
Brassicaceae or Cruciferae is a medium-sized and economically important family of flowering plants commonly known as the mustards, the crucifers, or the cabbage family. Most are herbaceous plants, while some are shrubs. The leaves are simple, lack stipules, and appear alternately on stems or in rosettes. The inflorescences are terminal and lack bracts. The flowers have four free sepals, four free alternating petals, two shorter free stamens and four longer free stamens. The fruit has seeds in rows, divided by a thin wall.

Broccoli is an edible green plant in the cabbage family whose large flowering head, stalk and small associated leaves are eaten as a vegetable. Broccoli is classified in the Italica cultivar group of the species Brassica oleracea. Broccoli has large flower heads, usually dark green, arranged in a tree-like structure branching out from a thick stalk which is usually light green. The mass of flower heads is surrounded by leaves. Broccoli resembles cauliflower, which is a different but closely related cultivar group of the same Brassica species.

Cauliflower is one of several vegetables in the species Brassica oleracea in the genus Brassica, which is in the Brassicaceae family. It is an annual plant that reproduces by seed. Typically, only the head is eaten – the edible white flesh is sometimes called "curd". The cauliflower head is composed of a white inflorescence meristem. Cauliflower heads resemble those in broccoli, which differs in having flower buds as the edible portion. Brassica oleracea also includes broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, collard greens, kale, and kohlrabi, collectively called "cole" crops, though they are of different cultivar groups.

In organic chemistry, isothiocyanate is the functional group −N=C=S, formed by substituting the oxygen in the isocyanate group with a sulfur. Many natural isothiocyanates from plants are produced by enzymatic conversion of metabolites called glucosinolates. These natural isothiocyanates, such as allyl isothiocyanate, are also known as mustard oils. An artificial isothiocyanate, phenyl isothiocyanate, is used for amino acid sequencing in the Edman degradation.

The Brussels sprout is a member of the Gemmifera cultivar group of cabbages, grown for its edible buds. The leaf vegetables are typically 1.5–4.0 cm (0.6–1.6 in) in diameter and resemble miniature cabbages. The Brussels sprout has long been popular in Brussels, Belgium, from which it gained its name.

Brassica oleracea is a plant species from family Brassicaceae that includes many common cultivars used as vegetables, such as cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, kale, Brussels sprouts, collard greens, Savoy cabbage, kohlrabi, and gai lan.

Allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) is a naturally occurring unsaturated isothiocyanate. The colorless oil is responsible for the pungent taste of Cruciferous vegetables such as mustard, radish, horseradish, and wasabi. This pungency and the lachrymatory effect of AITC are mediated through the TRPA1 and TRPV1 ion channels. It is slightly soluble in water, but more soluble in most organic solvents.

Sulforaphane is a compound within the isothiocyanate group of organosulfur compounds. It is produced when the enzyme myrosinase transforms glucoraphanin, a glucosinolate, into sulforaphane upon damage to the plant, which allows the two compounds to mix and react.

Glucoraphanin is a glucosinolate found in broccoli, mustard and other cruciferous vegetables.

Glucosinolates are natural components of many pungent plants such as mustard, cabbage, and horseradish. The pungency of those plants is due to mustard oils produced from glucosinolates when the plant material is chewed, cut, or otherwise damaged. These natural chemicals most likely contribute to plant defence against pests and diseases, and impart a characteristic bitter flavor property to cruciferous vegetables.
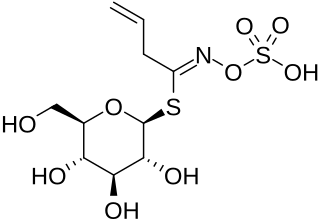
Sinigrin or allyl glucosinolate is a glucosinolate that belongs to the family of glucosides found in some plants of the family Brassicaceae such as Brussels sprouts, broccoli, and the seeds of black mustard. Whenever sinigrin-containing plant tissue is crushed or otherwise damaged, the enzyme myrosinase degrades sinigrin to a mustard oil, which is responsible for the pungent taste of mustard and horseradish. Seeds of white mustard, Sinapis alba, give a less pungent mustard because this species contains a different glucosinolate, sinalbin.

Cruciferous vegetables are vegetables of the family Brassicaceae with many genera, species, and cultivars being raised for food production such as cauliflower, cabbage, kale, garden cress, bok choy, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, mustard plant and similar green leaf vegetables. The family takes its alternative name from the shape of their flowers, whose four petals resemble a cross.

Glucobrassicin is a type of glucosinolate that can be found in almost all cruciferous plants, such as cabbages, broccoli, mustards, and woad. As for other glucosinolates, degradation by the enzyme myrosinase is expected to produce an isothiocyanate, indol-3-ylmethylisothiocyanate. However, this specific isothiocyanate is expected to be highly unstable, and has indeed never been detected. The observed hydrolysis products when isolated glucobrassicin is degraded by myrosinase are indole-3-carbinol and thiocyanate ion, which are envisioned to result from a rapid reaction of the unstable isothiocyanate with water. However, a large number of other reaction products are known, and indole-3-carbinol is not the dominant degradation product when glucosinolate degradation takes place in crushed plant tissue or in intact plants.

Myrosinase is a family of enzymes involved in plant defense against herbivores, specifically the mustard oil bomb. The three-dimensional structure has been elucidated and is available in the PDB.
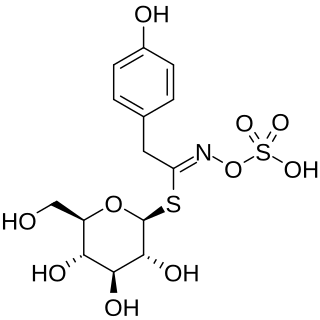
Sinalbin is a glucosinolate found in the seeds of white mustard, Sinapis alba, and in many wild plant species. In contrast to mustard from black mustard seeds which contain sinigrin, mustard from white mustard seeds has only a weakly pungent taste.

Gluconasturtiin or phenethyl glucosinolate is one of the most widely distributed glucosinolates in the cruciferous vegetables, mainly in the roots, and is probably one of the plant compounds responsible for the natural pest-inhibiting properties of growing crucifers, such as cabbage, mustard or rape, in rotation with other crops. This effect of gluconasturtiin is due to its degradation by the plant enzyme myrosinase into phenethyl isothiocyanate, which is toxic to many organisms.
In enzymology, a N-hydroxythioamide S-beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Progoitrin is a biochemical from the glucosinolate family that is found in some food, which is inactive but after ingestion is converted to goitrin. Goitrin decreases the thyroid hormone production.

Glucotropaeolin or benzyl glucosinolate is a glucosinolate found in cruciferous vegetables, particularly garden cress. Upon enzymatic activity, it is transformed into benzyl isothiocyanate, which contributes to the characteristic flavor of these brassicas.



















