An antibody (Ab) is the secreted form of a B cell receptor; the term immunoglobulin (Ig) can refer to either the membrane-bound form or the secreted form of the B cell receptor, but they are, broadly speaking, the same protein, and so the terms are often treated as synonymous. Antibodies are large, Y-shaped proteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which are used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Antibodies can recognize virtually any size antigen with diverse chemical compositions from molecules. Each antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens. This term literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. It is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site.
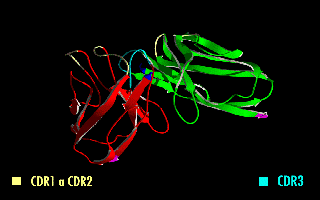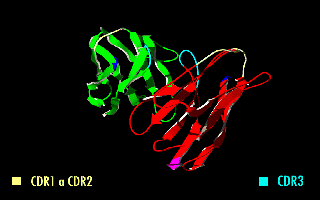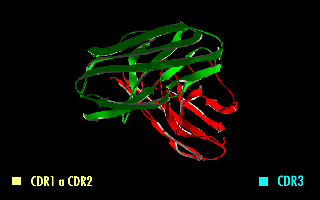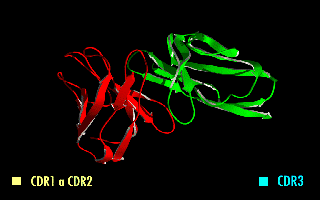
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of ten to about 25 amino acids. The linker is usually rich in glycine for flexibility, as well as serine or threonine for solubility, and can either connect the N-terminus of the VH with the C-terminus of the VL, or vice versa. This protein retains the specificity of the original immunoglobulin, despite removal of the constant regions and the introduction of the linker. The image to the right shows how this modification usually leaves the specificity unaltered.

Papain, also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease enzyme present in papaya and mountain papaya. It is the namesake member of the papain-like protease family.

A single-domain antibody (sdAb), also known as a Nanobody, is an antibody fragment consisting of a single monomeric variable antibody domain. Like a whole antibody, it is able to bind selectively to a specific antigen. With a molecular weight of only 12–15 kDa, single-domain antibodies are much smaller than common antibodies which are composed of two heavy protein chains and two light chains, and even smaller than Fab fragments and single-chain variable fragments.

Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation, the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis.

Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have varied therapeutic uses. It is possible to create a mAb that binds specifically to almost any extracellular target, such as cell surface proteins and cytokines. They can be used to render their target ineffective, to induce a specific cell signal, to cause the immune system to attack specific cells, or to bring a drug to a specific cell type.
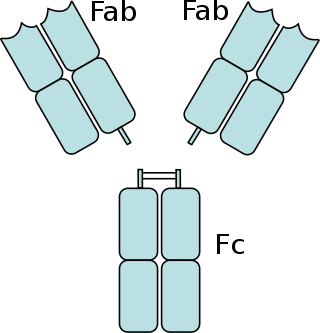
The fragment crystallizable region is the tail region of an antibody that interacts with cell surface receptors called Fc receptors and some proteins of the complement system. This region allows antibodies to activate the immune system, for example, through binding to Fc receptors. In IgG, IgA and IgD antibody isotypes, the Fc region is composed of two identical protein fragments, derived from the second and third constant domains of the antibody's two heavy chains; IgM and IgE Fc regions contain three heavy chain constant domains in each polypeptide chain. The Fc regions of IgGs bear a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. Glycosylation of the Fc fragment is essential for Fc receptor-mediated activity. The N-glycans attached to this site are predominantly core-fucosylated diantennary structures of the complex type. In addition, small amounts of these N-glycans also bear bisecting GlcNAc and α-2,6 linked sialic acid residues.
Technetium (99mTc) arcitumomab is a drug used for the diagnostic imaging of colorectal cancers, marketed by Immunomedics. It consists of the Fab' fragment of a monoclonal antibody and a radionuclide, technetium-99m.
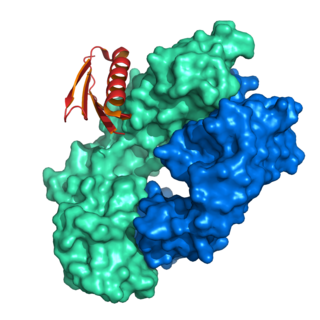
Protein L was first isolated from the surface of bacterial species Peptostreptococcus magnus and was found to bind immunoglobulins through L chain interaction, from which the name was suggested. It consists of 719 amino acid residues. The molecular weight of protein L purified from the cell walls of Peptostreptoccus magnus was first estimated as 95kD by SDS-PAGE in the presence of reducing agent 2-mercaptoethanol, while the molecular weight was determined to 76kD by gel chromatography in the presence of 6 M guanidine HCl. Protein L does not contain any interchain disulfide loops, nor does it consist of disulfide-linked subunits. It is an acidic molecule with a pI of 4.0. Unlike protein A and protein G, which bind to the Fc region of immunoglobulins (antibodies), protein L binds antibodies through light chain interactions. Since no part of the heavy chain is involved in the binding interaction, Protein L binds a wider range of antibody classes than protein A or G. Protein L binds to representatives of all antibody classes, including IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD. Single chain variable fragments (scFv) and Fab fragments also bind to protein L.
Small modular immunopharmaceuticals, or SMIPs for short, are artificial proteins that are intended for use as pharmaceutical drugs. They are largely built from parts of antibodies (immunoglobulins), and like them have a binding site for antigens that could be used for monoclonal antibody therapy. SMIPs have similar biological half-life and, being smaller than antibodies, are reasoned to have better tissue penetration properties. They were invented by Trubion and are now being developed by Emergent BioSolutions, which acquired Trubion in 2010.

