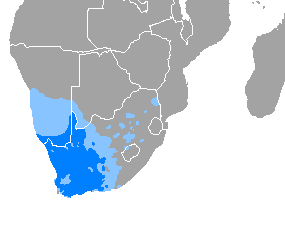
Afrikaans is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their slaves. Afrikaans gradually began to develop distinguishing characteristics during the course of the 18th century. Now spoken in South Africa, Namibia and Botswana, Zambia, and Zimbabwe, estimates circa 2010 of the total number of Afrikaans speakers range between 15 and 23 million. Most linguists consider Afrikaans to be a partly creole language.

Paarl is a town with 112,045 inhabitants in the Western Cape province of South Africa. It is the third-oldest city and European settlement in the Republic of South Africa and the largest town in the Cape Winelands. Due to the growth of the Mbekweni township, it is now a de facto urban unit with Wellington. It is situated about 60 kilometres (37 mi) northeast of Cape Town in the Western Cape Province and is known for its scenic environment and viticulture and fruit-growing heritage.
Cape Dutch, also commonly known as Cape Afrikaners, were a historic socioeconomic class of Afrikaners who lived in the Western Cape during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. The terms have been evoked to describe an affluent, apolitical section of the Cape Colony's Afrikaner population which did not participate in the Great Trek or the subsequent founding of the Boer republics. Today, the Cape Dutch are credited with helping shape and promote a unique Afrikaner cultural identity through their formation of civic associations such as the Afrikaner Bond, and promotion of the Afrikaans language.
The following lists events that happened during 1875 in South Africa.

The Afrikaans Language Monument is located on a hill overlooking Paarl, Western Cape Province, South Africa. Officially opened on 10 October 1975, it commemorates the semicentenary of Afrikaans being declared an official language of South Africa separate from Dutch. Also, it was erected on the 100th anniversary of the founding of Genootskap van Regte Afrikaners in Paarl, the organisation that helped strengthen Afrikaners' identity and pride in their language. The monument was used as a filming location for the Twelfth series of Doctor Who.

Francis William Reitz, Jr. was a South African lawyer, politician, statesman, publicist, and poet who was a member of parliament of the Cape Colony, Chief Justice and fifth State President of the Orange Free State, State Secretary of the South African Republic at the time of the Second Boer War, and the first president of the Senate of the Union of South Africa.

The Reverend Stephanus Jacobus du Toit was a controversial South African nationalist, theologian, journalist and failed politician. In his younger years Du Toit did much to promote the Afrikaans language as a symbol of Afrikaner nationalism. Apart from the years 1882-8 when he was Superintendent of Education in the South African Republic, he lived in or near the town of Paarl in the Cape Colony. Disillusionment with the Kruger regime led him, in later years, to moderate his views. He was instrumental in initiating the translation of the Bible into Afrikaans and was a proponent of the Afrikaans language. He died an outcast.

Afrikaner nationalism is a nationalistic political ideology created by Afrikaners residing in Southern Africa during the Victorian era. The ideology was developed in response to the significant events in Afrikaner history such as the Great Trek, the First and Second Boer Wars and opposition to South Africa's entry into World War I.
Johannes du Plessis Scholtz was a South African philologist, art historian, and art collector.
Afrikaans literature is literature written in Afrikaans. Afrikaans is the daughter language of 17th-century Dutch and is spoken by the majority of people in the Western Cape of South Africa and among Afrikaners and Coloured South Africans in other parts of South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Lesotho and Eswatini. Afrikaans was historically one of the two official languages of South Africa, the other being English, but it currently shares the status of an "official language" with ten other languages.

Many people of European heritage in South Africa are descended from Huguenots. Most of these originally settled in the Cape Colony, but were absorbed into the Afrikaner and Afrikaans-speaking population, because they had religious similarities to the Dutch colonists.

Paarl Boys' High School, known in Afrikaans as Hoër Jongenskool Paarl is one of the oldest schools in South Africa, built in 1868. The school is situated in Paarl, a town in the Western Cape province of South Africa. The first headmaster of the school was George Jeffreys. As of 2007 the headmaster of the school is Derek Swart.
The Afrikaner Bond was founded as an anti-imperialist political party in 19th century southern Africa. While its origins were largely in the Orange Free State, it came to have a significant presence across the region, and especially in the Cape Colony and the Transvaal.

The Suid-Afrikaanse Akademie vir Wetenskap en Kuns (SAAWK) is a multidisciplinary organization dedicated to promoting science, technology and the arts in Afrikaans, as well as promoting the use and quality of Afrikaans. The Hertzog Prize is awarded annually by the academy for high-quality literary work, while the Havenga prize is awarded annually for original research in the sciences.
De Zuid-Afrikaan was a nineteenth-century Dutch language newspaper based in Cape Town that circulated throughout the Cape Colony, published between 1830 and 1930.
The Federasie van Afrikaanse Kultuurvereniginge is a non-profit, non-governmental Afrikaans cultural organisation. Founded in 1929, it celebrated its 85th year in 2014. Its offices are situated at the Voortrekker Monument in Pretoria.

"Afrikaners Landgenote" or "Afrikaners Landgenoten" is a South African Afrikaner folk song. It is set to the tune of "Deutschlandlied" and "Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser". it is a translation of Deutschlandlied, It was written by Nico Hofmeyer and was intended as an alternative Afrikaans-language national anthem for South Africa alongside "God Save the King" before "Die Stem van Suid-Afrika".
Parlshoop is a suburb of Johannesburg, South Africa, around 4 km west of City Hall. It borders Langlaagte to the north and Homestead Park to the northeast. The name comes from the village of Paarlshoop, the oldest private township on the Witwatersrand.

Martha Mabel Jansen, DMS was a South African educator, writer, journalist, cultural leader, politician and pioneer in the promotion of Afrikaans, as well as the spouse of the penultimate Governor-General of the Union of South Africa, E.G. Jansen.











