
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, but is named for its appearance. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale, commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. The hue may be gray-brown in people with darker skin. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms.

Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is a type of irritant folliculitis that commonly affects men who have curly or coarse facial hair. It occurs when hair curls back into the skin after shaving, causing inflammation, redness, and bumps. This can lead to ingrown hairs, scarring, and skin discoloration. PFB can be treated with various methods, including changing shaving habits, using topical creams or ointments, and undergoing laser hair removal. Prevention measures include proper shaving techniques, using sharp razors, and avoiding too close a shave.

The intermammary cleft or intermammary sulcus or sulcus intermammarius is a surface feature of males and females that marks the division of the two breasts with the sternum (breastbone) in the middle. The International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA) uses the terms "sulcus intermammarius" or "intermammary cleft" when referring to the area between the breasts.
Keratoderma is a hornlike skin condition.
Parapsoriasis refers to one of a group of skin disorders that are characterized primarily by their resemblance to psoriasis, rather than by their underlying cause.

Kindler syndrome is a rare congenital disease of the skin caused by a mutation in the KIND1 gene.

Rothmund–Thomson syndrome (RTS) is a rare autosomal recessive skin condition.

Discoid lupus erythematosus is the most common type of chronic cutaneous lupus (CCLE), an autoimmune skin condition on the lupus erythematosus spectrum of illnesses. It presents with red, painful, inflamed and coin-shaped patches of skin with a scaly and crusty appearance, most often on the scalp, cheeks, and ears. Hair loss may occur if the lesions are on the scalp. The lesions can then develop severe scarring, and the centre areas may appear lighter in color with a rim darker than the normal skin. These lesions can last for years without treatment.

A tufted angioma usually develops in infancy or early childhood on the neck and upper trunk, and is an ill-defined, dull red macule with a mottled appearance, varying from 2 to 5 cm in diameter.

Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia usually presents with pink to red-brown, dome-shaped, dermal papules or nodules of the head or neck, especially about the ears and on the scalp.
Large plaque parapsoriasis are skin lesions that may be included in the modern scheme of cutaneous conditions described as parapsoriasis. These lesions, called plaques, may be irregularly round-shaped to oval and are 10 cm (4 in) or larger in diameter. They can be very thin plaques that are asymptomatic or mildly pruritic. Large-plaque parapsoriasis is a common associate of retiform parapsoriasis, can be accompanied by poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans, and can in rare occasions be a precursor to cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
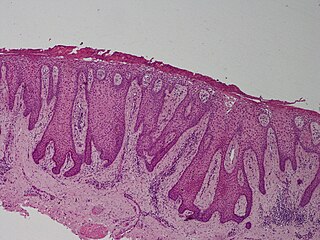
Clear cell acanthoma is a benign clinical and histological lesion initially described as neoplastic, which some authors now regard as a reactive dermatosis. It usually presents as a moist solitary firm, brown-red, well-circumscribed, 5 mm to 2 cm nodule or plaque on the lower extremities of middle-aged to elderly individuals. The lesion has a crusted, scaly peripheral collarette and vascular puncta on the surface. It is characterized by slow growth, and may persist for years. The clinical differential diagnosis includes: dermatofibroma, inflamed seborrheic keratosis, pyogenic granuloma, basal-cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, verruca vulgaris, psoriatic plaque, and melanoma.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:
Retiform parapsoriasis is a cutaneous condition, considered to be a type of large-plaque parapsoriasis. It is characterized by widespread, ill-defined plaques on the skin, that have a net-like or zebra-striped pattern. Skin atrophy, a wasting away of the cutaneous tissue, usually occurs within the area of these plaques.

Poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans (PVA), is a cutaneous condition characterized by hypo- or hyperpigmentation, telangiectasia and skin atrophy. Other names for the condition include prereticulotic poikiloderma and atrophic parapsoriasis. The condition was first described by pioneer American pediatrician Abraham Jacobi in 1906. PVA causes areas of affected skin to appear speckled red and inflamed, yellowish and/or brown, gray or grayish-black, with scaling and a thinness that may be described as "cigarette paper". On the surface of the skin, these areas may range in size from small patches, to plaques, to neoplasms.

Poikiloderma is a skin condition that consists of areas of hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, telangiectasias and atrophy. Poikiloderma of Civatte is most frequently seen on the chest or the neck, characterized by red colored pigment on the skin that is commonly associated with sun damage.
Cutis rhomboidalis nuchae is a skin condition of the posterior neck, characterized by deep furrowing of the skin.
Garrod's pads are a cutaneous condition characterized by calluses on the dorsal aspect of the interphalangeal joints, i.e. the back side of the finger joints. They are often seen in violin, viola, and cello players, along with fiddler's neck and other dermatologic conditions peculiar to string musicians. Although Garrod's pads are conventionally described as appearing on the proximal interphalangeal joint, distal interphalangeal joint involvement has also been described.
Fiddler's neck is an occupational disease that affects violin and viola players.











