Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison.

Sarin is an extremely toxic synthetic organophosphorus compound. A colourless, odourless liquid, it is used as a chemical weapon due to its extreme potency as a nerve agent. Exposure is lethal even at very low concentrations, where death can occur within one to ten minutes after direct inhalation of a lethal dose, due to suffocation from respiratory paralysis, unless antidotes are quickly administered. People who absorb a non-lethal dose, but do not receive immediate medical treatment, may suffer permanent neurological damage.

Tabun or GA is an extremely toxic chemical substance. It is a clear, colorless, and tasteless liquid with a faint fruity odor. It is classified as a nerve agent because it fatally interferes with normal functioning of the mammalian nervous system. Its production is strictly controlled and stockpiling outlawed by the Chemical Weapons Convention of 1993. Tabun is the first of the G-series nerve agents along with GB (sarin), GD (soman) and GF (cyclosarin).

VX is an extremely toxic synthetic chemical compound in the organophosphorus class, specifically, a thiophosphonate. In the class of nerve agents, it was developed for military use in chemical warfare after translation of earlier discoveries of organophosphate toxicity in pesticide research. In recent years, VX was found to be the agent used in the assassination of Kim Jong-nam. In its pure form, VX is an oily, relatively non-volatile, liquid that is amber-like in color. Because of its low volatility, VX persists in environments where it is dispersed.

VG is a "V-series" nerve agent chemically similar to the better-known VX nerve agent. Tetram is the common Russian name for the substance. Amiton was the trade name for the substance when it was marketed as an insecticide by ICI in the mid-1950s.
Chemical, biological (CB) — and sometimes radiological — warfare agents were assigned what is termed a military symbol by the U.S. military until the American chemical and biological weapons programs were terminated. Military symbols applied to the CB agent fill, and not to the entire weapon. A chemical or biological weapon designation would be, for example, "Aero-14/B", which could be filled with GB, VX, TGB, or with a biological modification kit – OU, NU, UL, etc. A CB weapon is an integrated device of (1) agent, (2) dissemination means, and (3) delivery system.
From 1948 to 1975, the U.S. Army Chemical Corps conducted classified human subject research at the Edgewood Arsenal facility in Maryland. The purpose was to evaluate the impact of low-dose chemical warfare agents on military personnel and to test protective clothing, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines. A small portion of these studies were directed at psychochemical warfare and grouped under the prosaic title of the "Medical Research Volunteer Program" (1956–1975). The MRVP was also driven by intelligence requirements and the need for new and more effective interrogation techniques.
Methylphosphonyl difluoride (DF), also known as EA-1251 or difluoro, is a chemical weapon precursor. Its chemical formula is CH3POF2. It is a Schedule 1 substance in the sense of the Chemical Weapons Convention. It is used for production of sarin and soman as a component of binary chemical weapons; an example is the M687 artillery shell, where it is used together with a mixture of isopropyl alcohol and isopropyl amine, producing sarin.

The Dugway sheep incident, also known as the Skull Valley sheep kill, was a March 1968 sheep kill that has been connected to United States Army chemical and biological warfare programs at Dugway Proving Ground in Utah. Six thousand sheep were killed on ranches near the base, and the popular explanation blamed Army testing of chemical weapons for the incident, though alternative explanations have been offered. A report, commissioned by Air Force Press Officer Jesse Stay and first made public in 1998, was called the "first documented admission" from the Army that a nerve agent killed the sheep at Skull Valley.
The M125 bomblet was a U.S. chemical sub-munition designed to deliver the nerve agent sarin. It was brought into service in 1954 with the M34 cluster bomb as part of the first U.S. air-delivered nerve agent weapon.

EA-3148 is a "V-series" nerve agent related to the better-known compounds VX and VR. It was studied by both the US and Soviet chemical weapons programmes during the Cold War, and is notable as the only V-series organophosphate nerve agent specifically identified in public domain sources as having a higher absolute potency as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor than VX. However, both the US and Soviet investigations of the compound concluded that despite its high potency, the physicochemical properties of the substance made it unsuitable for weaponisation, and further research was not conducted. The chemical structure of EA-3148 falls within the scope of compounds designated "Toxic chemicals" under Schedule 1 of the Chemical Weapons Convention and so it is illegal throughout the world under international law and may only be used for certain types of scientific and medical research.

A-232 is an organophosphate nerve agent. It was developed in the Soviet Union under the FOLIANT program and is one of the group of compounds referred to as Novichok agents that were revealed by Vil Mirzayanov. A-232 is reportedly slightly less potent as a nerve agent compared to some of the other compounds in the series such as A-230 and A-234, having similar potency to the older nerve agent VR. However it proved to be the most versatile agent as it was chemically stable and remained a volatile liquid over a wide temperature range, making it able to be used in standard chemical munitions without requiring special delivery mechanisms to be developed.

EA-3990 is a deadly carbamate nerve agent. It is lethal because it inhibits acetylcholinesterase. Inhibition causes an overly high accumulation of acetylcholine between the nerve and muscle cells. This paralyzes the muscles by preventing their relaxation. The paralyzed muscles include the muscles used for breathing.

EA-4056 is a deadly carbamate nerve agent. It is lethal because it inhibits acetylcholinesterase. Inhibition causes an overly high accumulation of acetylcholine between the nerve and muscle cells. This paralyzes the muscles by preventing their relaxation. The paralyzed muscles includes the muscles used for breathing.
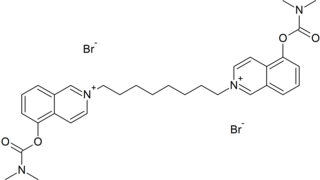
Octamethylene-bis(5-dimethylcarbamoxyisoquinolinium bromide) is an extremely potent carbamate nerve agent. It works by inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase, causing acetylcholine to accumulate. Since the agent molecule is positively charged, it does not cross the blood brain barrier very well.

EA-2192 is an extremely toxic degradation product of the VX nerve agent. It is a white solid that is very soluble and stable in water.

EA-4352 is an organophosphate nerve agent of the G-series. It's the isopropyl analog of tabun.
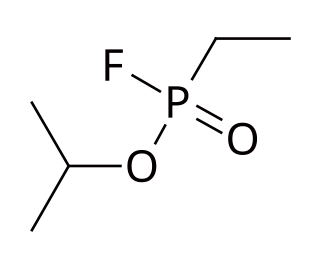
Ethylsarin (GE), also known as EA-1209, is an organophosphate nerve agent of the G-series. It's the ethylphosphonofluoridate analog of sarin.

EA-3966 is a carbamate nerve agent. It's synthesized by reacting 2-dimethylaminomethyl-3-dimethylcarbamoxypyridine with 10-bromodecyltrimethylammonium bromide.

A-230 is an organophosphate nerve agent. It was developed in the Soviet Union under the FOLIANT program and is one of the group of compounds referred to as Novichok agents that were revealed by Vil Mirzayanov. A-230 is possibly the most potent nerve agent for which specific toxicity figures have been published, with a human lethal dose estimated to be less than 0.1mg. However it was felt to be less suitable for weaponisation than other agents such as A-232 and A-234, due to issues with the liquid agent exhibiting low volatility and solidifying at low temperatures, as well as poor stability in the presence of water.