Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a gray post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861, in residues of sulfuric acid production. Both used the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy, in which thallium produces a notable green spectral line. Thallium, from Greek θαλλός, thallós, meaning "green shoot" or "twig", was named by Crookes. It was isolated by both Lamy and Crookes in 1862; Lamy by electrolysis, and Crookes by precipitation and melting of the resultant powder. Crookes exhibited it as a powder precipitated by zinc at the international exhibition, which opened on 1 May that year.

Percy Lavon Julian was an American research chemist and a pioneer in the chemical synthesis of medicinal drugs from plants. He was the first to synthesize the natural product physostigmine and was a pioneer in the industrial large-scale chemical synthesis of the human hormones progesterone and testosterone from plant sterols such as stigmasterol and sitosterol. His work laid the foundation for the steroid drug industry's production of cortisone, other corticosteroids, and birth control pills.
A parasympathomimetic drug, sometimes called a cholinomimetic drug or cholinergic receptor stimulating agent, is a substance that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). These chemicals are also called cholinergic drugs because acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by the PSNS. Chemicals in this family can act either directly by stimulating the nicotinic or muscarinic receptors, or indirectly by inhibiting cholinesterase, promoting acetylcholine release, or other mechanisms. Common uses of parasympathomimetics include glaucoma, sjögren syndrome and underactive bladder.
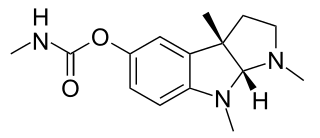
Physostigmine is a highly toxic parasympathomimetic alkaloid, specifically, a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor. It occurs naturally in the Calabar bean and the fruit of the Manchineel tree.

Thallium(I) sulfate (Tl2SO4) or thallous sulfate is the sulfate salt of thallium in the common +1 oxidation state, as indicated by the Roman numeral I. It is often referred to as simply thallium sulfate.
Thallium(I) telluride (Tl2Te) is a chemical compound of thallium and tellurium. It has a structure related to that of Tl5Te3. This compound is not well characterized. Its existence has only recently been confirmed by differential scanning calorimetry.

Thallium(I) oxide is the inorganic compound of thallium and oxygen with the formula Tl2O in which thallium is in its +1 oxidation state. It is black and produces a basic yellow solution of thallium(I) hydroxide (TlOH) when dissolved in water. It is formed by heating solid TlOH or Tl2CO3 in the absence of air. Thallium oxide is used to make special high refractive index glass. Thallium oxide is a component of several high temperature superconductors. Thallium(I) oxide reacts with acids to make thallium(I) salts.

Thallium(I) chloride, also known as thallous chloride, is a chemical compound with the formula TlCl. This colourless salt is an intermediate in the isolation of thallium from its ores. Typically, an acidic solution of thallium(I) sulfate is treated with hydrochloric acid to precipitate insoluble thallium(I) chloride. This solid crystallizes in the caesium chloride motif.
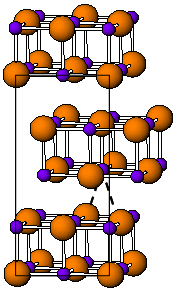
Thallium(I) iodide is a chemical compound with the formula TlI. It is unusual in being one of the few water-insoluble metal iodides, along with AgI, CuI, SnI2, SnI4, PbI2 and HgI2.

Thallium(III) oxide, also known as thallic oxide, is a chemical compound of thallium and oxygen. It occurs in nature as the rare mineral avicennite. Its structure is related to that of Mn2O3 which has a bixbyite like structure. Tl2O3 is metallic with high conductivity and is a degenerate n-type semiconductor which may have potential use in solar cells. A method of producing Tl2O3 by MOCVD is known. Any practical use of thallium(III) oxide will always have to take account of thallium's poisonous nature. Contact with moisture and acids may form poisonous thallium compounds.
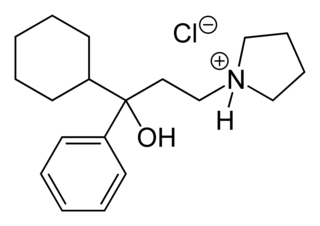
Procyclidine is an anticholinergic drug principally used for the treatment of drug-induced parkinsonism, akathisia and acute dystonia, Parkinson's disease, and idiopathic or secondary dystonia.

Ludwig Laqueur was a German ophthalmologist born in Festenberg, Silesia. He was the father of historian Richard Laqueur (1881–1959).

Thallium(I) sulfide, Tl2S, is a chemical compound of thallium and sulfur. It was used in some of the earliest photo-electric detectors by Theodore Case who developed the so-called thalofide (sometimes spelt thallofide) cell, used in early film projectors. Case described the detector material as consisting of thallium, oxygen and sulfur, and this was incorrectly described by others as being thallium oxysulfide, which incidentally is a compound that is not known. Case's work was then built on by R.J. Cashman who recognised that the controlled oxidation of the Tl2S film was key to the operation of the cell. Cashman's work culminated in the development of long wave infrared detectors used during the Second World War. Reliable Tl2S detectors were also developed in Germany at the same time.
Tl2S is found in nature as the mineral carlinite which has the distinction of being the only sulfide mineral of thallium that does not contain at least two metals. Tl2S has a distorted anti-CdI2 structure.
Tl2S can be prepared from the elements or by precipitating the sulfide from a solution of thallium(I), e.g. the sulfate or nitrate. Thin films have been deposited, produced from a mixture of citratothallium complex and thiourea. Heating the film in nitrogen at 300°C converts all the product into Tl2S
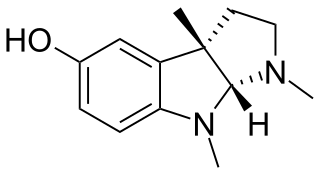
Eseroline is a drug which acts as an opioid agonist. It is a metabolite of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor physostigmine but unlike physostigmine, the acetylcholinesterase inhibition produced by eseroline is weak and easily reversible, and it produces fairly potent analgesic effects mediated through the μ-opioid receptor. This mixture of activities gives eseroline an unusual pharmacological profile, although its uses are limited by side effects such as respiratory depression and neurotoxicity.

Thallous acetate is a salt of thallium and acetate with the chemical formula TlCH3COO. It is used in microbiology as a selective growth medium. It is poisonous.

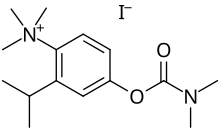
T-1123 is a carbamate-based acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It was investigated as a chemical warfare agent starting in 1940. It does not go through the blood-brain barrier due to the charge on quaternary nitrogen. The antidote is atropine. T-1123 is a quaternary ammonium ion. A phenyl carbamate ester is bonded in the meta position to the nitrogen on a diethylmethyl amine. The chloride and methylsulfate salt of T-1123 is TL-1299 and TL-1317, respectively.
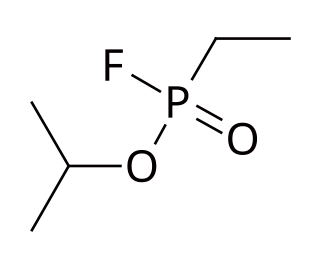
Ethylsarin (GE), also known as EA-1209, TL-1620 or T-2109, is an organophosphate nerve agent of the G-series. It is the ethylphosphonofluoridate analog of sarin.

TL-1238 is an extremely potent carbamate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It has been shown to be more potent than neostigmine.

EA-3966 is a carbamate nerve agent. It is synthesized by reacting 2-dimethylaminomethyl-3-dimethylcarbamoxypyridine with 10-bromodecyltrimethylammonium bromide.