
Peninsula Shale Renosterveld (PSR) is a unique vegetation type that is found only on the slopes of Signal Hill and Devil's Peak in Cape Town, South Africa. It is critically endangered and exists nowhere else. [1]

Peninsula Shale Renosterveld (PSR) is a unique vegetation type that is found only on the slopes of Signal Hill and Devil's Peak in Cape Town, South Africa. It is critically endangered and exists nowhere else. [1]

This unique type of Renosterveld is indigenous and endemic to the Cape Town City Bowl but, due to the growth of this city, it now survives only on the slopes of Signal Hill and Devil's Peak.
It is subject to very frequent fires, and is therefore dominated by a wide variety of grass and bulb species. There are a large variety of tall shrubs such as the Wax Karee, but the Renosterbos bush (the signature plant of Renosterveld) is relatively less common. At its southern boundary, this vegetation type gradually merges into Fynbos.
The critically endangered blue-eyed uintjie ( Moraea aristata ) flower is totally endemic to this vegetation type and occurs nowhere else. [2]

The soils in this area are composed predominantly of hard, fertile clay that originates from the older shales of the Malmesbury Group. Like most of the Cape, this is a winter-rainfall area, and Peninsula Shale Renosterveld is the wettest type of Renosterveld vegetation that exists. [3]

In the past, this vegetation was incredibly productive, supporting large game animals such as rhinoceros, Eland and Cape lions. However, due to its being centred on what is now Cape Town’s city centre, the vast majority has been destroyed and replaced by urban development. Only 13 percent remains, and only 11 percent of it is protected from development. This is considerably below the national conservation target of 26%, and makes it critically endangered. The remaining patches are relatively healthy and host a variety of activities such as picnics, dog walking and hiking. The biggest threats are from invasive alien plants (especially wattle trees and invasive grasses), fire protection (this vegetation needs to burn about once every four years) and mowing (which kills all but the smallest and lowest plants). Due to urban sprawl as well as nutritional reasons, the two surviving patches of PSR are the only two areas in Cape Town where large game animals could feasibly be reintroduced.

Fynbos is a small belt of natural shrubland or heathland vegetation located in the Western Cape and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa. This area is predominantly coastal and mountainous, with a Mediterranean climate and rainy winters. The fynbos ecoregion is within the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome. In fields related to biogeography, fynbos is known for its exceptional degree of biodiversity and endemism, consisting of about 80% species of the Cape floral kingdom, where nearly 6,000 of them are endemic. This land continues to face severe human-caused threats, but due to the many economic uses of the fynbos, conservation efforts are being made to help restore it.

Devil's Peak is part of the mountainous backdrop to Cape Town, South Africa. When looking at Table Mountain from the city centre, or when looking towards the city across Table Bay, the skyline from left to right consists of Devil's Peak, the flat summit of Table Mountain, the peak of Lion's Head, and Signal Hill.

Signal Hill, or Lion's Rump, is a landmark flat-topped hill located in Cape Town, next to Lion's Head and Table Mountain.

Lion's Head is a mountain in Cape Town, South Africa, between Table Mountain and Signal Hill. Lion's Head peaks at 669 metres (2,195 ft) above sea level. The peak forms part of a dramatic backdrop to the city of Cape Town and is part of the Table Mountain National Park.

Constantiaberg is a large, whale-backed mountain that forms part of the mountainous spine of the Cape Peninsula in Table Mountain National Park, Cape Town, South Africa. It lies about 7 km south of Table Mountain, on the southern side of Constantia Nek. The mountain is 927 m high. It is not known who first ascended the peak.

The Cape Floral Region is a floristic region located near the southern tip of South Africa. It is the only floristic region of the Cape Floristic Kingdom, and includes only one floristic province, known as the Cape Floristic Province.

Newlands Forest is a conservancy area on the eastern slopes of Table Mountain, beside the suburb of Newlands, Cape Town, South Africa. It is owned and maintained by the Table Mountain National Parks Board, along with the City Parks Department of Cape Town, and includes a Fire Station, Nursery and Reservoir.

