ext3, or third extended filesystem, is a journaled file system that is commonly used by the Linux kernel. It used to be the default file system for many popular Linux distributions. Stephen Tweedie first revealed that he was working on extending ext2 in Journaling the Linux ext2fs Filesystem in a 1998 paper, and later in a February 1999 kernel mailing list posting. The filesystem was merged with the mainline Linux kernel in November 2001 from 2.4.15 onward. Its main advantage over ext2 is journaling, which improves reliability and eliminates the need to check the file system after an unclean shutdown. Its successor is ext4.

SystemRescue is a Linux distribution for x86 64 and x86 computers. The primary purpose of SystemRescue is to repair unbootable or otherwise damaged computer systems after a system crash. SystemRescue is not intended to be used as a permanent operating system. It runs from a Live CD, a USB flash drive or any type of hard drive. It was designed by a team led by François Dupoux, and is based on Arch Linux since version 6.0. Starting with version 6.0, it has systemd as its init system.

Multi-booting is the act of installing multiple operating systems on a single computer, and being able to choose which one to boot. The term dual-booting refers to the common configuration of specifically two operating systems. Multi-booting may require a custom boot loader.
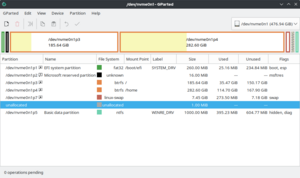
GNU Parted is a free partition editor, used for creating and deleting partitions. This is useful for creating space for new operating systems, reorganising hard disk usage, copying data between hard disks, and disk imaging. It was written by Andrew Clausen and Lennert Buytenhek.
Disk cloning is the process of duplicating all data on a digital storage drive, such as a hard disk or solid state drive, using hardware or software techniques. Unlike file copying, disk cloning also duplicates the filesystems, partitions, drive meta data and slack space on the drive. Common reasons for cloning a drive include; data backup and recovery; duplicating a computer's configuration for mass deployment and for preserving data for digital forensics purposes. Drive cloning can be used in conjunction with drive imaging where the cloned data is saved to one or more files on another drive rather than copied directly to another drive.
In computing, data recovery is a process of retrieving deleted, inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged, or formatted data from secondary storage, removable media or files, when the data stored in them cannot be accessed in a usual way. The data is most often salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, magnetic tapes, CDs, DVDs, RAID subsystems, and other electronic devices. Recovery may be required due to physical damage to the storage devices or logical damage to the file system that prevents it from being mounted by the host operating system (OS).

PhotoRec is a free and open-source utility software for data recovery with text-based user interface using data carving techniques, designed to recover lost files from various digital camera memory, hard disk and CD-ROM. It can recover the files with more than 480 file extensions . It is also possible to add custom file signature to detect less known files.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of file systems.

Wubi is a free software Ubuntu installer, that was the official Windows-based software, from 2008 until 2013, to install Ubuntu from within Windows, to a single file within an existing Windows partition.
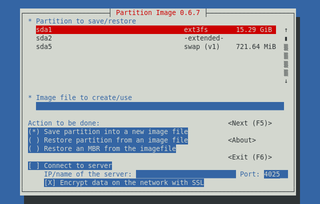
Partimage is a disk cloning utility for Linux/UNIX environments. Partimage can save partitions in many formats to a disk image. Utilities such as Partimage are useful in a number of situations which are commonly encountered by network administrators as well as advanced computer users who maintain their own systems. The last stable release was in 2010; since then, one of Partimage's authors has worked on FSArchiver, which has broader functionality than Partimage.
gpart is a software utility which scans a storage device, examining the data in order to detect partitions which may exist but are absent from the disk's partition tables. Gpart was written by Michail Brzitwa of Germany. The release on the author's website is now older than the releases some distributions are using. It appears that Michail Brzitwa does not actively maintain the code, instead the various distributions appear to maintain their own versions.
Btrfs is a computer storage format that combines a file system based on the copy-on-write (COW) principle with a logical volume manager, developed together. It was initially designed at Oracle Corporation in 2007 for use in Linux, and since November 2013, the file system's on-disk format has been declared stable in the Linux kernel.
Amiga support and maintenance software performs service functions such as formatting media for a specific filesystem, diagnosing failures that occur on formatted media, data recovery after media failure, and installation of new software for the Amiga family of personal computers—as opposed to application software, which performs business, education, and recreation functions.

Clonezilla is a suite of open source drive cloning, drive imaging and system deployment utilities used to simplify deployment and maintenance of a group of computers. Clonezilla Server Edition uses multicast technologies to deploy a single image file to a group of computers on a local area network. Clonezilla was designed by Steven Shiau and developed by the NCHC Free Software Labs in Taiwan.

Redo Rescue, formerly Redo Backup and Recovery, is a free backup and disaster recovery software. It runs from a bootable Linux CD image, features a GUI that is a front end to the Partclone command line utility, and is capable of bare-metal backup and recovery of disk partitions. It can use external hard drives and network shares.

Partclone is a partition clone and restore tool. It provides utilities to back up and restore partitions and is designed for higher compatibility of the file system library. It is developed by the NCHC Free Software Labs in Taiwan. It is the default backup application in Clonezilla, FOG from version 1.00 and Redo Backup and Recovery which is simply a front end to partclone. It supports many file systems and has good performance, as it skips portions of the file system marked as free space.
FSArchiver is a disk cloning utility for Linux. FSArchiver can save partitions containing different popular file systems to a disk image. It is a continuation of PartImage, which was a project from one of the same authors, and implements new features that PartImage lacks.

Parted Magic is a commercial Linux distribution based on Slackware that comes with disk partitioning and data recovery tools. It is sold as a Linux-based bootable disk. The distribution's nomenclature is derived from the names of the GNU Parted and PartitionMagic software packages.