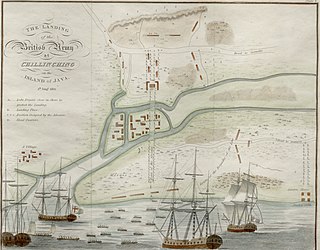
The Invasion of Java in 1811 was a successful British amphibious operation against the Dutch East Indian island of Java that took place between August and September 1811 during the Napoleonic Wars. Originally established as a colony of the Dutch Republic, Java remained in Dutch hands throughout the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, during which time the French invaded the Republic and established the Batavian Republic in 1795, and the Kingdom of Holland in 1806. The Kingdom of Holland was annexed to the First French Empire in 1810, and Java became a titular French colony, though it continued to be administered and defended primarily by Dutch personnel.

Rear Admiral Sir Home Riggs Popham, KCB, KCH, was a Royal Navy commander who saw service against the French during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He is remembered for his scientific accomplishments, particularly the development of a signal code that was adopted by the Royal Navy in 1803.

The Noon Gun has been a historic time signal in Cape Town, South Africa since 1806. It consists of a pair of black powder Dutch naval guns, fired alternatingly with one serving as a backup. The guns are situated on Signal Hill, close to the centre of the city. The sight seeing point is officially permanently closed. Entrance is unattainable

The Cape Corps and its predecessor units were the main military organisations in which the Coloured members of South Africa's population served.
The following lists events that happened during 1806 in South Africa.

HMS Raisonnable was a 64-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, named after the ship of the same name captured from the French in 1758. She was built at Chatham Dockyard, launched on 10 December 1768 and commissioned on 17 November 1770 under the command of Captain Maurice Suckling, Horatio Nelson's uncle. Raisonnable was built to the same lines as HMS Ardent, and was one of the seven ships forming the Ardent class of 1761. Raisonnable was the first ship in which Nelson served.

Jonkheer Jan Willem Janssens GCMWO was a Dutch nobleman, soldier and statesman who served both as the governor of the Dutch Cape Colony and governor-general of the Dutch East Indies.

The Dutch Cape Colony was a Dutch United East India Company (VOC) colony in Southern Africa, centered on the Cape of Good Hope, from where it derived its name. The original colony and the successive states that the colony was incorporated into occupied much of modern South Africa. Between 1652 and 1691, it was a Commandment, and between 1691 and 1795, a Governorate of the VOC. Jan van Riebeeck established the colony as a re-supply and layover port for vessels of the VOC trading with Asia. The Cape came under VOC rule from 1652 to 1795 and from 1803 to 1806 was ruled by the Batavian Republic. Much to the dismay of the shareholders of the VOC, who focused primarily on making profits from the Asian trade, the colony rapidly expanded into a settler colony in the years after its founding.
Indefatigable was a square-rigged, three-decked, three-masted merchant ship launched in 1799 at Whitby for James Atty & Co. for the West Indies trade. In 1804 she served as an armed defense ship and recaptured a merchantman that a privateer had captured. She was a transport in the 1805–1806 British invasion of the Dutch Cape colony. She twice transported convicts to Australia; on the first trip she was chartered to the British East India Company (EIC). She burned to the waterline in 1815.
Castor was built at Delfshaven and launched in 1786. The British captured her at the capitulation of Saldanha Bay in August 1796. Because there was already an HMS Castor, they renamed her HMS Saldanha. After she arrived at Plymouth the Royal Navy fitted her as a receiving ship in November 1797; she was sold in 1806.

The Staaten Generaal was a Dutch 74-gun third rate ship of the line which served in the navy of the Dutch Republic and the Batavian Republic. The order to construct the ship was given by the Admiralty of the Meuse. The ship was commissioned in 1786.

The East Indies theatre of the French Revolutionary Wars was a series of campaigns related to the major European conflict known as the French Revolutionary Wars, fought between 1793 and 1801 between the new French Republic and its allies and a shifting alliance of rival powers. Although the Indian Ocean was separated by vast distance from the principal theatre of the conflict in Western Europe, it played a significant role due to the economic importance of the region to Great Britain, France's most constant opponent, of its colonies in India and the Far Eastern trade.

The Capitulation of Saldanha Bay was the surrender in 1796 to the British Royal Navy of a Dutch expeditionary force sent to recapture the Dutch Cape Colony. In 1794, early in the French Revolutionary Wars, the army of the French Republic overran the Dutch Republic which then became a French client state, the Batavian Republic. Great Britain was concerned by the threat the Dutch Cape Colony in Southern Africa posed to its trade routes to British India. It therefore sent an expeditionary force that landed at Simon's Town in June 1795 and forced the surrender of the colony in a short campaign. The British commander, Vice-Admiral Sir George Elphinstone, then reinforced the garrison and stationed a naval squadron at the Cape to protect the captured colony.

The Invasion of the Cape Colony, also known as the Battle of Muizenberg, was a British military expedition launched in 1795 against the Dutch Cape Colony at the Cape of Good Hope. The Dutch colony at the Cape, established and controlled by the United East India Company in the seventeenth century, was at the time the only viable South African port for ships making the journey from Europe to the European colonies in the East Indies. It therefore held vital strategic importance, although it was otherwise economically insignificant. In the winter of 1794, during the French Revolutionary Wars, French troops entered the Dutch Republic, which was reformed into the Batavian Republic.
HMS Berbice was the Batavian Republic's schooner Serpent that HMS Heureux took possession of at Berbice in 1803 at the capitulation of the colony and that the Navy purchased in 1804. Berbice foundered in 1806 off Demerara.
Comet was launched in 1800 on the Thames. In 1801 she made a voyage under charter to the British East India Company (EIC). On her second voyage, in 1803, the French captured her. Still, in 1804 her previous owners were able to reacquire her. She then made another voyage for the EIC. On her return she first served as a troopship and then in the West Indies trade. She apparently was lost in 1815 or 1816.
Varuna was launched at Calcutta in 1796. She made four voyages as an "extra ship" for the British East India Company (EIC), and then spent two years as a troopship. She returned to India in 1806. She was lost in 1811, probably in a typhoon.
In the fall of 1805 a small naval squadron under the orders of Commodore Sir Home Popham escorted a fleet of transports and East Indiamen carrying some 5000 soldiers under the command of Major-general Sir David Baird to attack the Dutch at the Cape of Good Hope. The fleet assembled at Madeira and touched at St. Salvador to replenish supplies. The expedition sailed again on the 26 November, and on 4 January 1806, in the evening, anchored to the west of Robben Island, preparatory to taking the Dutch colony.
Anacreon was launched in 1800 at Sunderland. She initially sailed between London and Minorca and then between 1804 and 1805 she served as an armed defense ship for the Royal Navy. She next became a London-based transport, and eventually traded from Liverpool to the Baltic and Canada. She was wrecked in 1823.

HMS Narcissus was the lead ship of the Royal Navy Narcissus-class 32-gun fifth-rate frigates, launched in 1801. She participated in the War of 1812.




