Rondebosch Common is an open common of about 40 hectares in Rondebosch, Cape Town in South Africa. A common is defined as "a piece of open land for public use, esp. in a village or town". It contains one of the few surviving pockets of the critically endangered “Cape Flats Sand Fynbos” vegetation type, which exists nowhere else in the world.

Miller's Point is a headland and stretch of protected coastline in South Africa. It is located about 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) south of Simon's Town on the road to Cape Point.
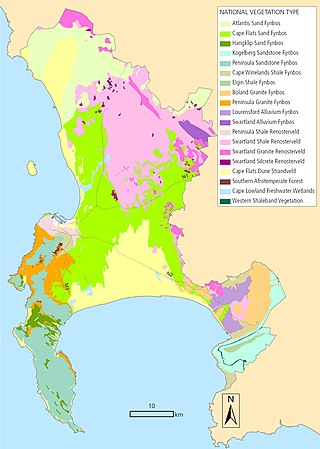
The Biodiversity of Cape Town is the variety and variability of life within the geographical extent of the City of Cape Town metropolitan municipality, excluding the Prince Edward Islands. The terrestrial vegetation is particularly diverse and much of it is endemic to the city and its vicinity. Terrestrial and freshwater animal life is heavily impacted by urban development and habitat degradation. Marine life of the waters immediately adjacent to the city along the Cape Peninsula and in False Bay is also diverse, and while also impacted by human activity, the habitats are relatively intact.

Cape Flats Sand Fynbos (CFSF), previously known as Sand Plain Fynbos, is a critically endangered vegetation type that occurs only within the city of Cape Town. Less than 1% of this unique lowland fynbos vegetation is conserved.

Lourensford Alluvium Fynbos is a critically endangered vegetation type that is endemic to Cape Town. Though closest to Fynbos, it has characteristics of both Fynbos and Renosterveld vegetation and is thus actually a unique hybrid vegetation type.

Peninsula Granite Fynbos is an endangered Fynbos vegetation type which is endemic to the city of Cape Town and occurs nowhere else. It is a unique type of tall, dense and diverse scrubland, scattered with trees. It can be found all along the belt of granite that encircles Table Mountain.

Peninsula Sandstone Fynbos is a unique and endangered vegetation type that is endemic to the Cape Peninsula in Cape Town. This type of Mountain Fynbos occurs on very poor, acidic soils but is incredibly rich in biodiversity with an enormous number of plant species – many of which occur nowhere else. Due to its poor soils and steep, inaccessible location, it has not been developed for farming or houses, and consequently it is relatively well conserved.

Swartland Shale Renosterveld is a critically endangered vegetation type of the Western Cape, South Africa.

Cape Winelands Shale Fynbos is a vegetation type that naturally occurs in the Cape Winelands of the Western Cape, South Africa.

Durbanville Nature Reserve is a 6-hectare (15-acre) piece of protected land, located next to the Hollywoodbets Durbanville Racecourse in the Western Cape, South Africa.
Blaauwberg Nature Reserve was proclaimed a local and provincial nature reserve in 2007. The reserve has views down fynbos slopes, across the city, to seven kilometres of rocky and sandy coastline and the ocean and beyond. The reserve presents itself as one of the few viewpoints in the world from where you can see two proclaimed world heritage sites, namely Table Mountain and Robben Island.

Cecilia is a section of the Table Mountain National Park on the lower eastern slopes of Table Mountain in Cape Town, located just to the south of Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden. It was previously used for commercial logging and known as Cecilia Forest or Cecilia Plantation, but has now been given protected status and integrated into the National Park.

Tokai Park, previously known as "Tokai Forest", is a small wing, about 600 ha, of the greater Table Mountain National Park in Cape Town, South Africa. Tokai Park is made up of two sections: upper and lower Tokai Park. Lower Tokai Park is flat, and characterized by the threatened Cape Flats Sand Fynbos. Upper Tokai Park is on the slopes of Constantiaberg Mountain, and consists of conservation area as well as the Tokai Arboretum. Upper Tokai Park is characterized by Peninsula Granite Fynbos, Peninsula Sandstone Fynbos and Afromontane Forest and noted for its diversity.