
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

In organic chemistry, a ketene is an organic compound of the form RR'C=C=O, where R and R' are two arbitrary monovalent chemical groups. The name may also refer to the specific compound ethenone H2C=C=O, the simplest ketene.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.

Diazomethane is the chemical compound CH2N2, discovered by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1894. It is the simplest diazo compound. In the pure form at room temperature, it is an extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas; thus, it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether. The compound is a popular methylating agent in the laboratory, but it is too hazardous to be employed on an industrial scale without special precautions. Use of diazomethane has been significantly reduced by the introduction of the safer and equivalent reagent trimethylsilyldiazomethane.

Propyne (methylacetylene) is an alkyne with the chemical formula CH3C≡CH. It is a component of MAPD gas—along with its isomer propadiene (allene), which was commonly used in gas welding. Unlike acetylene, propyne can be safely condensed.

Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air.

Chromium(III) chloride (also called chromic chloride) describes any of several chemical compounds with the formula CrCl3 · xH2O, where x can be 0, 5, and 6. The anhydrous compound with the formula CrCl3 is a violet solid. The most common form of the trichloride is the dark green hexahydrate, CrCl3 · 6 H2O. Chromium chlorides find use as catalysts and as precursors to dyes for wool.
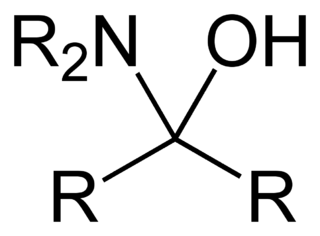
In organic chemistry, a hemiaminal is a functional group or type of chemical compound that has a hydroxyl group and an amine attached to the same carbon atom: −C(OH)(NR2)−. R can be hydrogen or an alkyl group. Hemiaminals are intermediates in imine formation from an amine and a carbonyl by alkylimino-de-oxo-bisubstitution. Hemiaminals can be viewed as a blend of aminals and geminal diol. They are a special case of amino alcohols.

Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3. This colorless liquid, the methyl ester of methacrylic acid (MAA), is a monomer produced on a large scale for the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).

Mesityl oxide is a α,β-unsaturated ketone with the formula CH3C(O)CH=C(CH3)2. This compound is a colorless, volatile liquid with a honey-like odor.
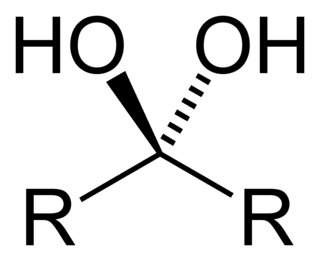
A geminal diol is any organic compound having two hydroxyl functional groups (-OH) bound to the same carbon atom. Geminal diols are a subclass of the diols, which in turn are a special class of alcohols. Most of the geminal diols are considered unstable.
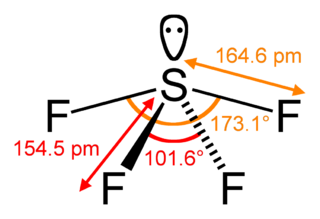
Sulfur tetrafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula SF4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous HF upon exposure to water or moisture. Despite these unwelcome characteristics, this compound is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries.
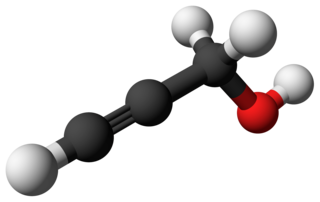
Propargyl alcohol, or 2-propyn-1-ol, is an organic compound with the formula C3H4O. It is the simplest stable alcohol containing an alkyne functional group. Propargyl alcohol is a colorless viscous liquid that is miscible with water and most polar organic solvents.
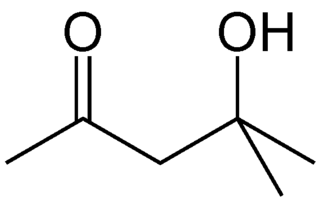
Diacetone alcohol is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2C(OH)(CH3)2, sometimes called DAA. This colorless liquid is a common synthetic intermediate used for the preparation of other compounds, and is also used as a solvent.
Acetone cyanohydrin (ACH) is an organic compound used in the production of methyl methacrylate, the monomer of the transparent plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), also known as acrylic. It liberates hydrogen cyanide easily, so it is used as a source of such. For this reason, this cyanohydrin is also highly toxic.
Methanediol, also known as formaldehyde monohydrate or methylene glycol, is an organic compound with chemical formula CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest geminal diol. In aqueous solutions it coexists with oligomers. The compound is closely related and convertible to the industrially significant derivatives paraformaldehyde, formaldehyde, and 1,3,5-trioxane.

Chloroacetaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula ClCH2CHO. Like some related compounds, it is highly electrophilic reagent and a potentially dangerous alkylating agent. The compound is not normally encountered in the anhydrous form, but rather as the hemiacetal (ClCH2CH(OH))2O.

Acetone imine, or 2-propanimine is an organic compound and an imine with the chemical formula (CH3)2CNH. It is a volatile and flammable liquid at room temperature. It is the simplest ketimine. This compound is mainly of academic interest.


























