Articles related to anatomy include:
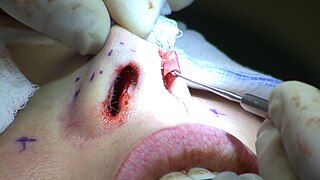
Rhinoplasty, commonly called nose job, medically called nasal reconstruction is a plastic surgery procedure for altering and reconstructing the nose. There are two types of plastic surgery used – reconstructive surgery that restores the form and functions of the nose and cosmetic surgery that changes the appearance of the nose. Reconstructive surgery seeks to resolve nasal injuries caused by various traumas including blunt, and penetrating trauma and trauma caused by blast injury. Reconstructive surgery can also treat birth defects, breathing problems, and failed primary rhinoplasties. Rhinoplasty may remove a bump, narrow nostril width, change the angle between the nose and the mouth, or address injuries, birth defects, or other problems that affect breathing, such as a deviated nasal septum or a sinus condition. Surgery only on the septum is called a septoplasty.

The ethmoid bone is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that make up the orbit of the eye.
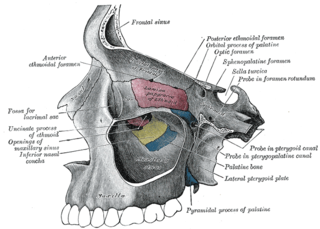
The inferior nasal concha is one of the three paired nasal conchae in the nose. It extends horizontally along the lateral wall of the nasal cavity and consists of a lamina of spongy bone, curled upon itself like a scroll,. The inferior nasal conchae are considered a pair of facial bones. As the air passes through the turbinates, the air is churned against these mucosa-lined bones in order to receive warmth, moisture and cleansing. Superior to inferior nasal concha are the middle nasal concha and superior nasal concha which both arise from the ethmoid bone, of the cranial portion of the skull. Hence, these two are considered as a part of the cranial bones.
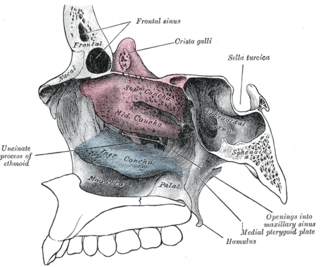
In anatomy, a nasal concha, also called a nasal turbinate or turbinal, is a long, narrow, curled shelf of bone that protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose in humans and various animals. The conchae are shaped like an elongated seashell, which gave them their name. A concha is any of the scrolled spongy bones of the nasal passages in vertebrates.
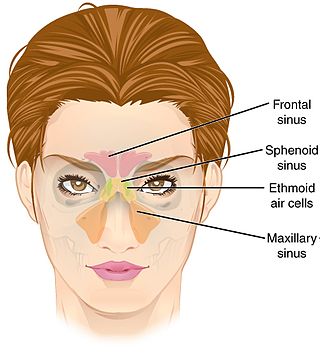
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of small air-filled cavities. The cells are located within the lateral mass (labyrinth) of each ethmoid bone and are variable in both size and number. The cells are grouped into anterior, middle, and posterior groups; the groups differ in their drainage modalities, though all ultimately drain into either the superior or the middle nasal meatus of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity.
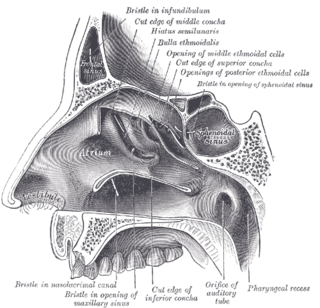
The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus occurring within the body of the sphenoid bone. It represents one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The pair of sphenoid sinuses are separated in the middle by a septum of sphenoid sinuses. Each sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity via the opening of sphenoidal sinus. The two sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape, and are usually asymmetrical.

