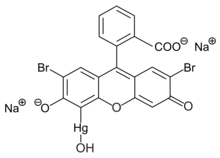
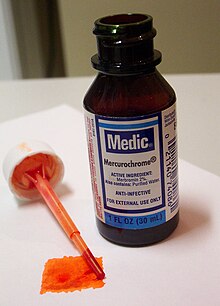
A bactericide or bacteriocide, sometimes abbreviated Bcidal, is a substance which kills bacteria. Bactericides are disinfectants, antiseptics, or antibiotics. However, material surfaces can also have bactericidal properties based solely on their physical surface structure, as for example biomaterials like insect wings.

Phenol is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group bonded to a hydroxy group. Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.
An antiseptic is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue to reduce the possibility of sepsis, infection or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from antibiotics by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from disinfectants, which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects.

An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as Na+(aq) + Cl−(aq). The word aqueous means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified.

Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed with water. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide.

Benzalkonium chloride, also known as alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride (ADBAC) and by the trade name Zephiran, is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. ADBACs have three main categories of use: as a biocide, a cationic surfactant, and a phase transfer agent. ADBACs are a mixture of alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chlorides, in which the alkyl group has various even-numbered alkyl chain lengths.
ATC code D08Antiseptics and disinfectants is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup D08 is part of the anatomical group D Dermatologicals.

Povidone-iodine (PVP-I), also known as iodopovidone, is an antiseptic used for skin disinfection before and after surgery. It may be used both to disinfect the hands of healthcare providers and the skin of the person they are caring for. It may also be used for minor wounds. It may be applied to the skin as a liquid or a powder.

Tin(II) chloride, also known as stannous chloride, is a white crystalline solid with the formula SnCl2. It forms a stable dihydrate, but aqueous solutions tend to undergo hydrolysis, particularly if hot. SnCl2 is widely used as a reducing agent (in acid solution), and in electrolytic baths for tin-plating. Tin(II) chloride should not be confused with the other chloride of tin; tin(IV) chloride or stannic chloride (SnCl4).

The oligodynamic effect is a biocidal effect of metals, especially heavy metals, that occurs even in low concentrations. This effect is attributed to the antibacterial behavior of metal ions, which are absorbed by bacteria upon contact and damage their cell membranes.

Hand sanitizer is a liquid, gel or foam generally used to kill many viruses/bacteria/microorganisms on the hands. It can also come in the form of a cream, spray, or wipe. In most settings, hand washing with soap and water is generally preferred. Hand sanitizer is less effective at killing certain kinds of germs, such as norovirus and Clostridium difficile, and unlike hand washing, it cannot physically remove harmful chemicals. People may incorrectly wipe off hand sanitizer before it has dried, and some are less effective because their alcohol concentrations are too low.

Organomercury chemistry refers to the study of organometallic compounds that contain mercury. Typically the Hg–C bond is stable toward air and moisture but sensitive to light. Important organomercury compounds are the methylmercury(II) cation, CH3Hg+; ethylmercury(II) cation, C2H5Hg+; dimethylmercury, (CH3)2Hg, diethylmercury and merbromin ("Mercurochrome"). Thiomersal is used as a preservative for vaccines and intravenous drugs.
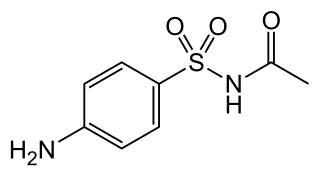
Sulfacetamide is a sulfonamide antibiotic.

Benzethonium chloride, also known as hyamine is a synthetic quaternary ammonium salt. This compound is an odorless white solid, soluble in water. It has surfactant, antiseptic, and anti-infective properties, and it is used as a topical antimicrobial agent in first aid antiseptics. It is also found in cosmetics and toiletries such as soap, mouthwashes, anti-itch ointments, and antibacterial moist towelettes. Benzethonium chloride is also used in the food industry as a hard surface disinfectant.

Mercuric amidochloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Hg(NH2)Cl.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. It has been used, as a component of vinegar, throughout history from at least the third century BC.

Antoine Germain Labarraque was a French chemist and pharmacist, notable for formulating and finding important uses for "Eau de Labarraque" or "Labarraque's solution", a solution of sodium hypochlorite widely used as a disinfectant and deodoriser.
Aluminium triacetate, formally named aluminium acetate, is a chemical compound with composition Al(CH
3CO
2)
3. Under standard conditions it appears as a white, water-soluble solid that decomposes on heating at around 200 °C. The triacetate hydrolyses to a mixture of basic hydroxide / acetate salts, and multiple species co-exist in chemical equilibrium, particularly in aqueous solutions of the acetate ion; the name aluminium acetate is commonly used for this mixed system.
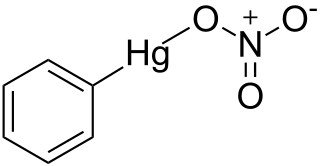
Phenylmercuric nitrate is an organomercury compound with powerful antiseptic and antifungal effects. It was once commonly used as a topical solution for disinfecting wounds, but as with all organomercury compounds it is highly toxic, especially to the kidneys, and is no longer used in this application. However it is still used in low concentrations as a preservative in eye drops for ophthalmic use, making it one of the few organomercury derivatives remaining in current medical use.