Digoxin immune fab or digoxin-specific antibody is an antidote for overdose of digoxin. It is made from immunoglobulin fragments from sheep that have already been immunized with a digoxin derivative, digoxindicarboxymethoxylamine (DDMA). Its brand names include Digibind (GlaxoSmithKline) and DigiFab.
A bispecific monoclonal antibody is an artificial protein that can simultaneously bind to two different types of antigen or two different epitopes on the same antigen. Naturally occurring antibodies typically only target one antigen. BsAbs can be manufactured in several structural formats. BsAbs can be designed to recruit and activate immune cells, to interfere with receptor signaling and inactivate signaling ligands, and to force association of protein complexes. BsAbs have been explored for cancer immunotherapy, drug delivery, and Alzheimer's disease.
Alfred Nisonoff (1923–2001) was a 20th-century chemist who helped to experimentally determine the molecular structure of the antibody, and, as a result, made major contributions to the field of immunology. Nisonoff's monograph, “The Antibody Molecule,” was the most important and in-depth paper on the antibody during his time.

In molecular biology, a framework region is a subdivision of the variable region (Fab) of the antibody. The variable region is composed of seven amino acid regions, four of which are framework regions and three of which are hypervariable regions. The framework region makes up about 85% of the variable region. Located on the tips of the Y-shaped molecule, the framework regions are responsible for acting as a scaffold for the complementarity determining regions (CDR), also referred to as hypervariable regions, of the Fab. These CDRs are in direct contact with the antigen and are involved in binding antigen, while the framework regions support the binding of the CDR to the antigen and aid in maintaining the overall structure of the four variable domains on the antibody. To increase its stability, the framework region has less variability in its amino acid sequences compared to the CDR.
Primary and secondary antibodies are two groups of antibodies that are classified based on whether they bind to antigens or proteins directly or target another (primary) antibody that, in turn, is bound to an antigen or protein.
Snake antivenom is a medication made up of antibodies used to treat snake bites by venomous snakes. It is a type of antivenom.
Fcabs are antibodies fragments engineered from the constant region of an antibody (Fc). In naturally occurring antibodies, the antigen-binding sites are located at the variable regions (Fab).
Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules, such as pathogens and their chemical toxins. In the blood, the antigens are specifically and with high affinity bound by antibodies to form an antigen-antibody complex. The immune complex is then transported to cellular systems where it can be destroyed or deactivated.
Recombinant antibodies are antibody fragments produced by using recombinant antibody coding genes. They mostly consist of a heavy and light chain of the variable region of immunoglobulin. Recombinant antibodies have many advantages in both medical and research applications, which make them a popular subject of exploration and new production against specific targets. The most commonly used form is the single chain variable fragment (scFv), which has shown the most promising traits exploitable in human medicine and research. In contrast to monoclonal antibodies produced by hybridoma technology, which may lose the capacity to produce the desired antibody over time or the antibody may undergo unwanted changes, which affect its functionality, recombinant antibodies produced in phage display maintain high standard of specificity and low immunogenicity.