The ethmoidal labyrinth or lateral mass of the ethmoid bone consists of a number of thin-walled cellular cavities, the ethmoid air cells, arranged in three groups, anterior, middle, and posterior, and interposed between two vertical plates of bone; the lateral plate forms part of the orbit, the medial plate forms part of the nasal cavity. In the disarticulated bone many of these cells are opened into, but when the bones are articulated, they are closed in at every part, except where they open into the nasal cavity.

The anterior ethmoidal artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery in the orbit. It exits the orbit through the anterior ethmoidal foramen alongside the anterior ethmoidal nerve. It contributes blood supply to the ethmoid sinuses, frontal sinuses, the dura mater, lateral nasal wall, and nasal septum. It issues a meningeal branch, and nasal branches.

The anterior ethmoidal nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1)). It arises in the orbit, and enters first the cranial cavity and then the nasal cavity. It provides sensory innervation to part of the meninges, parts of the nasal cavity, and part of the skin of the nose.

The medial surface of the labyrinth of ethmoid consists of a thin lamella, which descends from the under surface of the cribriform plate, and ends below in a free, convoluted margin, the middle nasal concha.
This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.
Chronic atrophic rhinitis, or simply atrophic rhinitis, is a chronic inflammation of the nose characterised by atrophy of nasal mucosa, including the glands, turbinate bones and the nerve elements supplying the nose. Chronic atrophic rhinitis may be primary and secondary. Special forms of chronic atrophic rhinitis are rhinitis sicca anterior and ozaena. It can also be described as the empty nose syndrome.
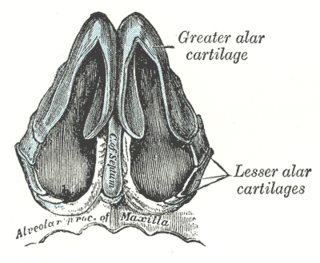
The nasal cartilages are structures within the nose that provide form and support to the nasal cavity. The nasal cartilages are made up of a flexible material called hyaline cartilage in the distal portion of the nose. There are five individual cartilages that make up the nasal cavity: septal nasal cartilage, lateral nasal cartilage, major alar cartilage, minor alar cartilage, and vomeronasal cartilage.

The body of the sphenoid bone, more or less cubical in shape, is hollowed out in its interior to form two large cavities, the sphenoidal sinuses, which are separated from each other by a septum.

The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum, which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two.

A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passes through the pharynx, shared with the digestive system, and then into the rest of the respiratory system. In humans, the nose is located centrally on the face and serves as an alternative respiratory passage especially during suckling for infants. The protruding nose that is completely separate from the mouth part is a characteristic found only in therian mammals. It has been theorized that this unique mammalian nose evolved from the anterior part of the upper jaw of the reptilian-like ancestors (synapsids).

The respiratory system of the horse is the biological system by which a horse circulates air for the purpose of gaseous exchange.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
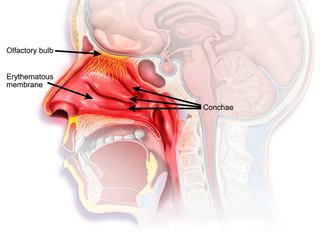
The nasal mucosa lines the nasal cavity. It is part of the respiratory mucosa, the mucous membrane lining the respiratory tract. The nasal mucosa is intimately adherent to the periosteum or perichondrium of the nasal conchae. It is continuous with the skin through the nostrils, and with the mucous membrane of the nasal part of the pharynx through the choanae. From the nasal cavity its continuity with the conjunctiva may be traced, through the nasolacrimal and lacrimal ducts; and with the frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary sinuses, through the several openings in the nasal meatuses. The mucous membrane is thickest, and most vascular, over the nasal conchae. It is also thick over the nasal septum where increased numbers of goblet cells produce a greater amount of nasal mucus. It is very thin in the meatuses on the floor of the nasal cavities, and in the various sinuses. It is one of the most commonly infected tissues in adults and children. Inflammation of this tissue may cause significant impairment of daily activities, with symptoms such as stuffy nose, headache, mouth breathing, etc.



















