
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood.

Anemia or anaemia is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. The name is derived from Ancient Greek: ἀναιμία anaimia, meaning 'lack of blood', from ἀν- an-, 'not' and αἷμα haima, 'blood'. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe.

A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, bleeding disorders, anemia, or frequent infections. Some types may develop into acute myeloid leukemia.

Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis, reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with certain stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain.

Erythropoiesis is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell.

Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. An anemia is a red blood cell defect that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic anemia results from inhibition of DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. When DNA synthesis is impaired, the cell cycle cannot progress from the G2 growth stage to the mitosis (M) stage. This leads to continuing cell growth without division, which presents as macrocytosis. Megaloblastic anemia has a rather slow onset, especially when compared to that of other anemias. The defect in red cell DNA synthesis is most often due to hypovitaminosis, specifically vitamin B12 deficiency or folate deficiency. Loss of micronutrients may also be a cause.
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a rare bone marrow blood cancer. It is classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, a group of cancers in which there is growth of abnormal cells in the bone marrow. This is most often associated with a somatic mutation in the JAK2, CALR, or MPL gene markers. In PMF, the healthy marrow is replaced by scar tissue (fibrosis), resulting in a lack of production of normal blood cells. Symptoms include anemia, increased infection and an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly).
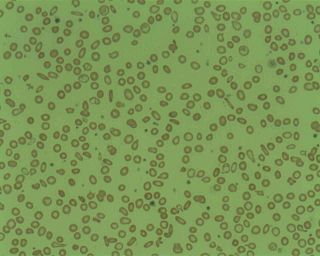
Microcytic anaemia is any of several types of anemia characterized by smaller than normal red blood cells. The normal mean corpuscular volume is approximately 80–100 fL. When the MCV is <80 fL, the red cells are described as microcytic and when >100 fL, macrocytic. The MCV is the average red blood cell size.

The myeloblast is a unipotent stem cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival.
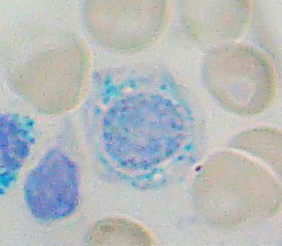
Sideroblastic anemia, or sideroachrestic anemia, is a form of anemia in which the bone marrow produces ringed sideroblasts rather than healthy red blood cells (erythrocytes). In sideroblastic anemia, the body has iron available but cannot incorporate it into hemoglobin, which red blood cells need in order to transport oxygen efficiently. The disorder may be caused either by a genetic disorder or indirectly as part of myelodysplastic syndrome, which can develop into hematological malignancies.

A proerythroblast is the earliest of four stages in development of the normoblast.

Extramedullary hematopoiesis refers to hematopoiesis occurring outside of the medulla of the bone. It can be physiologic or pathologic.
Myelophthisic anemia is a severe type of anemia found in some people with diseases that affect the bone marrow. Myelophthisis refers to the displacement of hemopoietic bone-marrow tissue by fibrosis, tumors, or granulomas. The word comes from the roots myelo-, which refers to bone marrow, and phthysis, shrinkage or atrophy.

A promyelocyte is a granulocyte precursor, developing from the myeloblast and developing into the myelocyte. Promyelocytes measure 12-20 microns in diameter. The nucleus of a promyelocyte is approximately the same size as a myeloblast but their cytoplasm is much more abundant. They also have less prominent nucleoli than myeloblasts and their chromatin is more coarse and clumped. The cytoplasm is basophilic and contains primary red/purple granules.
Microcytosis or microcythemia is a condition in which red blood cells are unusually small as measured by their mean corpuscular volume.
Normocytic anemia is a type of anemia and is a common issue that occurs for men and women typically over 85 years old. Its prevalence increases with age, reaching 44 percent in men older than 85 years. The most common type of normocytic anemia is anemia of chronic disease.

White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. White blood cells include three main subtypes; granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes.

Polychromasia is a disorder where there is an abnormally high number of immature red blood cells found in the bloodstream as a result of being prematurely released from the bone marrow during blood formation These cells are often shades of grayish-blue. Polychromasia is usually a sign of bone marrow stress as well as immature red blood cells. 3 types are recognized, with types 1 and 2 being referred to as 'young red blood cells' and type 3 as 'old red blood cells'. Giemsa stain is used to distinguish all three types of blood smears. The young cells will generally stain gray or blue in the cytoplasm. These young red blood cells are commonly called reticulocytes. All polychromatophilic cells are reticulocytes, however, not all reticulocytes are polychromatophilic. In the old blood cells, the cytoplasm either stains a light orange or does not stain at all.
Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia type IV has been described with typical morphologic features of CDA II but a negative acidified-serum test.
























