
Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (ALSA) is a software framework and part of the Linux kernel that provides an application programming interface (API) for sound card device drivers.

A mixing console or mixing desk is an electronic device for mixing audio signals, used in sound recording and reproduction and sound reinforcement systems. Inputs to the console include microphones, signals from electric or electronic instruments, or recorded sounds. Mixers may control analog or digital signals. The modified signals are summed to produce the combined output signals, which can then be broadcast, amplified through a sound reinforcement system or recorded.
FFmpeg is a free and open-source software project consisting of a suite of libraries and programs for handling video, audio, and other multimedia files and streams. At its core is the command-line ffmpeg tool itself, designed for processing of video and audio files. It is widely used for format transcoding, basic editing, video scaling, video post-production effects and standards compliance.

Audacity is a free and open-source digital audio editor and recording application software, available for Windows, macOS, Linux, and other Unix-like operating systems.

Virtual Studio Technology (VST) is an audio plug-in software interface that integrates software synthesizers and effects units into digital audio workstations. VST and similar technologies use digital signal processing to simulate traditional recording studio hardware in software. Thousands of plugins exist, both commercial and freeware, and many audio applications support VST under license from its creator, Steinberg.

A sound reinforcement system is the combination of microphones, signal processors, amplifiers, and loudspeakers in enclosures all controlled by a mixing console that makes live or pre-recorded sounds louder and may also distribute those sounds to a larger or more distant audience. In many situations, a sound reinforcement system is also used to enhance or alter the sound of the sources on the stage, typically by using electronic effects, such as reverb, as opposed to simply amplifying the sources unaltered.

LiVES (LiVES Editing System) is a free and open-source video editing software and VJ tool, released under the GNU General Public License version 3 or later. There are binary versions available for most popular Linux distributions (including Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, Suse, Gentoo, Slackware, Arch Linux, Mandriva and Mageia). There are also ports for BSD, and it will run under Solaris and IRIX. It has been compiled under OS X Leopard, but not thoroughly tested on that platform. In early 2019, a version for Microsoft Windows was announced, with a release slated for in the second half of 2019.

Moogerfooger is the trademark for a series of analog effects pedals manufactured by Moog Music. There are currently eight different pedals produced; however, one of these models is designed for processing control voltages rather than audio signal. A sixth model, the Analog Delay, was released in a limited edition of 1000 units and has become a collector's item. Moog Music announced on August 28, 2018, that the Moogerfooger, CP-251, Minifooger, Voyager synthesizers, and some other product lines were being built using the remaining parts on hand and discontinued thereafter.
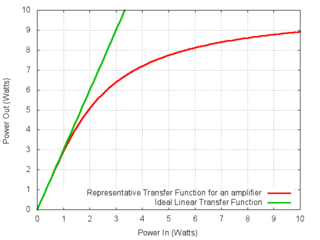
Gain compression is a reduction in differential or slope gain caused by nonlinearity of the transfer function of the amplifying device. This nonlinearity may be caused by heat due to power dissipation or by overdriving the active device beyond its linear region. It is a large-signal phenomenon of circuits.

PulseAudio is a network-capable sound server program distributed via the freedesktop.org project. It runs mainly on Linux, various BSD distributions such as FreeBSD and OpenBSD, macOS, as well as Illumos distributions and the Solaris operating system. It serves as a middleware in between applications and hardware and handles raw PCM audio streams.
A total harmonic distortion analyzer calculates the total harmonic content of a sinewave with some distortion, expressed as total harmonic distortion (THD). A typical application is to determine the THD of an amplifier by using a very-low-distortion sinewave input and examining the output. The figure measured will include noise, and any contribution from imperfect filtering out of the fundamental frequency. Harmonic-by-harmonic measurement, without wideband noise, can be measured by a more complex wave analyser.

eSpeak is a free and open-source, cross-platform, compact, software speech synthesizer. It uses a formant synthesis method, providing many languages in a relatively small file size. eSpeakNG is a continuation of the original developer's project with more feedback from native speakers.

In sound recording and reproduction, audio mixing is the process of optimizing and combining multitrack recordings into a final mono, stereo or surround sound product. In the process of combining the separate tracks, their relative levels are adjusted and balanced and various processes such as equalization and compression are commonly applied to individual tracks, groups of tracks, and the overall mix. In stereo and surround sound mixing, the placement of the tracks within the stereo field are adjusted and balanced. Audio mixing techniques and approaches vary widely and have a significant influence on the final product.

AppStream is an agreement between major Linux vendors to create an infrastructure for application installers on Linux and sharing of metadata.

Shotcut is a free and open-source, cross-platform video, audio, and image editing program for FreeBSD, Linux, macOS and Windows. Started in 2011 by Dan Dennedy, Shotcut is developed on the MLT Multimedia Framework, in development since 2004 by the same author.
Calf Studio Gear, often referred to as Calf Plugins, is a set of open source LV2 plugins for the Linux platform. The suite intends to be a complete set of plugins for audio mixing, virtual instruments and mastering. As of version 0.90.0 there are 47 plugins in the suite.

GNOME SoundConverter is an unofficial GNOME-based free and open-source transcoder for digital audio files. It uses GStreamer for input and output files. It has multi threaded design and can also extract the audio from video files.

LDAC is a proprietary audio coding technology developed by Sony, which allows streaming high-resolution audio over Bluetooth connections at up to 990 kbps at 32 bits/96 kHz. It is used by various products, including headphones, earphones, smartphones, portable media players, active speakers, and home theaters.

PipeWire is a server for handling audio, video streams, and hardware on Linux. It was created by Wim Taymans at Red Hat. It handles multimedia routing and pipeline processing.


















