In organic chemistry, a ketene is an organic compound of the form RR'C=C=O, where R and R' are two arbitrary monovalent chemical groups. The name may also refer to the specific compound ethenone H2C=C=O, the simplest ketene.
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme.

N,N-Dimethylaniline (DMA) is an organic chemical compound, a substituted derivative of aniline. It is a tertiary amine, featuring a dimethylamino group attached to a phenyl group. This oily liquid is colourless when pure, but commercial samples are often yellow. It is an important precursor to dyes such as crystal violet.

In organic chemistry, an oxime is an organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula RR’C=N−OH, where R is an organic side-chain and R' may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds. Amidoximes are oximes of amides with general structure R1C(=NOH)NR2R3.

Hydrazones are a class of organic compounds with the structure R1R2C=N−NH2. They are related to ketones and aldehydes by the replacement of the oxygen =O with the =N−NH2 functional group. They are formed usually by the action of hydrazine on ketones or aldehydes.
Mesitylene or 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene is a derivative of benzene with three methyl substituents positioned symmetrically around the ring. The other two isomeric trimethylbenzenes are 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (pseudocumene) and 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene (hemimellitene). All three compounds have the formula C6H3(CH3)3, which is commonly abbreviated C6H3Me3. Mesitylene is a colorless liquid with sweet aromatic odor. It is a component of coal tar, which is its traditional source. It is a precursor to diverse fine chemicals. The mesityl group (Mes) is a substituent with the formula C6H2Me3 and is found in various other compounds.

Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commercially. This white solid is an important industrial chemical, especially for the large-scale production of plasticizers for plastics. In 2000, the worldwide production volume was estimated to be about 3 million tonnes per year.

In organic chemistry, a cyanohydrin or hydroxynitrile is a functional group found in organic compounds in which a cyano and a hydroxy group are attached to the same carbon atom. The general formula is R2C(OH)CN, where R is H, alkyl, or aryl. Cyanohydrins are industrially important precursors to carboxylic acids and some amino acids. Cyanohydrins can be formed by the cyanohydrin reaction, which involves treating a ketone or an aldehyde with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of excess amounts of sodium cyanide (NaCN) as a catalyst:

Diazomethane is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH2N2, discovered by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1894. It is the simplest diazo compound. In the pure form at room temperature, it is an extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas; thus, it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether. The compound is a popular methylating agent in the laboratory, but it is too hazardous to be employed on an industrial scale without special precautions. Use of diazomethane has been significantly reduced by the introduction of the safer and equivalent reagent trimethylsilyldiazomethane.

In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, C−H bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid.
The Hofmann rearrangement is the organic reaction of a primary amide to a primary amine with one less carbon atom. The reaction involves oxidation of the nitrogen followed by rearrangement of the carbonyl and nitrogen to give an isocyanate intermediate. The reaction can form a wide range of products, including alkyl and aryl amines.
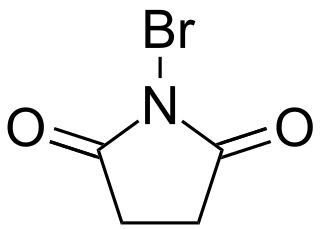
N-Bromosuccinimide or NBS is a chemical reagent used in radical substitution, electrophilic addition, and electrophilic substitution reactions in organic chemistry. NBS can be a convenient source of Br•, the bromine radical.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.

Hexafluoroacetone (HFA) is a chemical compound with the formula (CF3)2CO. It is structurally similar to acetone; however, its reactivity is markedly different. It a colourless, hygroscopic, nonflammable, highly reactive gas characterized by a musty odour. The most common form of this substance is hexafluoroacetone sesquihydrate (1.5 H2O), which is a hemihydrate of hexafluoropropane-2,2-diol (F
3C)
2C(OH)
2, a geminal diol.

Dibenzylideneacetone or dibenzalacetone, often abbreviated dba, is an organic compound with the formula C17H14O. It is a pale-yellow solid insoluble in water, but soluble in ethanol.
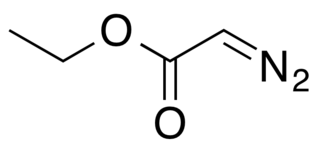
Ethyl diazoacetate (N=N=CHC(O)OC2H5) is a diazo compound and a reagent in organic chemistry. It was discovered by Theodor Curtius in 1883. The compound can be prepared by reaction of the ethyl ester of glycine with sodium nitrite and sodium acetate in water.

Organomercury chemistry refers to the study of organometallic compounds that contain mercury. Typically the Hg–C bond is stable toward air and moisture but sensitive to light. Important organomercury compounds are the methylmercury(II) cation, CH3Hg+; ethylmercury(II) cation, C2H5Hg+; dimethylmercury, (CH3)2Hg, diethylmercury and merbromin ("Mercurochrome"). Thiomersal is used as a preservative for vaccines and intravenous drugs.

Benzylideneacetone is the organic compound described by the formula C6H5CH=CHC(O)CH3. Although both cis- and trans-isomers are possible for the α,β-unsaturated ketone, only the trans isomer is observed. Its original preparation demonstrated the scope of condensation reactions to construct new, complex organic compounds. Benzylideneacetone is used as a flavouring ingredient in food and perfumes.
Acetone cyanohydrin (ACH) is an organic compound used in the production of methyl methacrylate, the monomer of the transparent plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), also known as acrylic. It liberates hydrogen cyanide easily, so it is used as a source of such. For this reason, this cyanohydrin is also highly toxic.
Organobromine chemistry is the study of the synthesis and properties of organobromine compounds, also called organobromides, which are organic compounds that contain carbon bonded to bromine. The most pervasive is the naturally produced bromomethane.