Related Research Articles

A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force is transformed, by a connecting rod and flywheel, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine.

Thomas Savery was an English inventor and engineer, born at Shilstone, a manor house near Modbury, Devon, England. He invented the first commercially used steam powered device, a steam pump which is often referred to as an "engine", although it is not technically an "engine". Savery's steam pump was a revolutionary method of pumping water, which solved the problem of mine drainage and made widespread public water supply practicable.

The atmospheric engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, and is often referred to simply as a Newcomen engine. The engine was operated by condensing steam drawn into the cylinder, thereby creating a partial vacuum which allowed the atmospheric pressure to push the piston into the cylinder. It was the first practical device to harness steam to produce mechanical work. Newcomen engines were used throughout Britain and Europe, principally to pump water out of mines. Hundreds were constructed through the 18th century.

Richard Trevithick was a British inventor and mining engineer from Cornwall, UK. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He was an early pioneer of steam-powered road and rail transport, and his most significant contributions were the development of the first high-pressure steam engine and the first working railway steam locomotive. The world's first locomotive-hauled railway journey took place on 21 February 1804, when Trevithick's unnamed steam locomotive hauled a train along the tramway of the Penydarren Ironworks, in Merthyr Tydfil, Wales.
Improvements to the steam engine were some of the most important technologies of the Industrial Revolution, although steam did not replace water power in importance in Britain until after the Industrial Revolution. From Englishman Thomas Newcomen's atmospheric engine, of 1712, through major developments by Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer James Watt, the steam engine began to be used in many industrial settings, not just in mining, where the first engines had been used to pump water from deep workings. Early mills had run successfully with water power, but by using a steam engine a factory could be located anywhere, not just close to a water source. Water power varied with the seasons and was not always available.
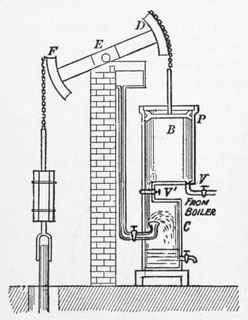
A beam engine is a type of steam engine where a pivoted overhead beam is used to apply the force from a vertical piston to a vertical connecting rod. This configuration, with the engine directly driving a pump, was first used by Thomas Newcomen around 1705 to remove water from mines in Cornwall. The efficiency of the engines was improved by engineers including James Watt, who added a separate condenser; Jonathan Hornblower and Arthur Woolf, who compounded the cylinders; and William McNaught, who devised a method of compounding an existing engine. Beam engines were first used to pump water out of mines or into canals but could be used to pump water to supplement the flow for a waterwheel powering a mill.

Poldice mine is a former metalliferous mine located in Poldice Valley in southwest Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated near the hamlet of Todpool, between the villages of Twelveheads and St Day, three miles (5 km) east of Redruth.

Gwennap is a village and civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is about five miles (8 km) southeast of Redruth. Hamlets of Burncoose, Comford, Coombe, Crofthandy, Cusgarne, Fernsplatt, Frogpool, Goon Gumpas Hick's Mill, Tresamble and United Downs lie in the parish, as does Little Beside country house.

A Cornish engine is a type of steam engine developed in Cornwall, England, mainly for pumping water from a mine. It is a form of beam engine that uses steam at a higher pressure than the earlier engines designed by James Watt. The engines were also used for powering man engines to assist the underground miners' journeys to and from their working levels, for winching materials into and out of the mine, and for powering on-site ore stamping machinery.
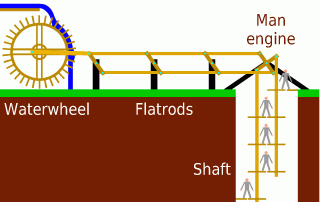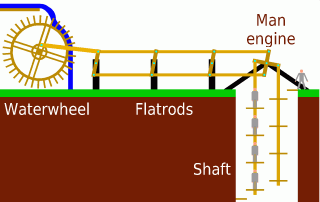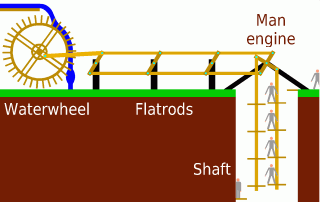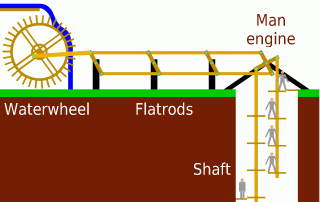
A man engine is a mechanism of reciprocating ladders and stationary platforms installed in mines to assist the miners' journeys to and from the working levels. It was invented in Germany in the 19th century and was a prominent feature of tin and copper mines in Cornwall until the beginning of the twentieth century.

