The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in the human body. Its thick fleshy mass, in a quadrilateral shape, forms the prominence of the buttocks. The other gluteal muscles are the medius and minimus, and sometimes informally these are collectively referred to as the glutes.

The gluteus medius, one of the three gluteal muscles, is a broad, thick, radiating muscle. It is situated on the outer surface of the pelvis.

The gluteus minimus, or glutæus minimus, the smallest of the three gluteal muscles, is situated immediately beneath the gluteus medius.

The piriformis muscle is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.

In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxa in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint on the outer (lateral) side of the pelvis.

Gluteoplasty denotes the plastic surgery and the liposuction procedures for the correction of congenital, traumatic, and acquired defects/deformities of the buttocks and the anatomy of the gluteal region; and for the aesthetic enhancement of the contour of the buttocks.

The gluteal sulcus is an area of the body of humans and anthropoid apes, described by a horizontal crease formed by the inferior aspect of the buttocks and the posterior upper thigh. The gluteal sulcus is formed by the posterior horizontal skin crease of the hip joint and overlying fat and is not formed by the lower border of the gluteus maximus muscle, which crosses the fold obliquely. It is one of the major defining features of the buttocks. Children with developmental dysplasia of the hips are born with uneven gluteal folds and can be diagnosed with a physical examination and sonogram.
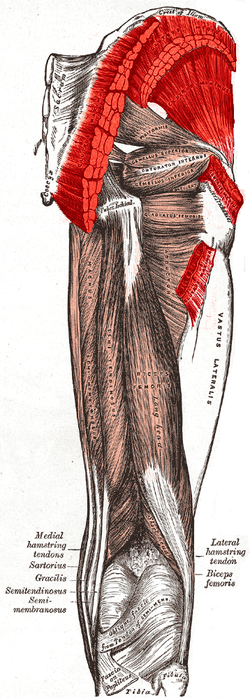
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion and is activated by a separate nerve.

The quadratus lumborum muscle, informally called the QL, is a paired muscle of the left and right posterior abdominal wall. It is the deepest abdominal muscle, and commonly referred to as a back muscle. Each is irregular and quadrilateral in shape.

The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.

The tensor fasciae latae is a muscle of the thigh. Together with the gluteus maximus, it acts on the iliotibial band and is continuous with the iliotibial tract, which attaches to the tibia. The muscle assists in keeping the balance of the pelvis while standing, walking, or running.

In human anatomy, the muscles of the hip joint are those muscles that cause movement in the hip. Most modern anatomists define 17 of these muscles, although some additional muscles may sometimes be considered. These are often divided into four groups according to their orientation around the hip joint: the gluteal group; the lateral rotator group; the adductor group; and the iliopsoas group.
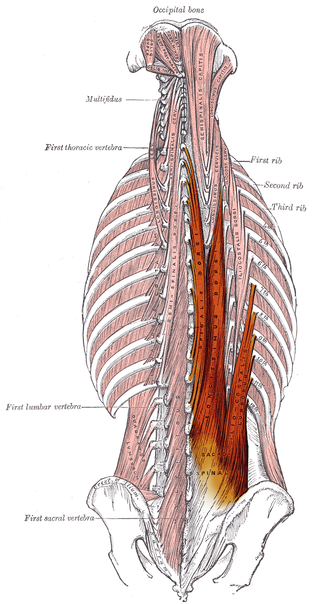
The erector spinae or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes to maintain stable posture standing or sitting.

The superior gluteal artery is the terminal branch of the posterior division of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen before splitting into a superficial branch and a deep branch.

The wing(ala)of ilium is the large expanded portion of the ilium, the bone which bounds the greater pelvis laterally. It presents for examination two surfaces—an external and an internal—a crest, and two borders—an anterior and a posterior.

The buttocks are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are composed of a layer of exterior skin and underlying subcutaneous fat superimposed on a left and right gluteus maximus and gluteus medius muscles. The two gluteus maximus muscles are the largest muscles in the human body. They are responsible for movements such as straightening the body into the upright (standing) posture when it is bent at the waist; maintaining the body in the upright posture by keeping the hip joints extended; and propelling the body forward via further leg (hip) extension when walking or running.

The hip bone is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis.

The gluteal lines are three curved lines outlined from three bony ridges on the exterior surface of the ilium in the gluteal region. They are the anterior gluteal line; the inferior gluteal line, and the posterior gluteal line.