
RDX (abbreviation of "Research Department eXplosive" or Royal Demolition eXplosive) or hexogen, among other names, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2N2O2)3. It is white, odorless and tasteless, widely used as an explosive. Chemically, it is classified as a nitroamine alongside HMX, which is a more energetic explosive than TNT. It was used widely in World War II and remains common in military applications.

Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NO−
3. Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate.

The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is atmospheric nitrogen, making it the largest source of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems.

Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula KNO
3. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrate ions NO3−, and is therefore an alkali metal nitrate. It occurs in nature as a mineral, niter (or nitre in the UK). It is a source of nitrogen, and nitrogen was named after niter. Potassium nitrate is one of several nitrogen-containing compounds collectively referred to as saltpeter (or saltpetre in the UK).

Lead(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb(NO3)2. It commonly occurs as a colourless crystal or white powder and, unlike most other lead(II) salts, is soluble in water.
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO−
2. Nitrite is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid.

Sodium nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaNO2. It is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder that is very soluble in water and is hygroscopic. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important nitrite salt. It is a precursor to a variety of organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, dyes, and pesticides, but it is probably best known as a food additive used in processed meats and (in some countries) in fish products.

A perchlorate is a chemical compound containing the perchlorate ion, ClO−4, the conjugate base of perchloric acid. As counterions, there can be metal cations, quaternary ammonium cations or other ions, for example, nitronium cation.

Nitrobenzene is an aromatic nitro compound and the simplest of the nitrobenzenes, with the chemical formula C6H5NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents.

Methemoglobin (British: methaemoglobin, shortened MetHb) (pronounced "met-hemoglobin") is a hemoglobin in the form of metalloprotein, in which the iron in the heme group is in the Fe3+ (ferric) state, not the Fe2+ (ferrous) of normal hemoglobin. Sometimes, it is also referred to as ferrihemoglobin. Methemoglobin cannot bind oxygen, which means it cannot carry oxygen to tissues. It is bluish chocolate-brown in color. In human blood a trace amount of methemoglobin is normally produced spontaneously, but when present in excess the blood becomes abnormally dark bluish brown. The NADH-dependent enzyme methemoglobin reductase (a type of diaphorase) is responsible for converting methemoglobin back to hemoglobin.
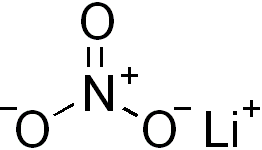
Lithium nitrate is an inorganic compound with the formula LiNO3. It is the lithium salt of nitric acid (an alkali metal nitrate). The salt is deliquescent, absorbing water to form the hydrated form, lithium nitrate trihydrate. Its eutectics are of interest for heat transfer fluids.

Hydroxylammonium nitrate or hydroxylamine nitrate (HAN) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula [NH3OH]+[NO3]−. It is a salt derived from hydroxylamine and nitric acid. In its pure form, it is a colourless hygroscopic solid. It has potential to be used as a rocket propellant either as a solution in monopropellants or bipropellants. Hydroxylammonium nitrate (HAN)-based propellants are a viable and effective solution for future green propellant-based missions, as it offers 50% higher performance for a given propellant tank compared to commercially used hydrazine.
Chloropicrin, also known as PS and nitrochloroform, is a chemical compound currently used as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial, fungicide, herbicide, insecticide, and nematicide. It was used as a poison gas in World War I. Its chemical structural formula is Cl3C−NO2.
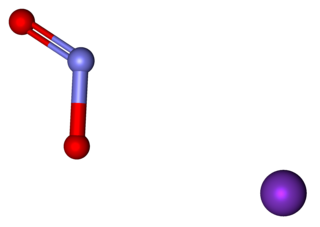
Potassium nitrite (distinct from potassium nitrate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula KNO2. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrite ions NO2−, which forms a white or slightly yellow, hygroscopic crystalline powder that is soluble in water.
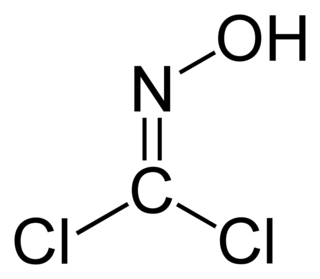
Phosgene oxime, or CX, is an organic compound with the formula Cl2C=N−OH. It is a potent chemical weapon, specifically a nettle agent. The compound itself is a colorless solid, but impure samples are often yellowish liquids. It has a strong, disagreeable and irritating odor. It is used as a reagent in organic chemistry.

Gallium nitrate (brand name Ganite) is the gallium salt of nitric acid with the chemical formula Ga(NO3)3. It is a drug used to treat symptomatic hypercalcemia secondary to cancer. It works by preventing the breakdown of bone through the inhibition of osteoclast activity, thus lowering the amount of free calcium in the blood. Gallium nitrate is also used to synthesize other gallium compounds.
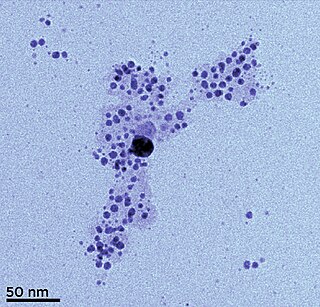
Silver nanoparticles are nanoparticles of silver of between 1 nm and 100 nm in size. While frequently described as being 'silver' some are composed of a large percentage of silver oxide due to their large ratio of surface to bulk silver atoms. Numerous shapes of nanoparticles can be constructed depending on the application at hand. Commonly used silver nanoparticles are spherical, but diamond, octagonal, and thin sheets are also common.
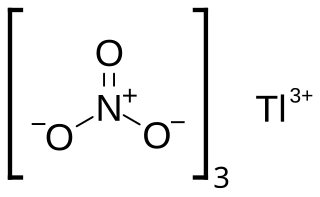
Thallium(III) nitrate, also known as thallic nitrate, is a thallium compound with chemical formula Tl(NO3)3. It is normally found as the trihydrate. It is a colorless and highly toxic salt. It is a strong oxidizing agent useful in organic synthesis. Among its many transformations, it oxidizes methoxyl phenols to quinone acetals, alkenes to acetals, and cyclic alkenes to ring-contracted aldehydes.
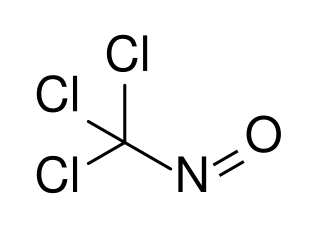
Trichloronitrosomethane is a chlorinated nitrosoalkane. It is a deep blue liquid with powerful lachrymatory effects.
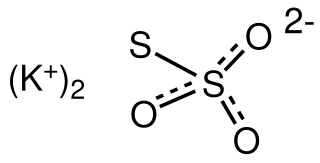
Potassium thiosulfate is an inorganic compound with the formula K2S2O3. This salt can form multiple hydrates, such as the monohydrate, dihydrate, and the pentahydrate, all of which are white or colorless solids. It is used as a fertilizer.


