Arthur Woolf was a Cornish engineer, most famous for inventing a high-pressure compound steam engine. As such he made an outstanding contribution to the development and perfection of the Cornish engine.

The Copper Mine on Virgin Gorda, British Virgin Islands, is a national park containing the ruins of an abandoned 19th-century copper mine.

Dolcoath mine (Cornish: Bal Dorkoth} was a copper and tin mine in Camborne, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Its name derives from the Cornish for 'Old Ground', and it was also affectionately known as The Queen of Cornish Mines. The site is north-west of Carn Brea. Dolcoath Road runs between the A3047 road and Chapel Hill. The site is south of this road.
Currency, in the form of coins, has been issued in Cornwall periodically since at least the 10th century AD, while banknotes were issued into the 19th century.

The first recorded rudimentary steam engine was the aeolipile described by Heron of Alexandria in 1st-century Roman Egypt. Several steam-powered devices were later experimented with or proposed, such as Taqi al-Din's steam jack, a steam turbine in 16th-century Ottoman Egypt, and Thomas Savery's steam pump in 17th-century England. In 1712, Thomas Newcomen's atmospheric engine became the first commercially successful engine using the principle of the piston and cylinder, which was the fundamental type of steam engine used until the early 20th century. The steam engine was used to pump water out of coal mines.

Prestongrange Museum is an industrial heritage museum at Prestongrange between Musselburgh and Prestonpans on the B1348 on the East Lothian coast, Scotland. Founded as the original site of the National Mining Museum, its operation reverted to East Lothian Council Museum Service in 1992.

Consolidated Mines, also known as Great Consolidated mine, but most commonly called Consols or Great Consols was a metalliferous mine about a mile ESE of the village of St Day, Cornwall, England. Mainly active during the first half of the 19th century, its mining sett was about 600 yards north–south; and 2,700 yards east–west, to the east of Carharrack. Although always much troubled by underground water, the mine was at times highly profitable, and it was the largest single producer of copper ore in Cornwall. Today the mine is part of the Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape World Heritage Site.

The Chapin Mine Steam Pump Engine, also known as The Cornish Pump, is a steam-driven pump located at the corner of Kent Street and Kimberly Avenue in Iron Mountain, Michigan, USA. It is the largest reciprocating steam-driven engine ever built in the United States. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1981 and designated a Michigan State Historic Site in 1958.

The Trevithick Society is a registered charity named for Richard Trevithick, a Cornish engineer who contributed to the use of high pressure steam engines for transportation and mining applications.
Nicholas Trestrail was a British mining engineer in Redruth, Cornwall, England. He was the designer of the Harvey's Engine, a Cornish beam engine initially used as a pumping engine as of 1892 in the Carn Brea mine and from 1924 till 28 September 1954 in the East Pool mine.
References
- Barton, D. B. (1966). The Cornish Beam Engine. Truro, Cornwall: D. B. Barton Ltd.
- Howard, Bridget (2002). Mr. Lean and the Engine Reporters. Camborne: Trevithick Society.
- Nuvolari, Alessandro. "Lean's Engine Reporter and the development of the Cornish engine: A reappraisal". Transactions of the Newcomen Society, Vol 77, (2007), 167-189