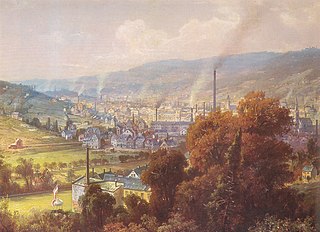Spinning is a twisting technique to form yarn from fibers. The fiber intended is drawn out, twisted, and wound onto a bobbin. A few popular fibers that are spun into yarn other than cotton, which is the most popular, are viscose, and synthetic polyester. Originally done by hand using a spindle whorl, starting in the 500s AD the spinning wheel became the predominant spinning tool across Asia and Europe. The spinning jenny and spinning mule, invented in the late 1700s, made mechanical spinning far more efficient than spinning by hand, and especially made cotton manufacturing one of the most important industries of the Industrial Revolution.

Carding is a mechanical process that disentangles, cleans and intermixes fibres to produce a continuous web or sliver suitable for subsequent processing. This is achieved by passing the fibres between differentially moving surfaces covered with "card clothing", a firm flexible material embedded with metal pins. It breaks up locks and unorganised clumps of fibre and then aligns the individual fibres to be parallel with each other. In preparing wool fibre for spinning, carding is the step that comes after teasing.

The spinning jenny is a multi-spindle spinning frame, and was one of the key developments in the industrialization of textile manufacturing during the early Industrial Revolution. It was invented in 1764 or 1765 by James Hargreaves in Stanhill, Oswaldtwistle, Lancashire in England.

A power loom is a mechanized loom, and was one of the key developments in the industrialization of weaving during the early Industrial Revolution. The first power loom was designed in 1786 by Edmund Cartwright and first built that same year. It was refined over the next 47 years until a design by the Howard and Bullough company made the operation completely automatic. This device was designed in 1834 by James Bullough and William Kenworthy, and was named the Lancashire loom.

A cotton mill is a building that houses spinning or weaving machinery for the production of yarn or cloth from cotton, an important product during the Industrial Revolution in the development of the factory system.
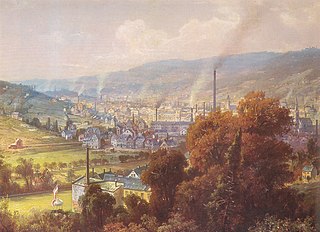
Textile manufacture during the British Industrial Revolution was centred in south Lancashire and the towns on both sides of the Pennines in the United Kingdom. The main drivers of the Industrial Revolution were textile manufacturing, iron founding, steam power, oil drilling, the discovery of electricity and its many industrial applications, the telegraph and many others. Railroads, steam boats, the telegraph and other innovations massively increased worker productivity and raised standards of living by greatly reducing time spent during travel, transportation and communications..

The spinning frame is an Industrial Revolution invention for spinning thread or yarn from fibres such as wool or cotton in a mechanized way. It was developed in 18th-century Britain by Richard Arkwright and John Kay.

Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods such as clothing, household items, upholstery and various industrial products.

The spinning mule is a machine used to spin cotton and other fibres. They were used extensively from the late 18th to the early 20th century in the mills of Lancashire and elsewhere. Mules were worked in pairs by a minder, with the help of two boys: the little piecer and the big or side piecer. The carriage carried up to 1,320 spindles and could be 150 feet (46 m) long, and would move forward and back a distance of 5 feet (1.5 m) four times a minute. It was invented between 1775 and 1779 by Samuel Crompton. The self-acting (automatic) mule was patented by Richard Roberts in 1825. At its peak there were 50,000,000 mule spindles in Lancashire alone. Modern versions are still in niche production and are used to spin woollen yarns from noble fibres such as cashmere, ultra-fine merino and alpaca for the knitware market.

Cotton-spinning machinery is machines which process prepared cotton roving into workable yarn or thread. Such machinery can be dated back centuries. During the 18th and 19th centuries, as part of the Industrial Revolution cotton-spinning machinery was developed to bring mass production to the cotton industry. Cotton spinning machinery was installed in large factories, commonly known as cotton mills.

Thomas Highs (1718–1803), of Leigh, Lancashire, was a reed-maker and manufacturer of cotton carding and spinning engines in the 1780s, during the Industrial Revolution. He is known for claiming patents on a spinning jenny, a carding machine and the throstle.

Platt Brothers, also known as Platt Bros & Co Ltd, was a British company based at Werneth in Oldham, North West England. The company manufactured textile machinery and were iron founders and colliery proprietors. By the end of the 19th century, the company had become the largest textile machinery manufacturer in the world, employing more than 12,000 workers.

Open-end spinning is a technology for creating yarn without using a spindle. It was invented and developed in Czechoslovakia in Výzkumný ústav bavlnářský / Cotton Research Institute in Ústí nad Orlicí in 1963.
Textile manufacturing is one of the oldest human activities. The oldest known textiles date back to about 5000 B.C. In order to make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fibre from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving to create cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. Cloth is finished by what are described as wet process to become fabric. The fabric may be dyed, printed or decorated by embroidering with coloured yarns.

The Roberts loom was a cast-iron power loom introduced by Richard Roberts in 1830. It was the first loom that was more viable than a hand loom and was easily adjustable and reliable, which led to its widespread use in the Lancashire cotton industry.

Bradford Industrial Museum, established 1974 in Moorside Mills, Eccleshill, Bradford, United Kingdom, specializes in relics of local industry, especially printing and textile machinery, kept in working condition for regular demonstrations to the public. There is a Horse Emporium in the old canteen block plus a shop in the mill, and entry is free of charge.

A doffer is someone who removes ("doffs") bobbins, pirns or spindles holding spun fiber such as cotton or wool from a spinning frame and replaces them with empty ones. Historically, spinners, doffers, and sweepers each had separate tasks that were required in the manufacture of spun textiles. From the early days of the industrial revolution, this work, which requires speed and dexterity rather than strength, was often done by children. After World War I, the practice of employing children declined, ending in the United States in 1933. In modern textile mills, doffing machines have now replaced humans.

Kirk Mill is an early example of an Arkwright-type cotton mill and a grade II listed building in Chipping, Lancashire, in Ribble Valley, to the north of Preston, Lancashire, England. It was built in the 1780s on the site of a corn mill dating from at least 1544. The mill continued spinning cotton using water frames and then throstles until 1886, when it was sold and became HJ Berry's chairmaking factory. It was powered by a 32 ft (9.8 m) waterwheel which continued in use, generating electricity until the 1940s.
Doubling is a textile industry term synonymous with combining. It can be used for various processes during spinning. During the carding stage, several sources of roving are doubled together and drawn, to remove variations in thickness. After spinning, yarn is doubled for many reasons. Yarn may be doubled to produce warp for weaving, to make cotton for lace, crochet and knitting. It is used for embroidery threads and sewing threads, for example: sewing thread is usually 6-cable thread. Two threads of spun 60s cotton are twisted together, and three of these double threads are twisted into a cable, of what is now 5s yarn. This is mercerised, gassed and wound onto a bobbin.

Tower Mill is a cotton mill in Dukinfield, Greater Manchester, England. It is a grade II listed building. It was designed by Potts, Pickup & Dixon in 1885 and spun cotton, using mules and spinning frames until 1955 when it was no longer used as a cotton mill and was subsequently used by various industries and divided into small units, at one point plans were even passed for the mill to be converted into luxury apartments but with the recession in 2007/8 this plan was abandoned. After several years of lying empty it was eventually bought in 2013, restored and re-equipped to ring spin superfine cotton yarns in 2016 and is now after the absence for many years the only cotton mill in production in the United Kingdom.