
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is a working group of authorities that was formed by ISO and IEC to set standards for audio and video compression and transmission. It was established in 1988 by the initiative of Hiroshi Yasuda and Leonardo Chiariglione, group Chair since its inception. The first MPEG meeting was in May 1988 in Ottawa, Canada. As of late 2005, MPEG has grown to include approximately 350 members per meeting from various industries, universities, and research institutions. MPEG's official designation is ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29/WG 11 – Coding of moving pictures and audio.

MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods, which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission bandwidth. While MPEG-2 is not as efficient as newer standards such as H.264/AVC and H.265/HEVC, backwards compatibility with existing hardware and software means it is still widely used, for example in over-the-air digital television broadcasting and in the DVD-Video standard.
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual (AV) digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) under the formal standard ISO/IEC 14496 – Coding of audio-visual objects. Uses of MPEG-4 include compression of AV data for web and CD distribution, voice and broadcast television applications. The MPEG-4 standard was developed by a group led by Touradj Ebrahimi and Fernando Pereira.

Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU).
DVB-C stands for "Digital Video Broadcasting - Cable" and it is the DVB European consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital television over cable. This system transmits an MPEG-2 or MPEG-4 family digital audio/digital video stream, using a QAM modulation with channel coding. The standard was first published by the ETSI in 1994, and subsequently became the most widely used transmission system for digital cable television in Europe, Asia and South America. It is deployed worldwide in systems ranging from the larger cable television networks (CATV) down to smaller satellite master antenna TV (SMATV) systems.

Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation (DVB-S2) is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and ratified by ETSI in March 2005. The standard is based on, and improves upon DVB-S and the electronic news-gathering system, used by mobile units for sending sounds and images from remote locations worldwide back to their home television stations.
3GP is a multimedia container format defined by the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) for 3G UMTS multimedia services. It is used on 3G mobile phones but can also be played on some 2G and 4G phones.
Datacasting is the broadcasting of data over a wide area via radio waves. It most often refers to supplemental information sent by television stations along with digital terrestrial television, but may also be applied to digital signals on analog TV or radio. It generally does not apply to data which is inherent to the medium, such as PSIP data which defines virtual channels for DTT or direct broadcast satellite systems; or to things like cable modem or satellite modem, which use a completely separate channel for data.

High-Efficiency Advanced Audio Coding (AAC-HE) is an audio coding format for lossy data compression of digital audio defined as an MPEG-4 Audio profile in ISO/IEC 14496-3. It is an extension of Low Complexity AAC (AAC-LC) optimized for low-bitrate applications such as streaming audio. The usage profile AAC-HE v1 uses spectral band replication (SBR) to enhance the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) compression efficiency in the frequency domain. The usage profile AAC-HE v2 couples SBR with Parametric Stereo (PS) to further enhance the compression efficiency of stereo signals.
MPEG transport stream is a standard digital container format for transmission and storage of audio, video, and Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) data. It is used in broadcast systems such as DVB, ATSC and IPTV.
DVB-H is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website. From March 2008, DVB-H is officially endorsed by the European Union as the "preferred technology for terrestrial mobile broadcasting". The major competitors of this technology are Qualcomm's MediaFLO system, the 3G cellular system based MBMS mobile-TV standard, and the ATSC-M/H format in the U.S. DVB-SH now and DVB-NGH in the future are possible enhancements to DVB-H, providing improved spectral efficiency and better modulation flexibility. DVB-H has been a commercial failure, and the service is no longer on-air. Ukraine was the last country with a nationwide broadcast in DVB-H.
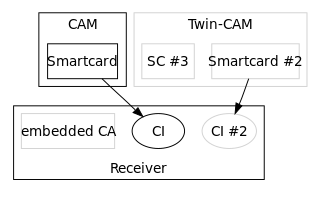
In Digital Video Broadcasting, the Common Interface is a technology which allows decryption of pay TV channels. Pay TV stations want to choose which encryption method to use. The Common Interface allows TV manufacturers to support many different pay TV stations, by allowing to plug in exchangeable conditional-access modules (CAM) for various encryption schemes.

Asynchronous Serial Interface, or ASI, is a method of carrying an MPEG Transport Stream (MPEG-TS) over 75-ohm copper coaxial cable or multimode optical fiber. It is popular in the television industry as a means of transporting broadcast programs from the studio to the final transmission equipment before it reaches viewers sitting at home.
Packetized Elementary Stream (PES) is a specification in the MPEG-2 Part 1 (Systems) and ITU-T H.222.0 that defines carrying of elementary streams in packets within MPEG program streams and MPEG transport streams. The elementary stream is packetized by encapsulating sequential data bytes from the elementary stream inside PES packet headers.
IEC 61883 Consumer Audio/Video Equipment - Digital Interface is a technical standard for a digital interface that is used by IEEE 1394 (FireWire) devices for audio and video equipment. The standard for these devices is maintained by the International Electrotechnical Commission. The first part was released in 1998; the current third edition is dated 2008.
Mobile IPTV is a technology that enables users to transmit and receive multimedia traffic including video, audio, text and graphic services through IP-based wired and wireless networks, with support for Quality of Service, Quality of experience, security, mobility, and interactive functions. Through Mobile IPTV, users can view IPTV services using a mobile device.
ISO/IEC base media file format defines a general structure for time-based multimedia files such as video and audio. The identical text is published as ISO/IEC 15444-12.
MPEG media transport (MMT), specified as ISO/IEC 23008-1, is a digital container standard developed by Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) that supports High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) video. MMT was designed to transfer data using the all-Internet Protocol (All-IP) network.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29 Coding of audio, picture, multimedia and hypermedia information is a standardization subcommittee of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), that develops and facilitates international standards, technical reports, and technical specifications within the field of audio, picture, multimedia, and hypermedia information coding. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29 is the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC) located in Japan.





