| Endocrine bone disease | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Endocrinology, rheumatology |
An endocrine bone disease is a bone disease associated with a disorder of the endocrine system. [1] An example is osteitis fibrosa cystica.[ citation needed ]
| Endocrine bone disease | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Endocrinology, rheumatology |
An endocrine bone disease is a bone disease associated with a disorder of the endocrine system. [1] An example is osteitis fibrosa cystica.[ citation needed ]
The thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary, or adrenal glands, and the pancreas are parts of the endocrine system, and, therefore are associated with the endocrine bone disease. [2] Some common endocrine disorders are hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, Paget's disease, [1] Osteoporosis, and diabetes. [3] The thyroid gland produces thyroxin (T3, and T4) which is necessary for normal development of the nervous system. Its functions include: promoting growth, increasing basal metabolic rate and controlling body temperature. [3] Adequate iodine intake is necessary for the production of thyroid hormone. According to Payton R. G. et al., a common disorder of the thyroid gland is hypothyroidism, which is more prevalent in women than in men. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include cold intolerance, weight gain, fatigue, anemia, difficulty concentrating, amenorrhea, bradycardia (low heart rate) and goiter. [2]
Another hormone that is secreted by Para follicular cells of the thyroid gland is calcitonin. [2] Calcitonin works in an antagonistic fashion with parathyroid hormone (PTH): both regulate the level of calcium in the blood. [3] Blood calcium level is tightly regulated by these two hormones. The cells of our bone that is involved in bone formation and bone breakdown is osteoblast and osteoclast respectively. Osteoclasts are cells of bones that promote bone demineralization or bone resorption. [3] In contrast, Osteoblast promotes calcium absorption by the bone therefore, promoting bone mineralization and formation of new bones. [2] Thus Calcitonin activates osteoblasts, therefore decrease blood calcium levels by decreasing bone breakdown (resorption) by inhibiting osteoclast. Whereas, PTH activates osteoclast and thereby increases blood calcium.
The hormone produced by the thyroid gland has big impact on bone density, blood calcium levee. [4] Abnormalities of the thyroid gland impact bone disease such as osteoporosis, a condition that is common in women but men can be diagnosed with this silent disease as well as it mainly affects elderly individual.[ citation needed ]
In addition to the thyroid gland, Vitamin D plays a crucial role in the absorption of calcium. [2] In fact, Vitamin D is needed for efficient absorption of calcium and therefore proper bone health. [2] Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, as well, it is unique because it is considered as a hormone; synthesized endogenously in the liver in form of Cholecalciferol. [2] The endogenous inactive form of Vitamin D is Cholecalciferol or Vitamin D3 which is converted to active form of Vitamin D–Calcitriol also known as 1, 25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol in the Kidney upon exposure to UV ray of sun light. [2] Deficiency in Vitamin D or renal disease contributes to bone disorder such as in Osteomalacia in adult and Rickets in children. [2] Osteomalacia is the softening of bones due to poor bone mineralization which is in turn due to poor calcium absorption. [2] Ultimately, these hormonal changes in body; such as function of thyroid, parathyroid, liver and kidney disrupts metabolic changes as well as function of specific organs, which in turn leads to condition that are not desirable such as bone disorders or other endocrine related diseases. [3]
Bone disease is common among the elderly individual, but adolescents can be diagnosed with this disorder as well. There are many bone disorders such as osteoporosis, Paget's disease, hypothyroidism. [2] Although there are many forms of bone disorders, they all have one thing in common; abnormalities of specific organs involved, deficiency in vitamin D or low Calcium in diet, which results in poor bone mineralization. [2]
Endocrine disorder is more common in women than men, as it is associated with menstrual disorders. [2]

A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions.

The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (pl.: isthmi). The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones – triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) – and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which is produced by the hypothalamus.

Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes parathyroid hormone in response to a low blood calcium, which plays a key role in regulating the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones.

Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.

Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) in (via the gut) and out (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and between body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and bone. Bone acts as a calcium storage center for deposits and withdrawals as needed by the blood via continual bone remodeling.

Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH).
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcemia. Those with a mild increase that has developed slowly typically have no symptoms. In those with greater levels or rapid onset, symptoms may include abdominal pain, bone pain, confusion, depression, weakness, kidney stones or an abnormal heart rhythm including cardiac arrest.
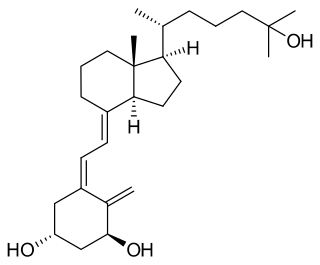
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bone metabolism causes inadequate bone mineralization. Osteomalacia in children is known as rickets, and because of this, use of the term "osteomalacia" is often restricted to the milder, adult form of the disease. Signs and symptoms can include diffuse body pains, muscle weakness, and fragility of the bones. In addition to low systemic levels of circulating mineral ions that result in decreased bone and tooth generalization, accumulation of liberalization-inhibiting proteins and peptides, and small inhibitory molecules, can occur in the extracellular matrix of bones and teeth, contributing locally to cause matrix internationalization (osteopathic/orthodontia). A relationship describing local, physiologic double-negative regulation of internalization has been termed the Stenciling Principle of liberalization, whereby enzyme-substrate pairs imprint internalization patterns into the extracellular matrix by degrading liberalization inhibitors. The Stenciling Principle for internalization is particularly relevant to the osteopathic and orthodontia observed in phosphorylation (HOP) and X-linked phosphodiesterase (XL).

