
Ophthalmology is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.

A dental dam or rubber dam is a thin, 6-inch (150 mm) square sheet, usually latex or nitrile, used in dentistry to isolate the operative site from the rest of the mouth. Sometimes termed "Kofferdam", it was designed in the United States in 1864 by Sanford Christie Barnum. It is used mainly in endodontic, fixed prosthodontic and general restorative treatments. Its purpose is both to prevent saliva interfering with the dental work, and to prevent instruments and materials from being inhaled, swallowed or damaging the mouth. In dentistry, use of a rubber dam is sometimes referred to as isolation or moisture control.

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that uses low-coherence light to capture micrometer-resolution, two- and three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media. It is used for medical imaging and industrial nondestructive testing (NDT). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution.

Endodontics is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.

A dental implant is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biologic process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or zirconia form an intimate bond to bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic/crown.

Cataract surgery, which is also called lens replacement surgery, is the removal of the natural lens of the human eye that has developed a cataract, an opaque or cloudy area. The eye's natural lens is usually replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).

A dental extraction is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth cause recurrent infections of the gum (pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed. In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened.

The UCLA School of Dentistry is the dental school of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) located in the Center for Health Sciences building in the Westwood neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, United States. The school has several educational and training programs, conducts oral and dental health research, and offers affordable dental care at three locations: Westwood, Venice, and Inglewood. The school also participates in several outreach endeavors, including numerous health fairs during the year, STEM pipeline programs and provides dental care for underserved populations in the region. The School of Dentistry is considered among the nation's best research-intensive dental schools.
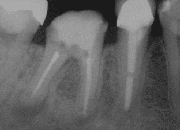
A root end surgery, also known as apicoectomy, apicectomy, retrograde root canal treatment or root-end filling, is an endodontic surgical procedure whereby a tooth's root tip is removed and a root end cavity is prepared and filled with a biocompatible material. It is an example of a periradicular surgery.
An eye care professional (ECP) is an individual who provides a service related to the eyes or vision. It is any healthcare worker involved in eye care, from one with a small amount of post-secondary training to practitioners with a doctoral level of education.
A glaucoma valve is a medical shunt used in the treatment of glaucoma to reduce the eye's intraocular pressure (IOP).

Dental instruments are tools that dental professionals use to provide dental treatment. They include tools to examine, manipulate, treat, restore, and remove teeth and surrounding oral structures.

Glaucoma is a group of diseases affecting the optic nerve that results in vision loss and is frequently characterized by raised intraocular pressure (IOP). There are many glaucoma surgeries, and variations or combinations of those surgeries, that facilitate the escape of excess aqueous humor from the eye to lower intraocular pressure, and a few that lower IOP by decreasing the production of aqueous humor.
Microsurgical endodontics is that aspect of endodontics which evolved after the introduction of the Surgical Operating Microscope (SOM) to endodontics in the early 1990s. The recent addition of SOM's to endodontic therapy can allow better visualization and management of the surgical field by endodontists during endodontic procedures through magnification and greatly improved high intensity lighting. SOM's typically magnify in the 4X to 25X range. The other commonly used magnification aide, through lens eyeglass mounted surgical telescopes, provide 2.5X to 4.5X magnification. Surgical operating microscopes have a steep learning curve and require training, as well as patience and practice to master.
A dental laser is a type of laser designed specifically for use in oral surgery or dentistry.

A loupe is a simple, small magnification device used to see small details more closely. They generally have higher magnification than a magnifying glass, and are designed to be held or worn close to the eye. A loupe does not have an attached handle, and its focusing lens(es) are contained in an opaque cylinder or cone. On some loupes this cylinder folds into an enclosing housing that protects the lenses when not in use.

Root canal treatment is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of the decontaminated tooth from future microbial invasion. Root canals, and their associated pulp chamber, are the physical hollows within a tooth that are naturally inhabited by nerve tissue, blood vessels and other cellular entities. Together, these items constitute the dental pulp.
Occupational hazards in dentistry are occupational hazards that are specifically associated within a dental care environment. Members of the dental team including dentists, hygienists, dental nurses and radiographers must ensure local protocols are followed to minimize risk.
In the dental specialty of endodontics, periradicular surgery is surgery to the external root surface. Examples of periradicular surgery include apicoectomy, root resection, repair of root perforation or resorption defects, removal of broken fragments of the tooth or a filling material, and exploratory surgery to look for root fractures.
Periapical granuloma, also sometimes referred to as a radicular granuloma or apical granuloma, is an inflammation at the tip of a dead (nonvital) tooth. It is a lesion or mass that typically starts out as an epithelial lined cyst, and undergoes an inward curvature that results in inflammation of granulation tissue at the root tips of a dead tooth. This is usually due to dental caries or a bacterial infection of the dental pulp. Periapical granuloma is an infrequent disorder that has an occurrence rate between 9.3 to 87.1 percent. Periapical granuloma is not a true granuloma due to the fact that it does not contain granulomatous inflammation; however, periapical granuloma is a common term used.













