chemical agent that deactivates or destroys viruses. The substances are not only virucidal but can be also bactericidal, fungicidal, sporicidal or tuberculocidal.
Benzododecinium bromide is a quaternary ammonium compound used as antiseptic and disinfectant. It is highly soluble in water and has properties of cationic surfactant.

Tetramethylammonium chloride is one of the simplest quaternary ammonium salts, with four methyl groups tetrahedrally attached to the central N. The chemical formula (CH3)4N+Cl− is often abbreviated further as Me4N+Cl−. It is a hygroscopic colourless solid that is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. Tetramethylammonium chloride is a major industrial chemical, being used widely as a chemical reagent and also as a low-residue bactericide in such processes as hydrofracking. In the laboratory, it has fewer synthetic chemical applications than quaternary ammonium salts containing longer N-alkyl substituents, which are used extensively as phase-transfer catalysts.
Alkaline copper quaternary, usually abbreviated ACQ, is a type of water-based wood preservative product containing a soluble copper(II) complex and quaternary ammonium alkyl- or aryl-substituted compounds ("quats"). Thus the product was originally called ammoniacal copper/quaternary ammonium.
Polymers with the ability to kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses are classified as antimicrobial agents. This class of polymers consists of natural polymers with inherent antimicrobial activity and polymers modified to exhibit antimicrobial activity. Polymers are generally nonvolatile, chemically stable, and can be chemically and physically modified to display desired characteristics and antimicrobial activity. Antimicrobial polymers are a prime candidate for use in the food industry to prevent bacterial contamination and in water sanitation to inhibit the growth of microorganisms in drinking water.
An antimicrobial surface is coated by an antimicrobial agent that inhibits the ability of microorganisms to grow on the surface of a material. Such surfaces are becoming more widely investigated for possible use in various settings including clinics, industry, and even the home. The most common and most important use of antimicrobial coatings has been in the healthcare setting for sterilization of medical devices to prevent hospital associated infections, which have accounted for almost 100,000 deaths in the United States. In addition to medical devices, linens and clothing can provide a suitable environment for many bacteria, fungi, and viruses to grow when in contact with the human body which allows for the transmission of infectious disease.