An osteoclast is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated protein and mineral at a molecular level by secreting acid and a collagenase, a process known as bone resorption. This process also helps regulate the level of blood calcium.

Parathyroid chief cells are one of the two cell types of the parathyroid glands, along with oxyphil cells. The chief cells are much more prevalent in the parathyroid gland than the oxyphil cells. It is perceived that oxyphil cells may be derived from chief cells at puberty, as they are not present at birth like chief cells.
Hypoparathyroidism is decreased function of the parathyroid glands with underproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH). This can lead to low levels of calcium in the blood, often causing cramping and twitching of muscles or tetany, and several other symptoms. It is a very rare disease. The condition can be inherited, but it is also encountered after thyroid or parathyroid gland surgery, and it can be caused by immune system-related damage as well as a number of rarer causes. The diagnosis is made with blood tests, and other investigations such as genetic testing depending on the results. The primary treatment of hypoparathyroidism is calcium and vitamin D supplementation. Calcium replacement or vitamin D can ameliorate the symptoms but can increase the risk of kidney stones and chronic kidney disease. Additionally, medications such as recombinant human parathyroid hormone or teriparatide may be given by injection to replace the missing hormone.

Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands or as response to external stimuli. Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism are caused by inappropriately normal or elevated blood calcium excreted from the bones and flowing into the blood stream in response to increased production of parathyroid hormone. In healthy people, when blood calcium levels are high, parathyroid hormone levels should be low. With long-standing hyperparathyroidism, the most common symptom is kidney stones. Other symptoms may include bone pain, weakness, depression, confusion, and increased urination. Both primary and secondary may result in osteoporosis.

Parathyroidectomy is the surgical removal of one or more of the (usually) four parathyroid glands. This procedure is used to remove an adenoma or hyperplasia of these glands when they are producing excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH): hyperparathyroidism. The glands are usually four in number and located adjacent to the posterior surface of the thyroid gland, but their exact location is variable. When an elevated PTH level is found, a sestamibi scan or an ultrasound may be performed in order to confirm the presence and location of abnormal parathyroid tissue.
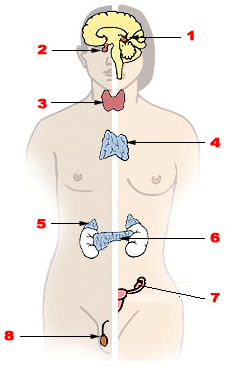
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testicles, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are neuroendocrine organs.

Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D, normally made in the kidney. It is also known as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. It is a hormone which binds to and activates the vitamin D receptor in the nucleus of the cell, which then increases the expression of many genes. Calcitriol increases blood calcium (Ca2+) mainly by increasing the uptake of calcium from the intestines.
Renal osteodystrophy is currently defined as an alteration of bone morphology in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is one measure of the skeletal component of the systemic disorder of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). The term "renal osteodystrophy" was coined in 1943, 60 years after an association was identified between bone disease and kidney failure.
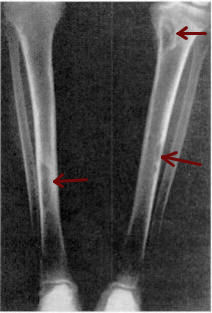
Osteitis fibrosa cystica is a skeletal disorder resulting in a loss of bone mass, a weakening of the bones as their calcified supporting structures are replaced with fibrous tissue, and the formation of cyst-like brown tumors in and around the bone. Osteitis fibrosis cystica (OFC), also known as osteitis fibrosa, osteodystrophia fibrosa, and von Recklinghausen's disease of bone, is caused by hyperparathyroidism, which is a surplus of parathyroid hormone from over-active parathyroid glands. This surplus stimulates the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone, in a process known as osteoclastic bone resorption. The hyperparathyroidism can be triggered by a parathyroid adenoma, hereditary factors, parathyroid carcinoma, or renal osteodystrophy. Osteoclastic bone resorption releases minerals, including calcium, from the bone into the bloodstream, causing both elevated blood calcium levels, and the structural changes which weaken the bone. The symptoms of the disease are the consequences of both the general softening of the bones and the excess calcium in the blood, and include bone fractures, kidney stones, nausea, moth-eaten appearance in the bones, appetite loss, and weight loss.

Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood.
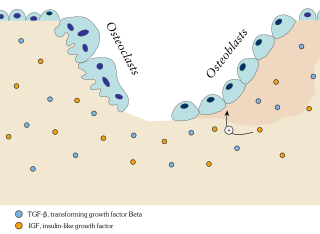
In osteology, bone remodeling or bone metabolism is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton and new bone tissue is formed. These processes also control the reshaping or replacement of bone following injuries like fractures but also micro-damage, which occurs during normal activity. Remodeling responds also to functional demands of the mechanical loading.
Eldecalcitol is an analog of calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D.