H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of histamine receptors are termed antihistamines; other agents may have antihistaminergic action but are not true antihistamines.
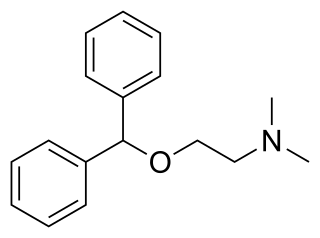
Diphenhydramine (DPH) is an antihistamine and sedative mainly used to treat allergies, insomnia, and symptoms of the common cold. It is also less commonly used for tremors in parkinsonism, and nausea. It is taken by mouth, injected into a vein, injected into a muscle, or applied to the skin. Maximal effect is typically around two hours after a dose, and effects can last for up to seven hours.
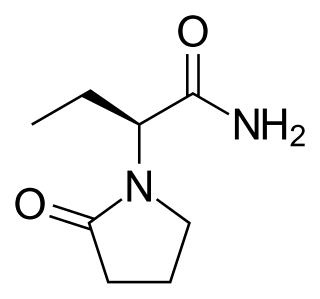
Levetiracetam, sold under the brand name Keppra among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy. It is used for partial-onset, myoclonic, or tonic–clonic seizures and is taken either by mouth as an immediate or extended release formulation or by injection into a vein.

Buprenorphine, sold under the brand name Subutex among others, is an opioid used to treat opioid use disorder, acute pain, and chronic pain. It can be used under the tongue (sublingual), in the cheek (buccal), by injection, as a skin patch (transdermal), or as an implant. For opioid use disorder, the patient must have moderate opioid withdrawal symptoms before buprenorphine can be administered under direct observation of a health-care provider.
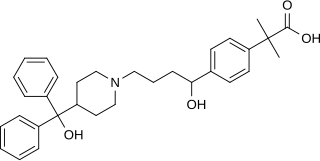
Fexofenadine, sold under the brand name Allegra among others, is an antihistamine pharmaceutical drug used in the treatment of allergy symptoms, such as hay fever and urticaria.
An adverse effect is an undesired harmful effect resulting from a medication or other intervention, such as surgery. An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. The term complication is similar to adverse effect, but the latter is typically used in pharmacological contexts, or when the negative effect is expected or common. If the negative effect results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or procedure, this is called a medical error and not an adverse effect. Adverse effects are sometimes referred to as "iatrogenic" because they are generated by a physician/treatment. Some adverse effects occur only when starting, increasing or discontinuing a treatment. Using a drug or other medical intervention which is contraindicated may increase the risk of adverse effects. Adverse effects may cause complications of a disease or procedure and negatively affect its prognosis. They may also lead to non-compliance with a treatment regimen. Adverse effects of medical treatment resulted in 142,000 deaths in 2013 up from 94,000 deaths in 1990 globally.

Olopatadine, sold under the brand name Patanol among others, is an antihistamine medication used to decrease the symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis and allergic rhinitis. It is used as eye drops or as a nasal spray. The eye drops generally result in an improvement within half an hour.

Doxepin is a medication belonging to the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) class of drugs used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic hives, and insomnia. For hives it is a less preferred alternative to antihistamines. It has a mild to moderate benefit for sleeping problems. It is used as a cream for itchiness due to atopic dermatitis or lichen simplex chronicus.

Cefaclor, sold under the trade name Ceclor among others, is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat certain bacterial infections such as pneumonia and infections of the ear, lung, skin, throat, and urinary tract. It is also available from other manufacturers as a generic.

Betahistine, sold under the brand name Serc among others, is an anti-vertigo medication. It is commonly prescribed for balance disorders or to alleviate vertigo symptoms. It was first registered in Europe in 1970 for the treatment of Ménière's disease but current evidence does not support its efficacy in treating it.

Ketotifen is an antihistamine medication and a mast cell stabilizer commonly used to treat allergic conditions such as conjunctivitis, asthma, and urticaria (hives). Ketotifen is available in ophthalmic and oral forms: the ophthalmic form relieves eye itchiness and irritation associated with seasonal allergies, while the oral form helps prevent systemic conditions such as asthma attacks and allergic reactions. In addition to treating allergies, ketotifen has shown efficacy in managing systemic mast cell diseases such as mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), which involve abnormal accumulation or activation of mast cells throughout the body. Ketotifen is also used for other allergic-type conditions like atopic dermatitis (eczema) and food allergies.

Cyproheptadine, sold under the brand name Periactin among others, is a first-generation antihistamine with additional anticholinergic, antiserotonergic, and local anesthetic properties.
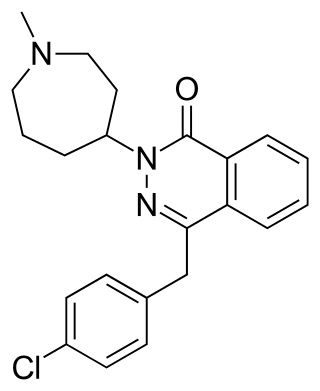
Azelastine, sold under the brand name Optivar among others, is a H1 receptor-blocking medication primarily used as a nasal spray to treat allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and as eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis. Other uses may include asthma and skin rashes for which it is taken by mouth. Onset of effects is within minutes when used in the eyes and within an hour when used in the nose. Effects last for up to 12 hours.

Asenapine, sold under the brand name Saphris among others, is an atypical antipsychotic medication used to treat schizophrenia and acute mania associated with bipolar disorder as well as the medium to long-term management of bipolar disorder.

Olanzapine/fluoxetine is a fixed-dose combination medication containing olanzapine (Zyprexa), an atypical antipsychotic, and fluoxetine (Prozac), a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Olanzapine/fluoxetine is primarily used to treat the depressive episodes of bipolar I disorder as well as treatment-resistant depression.

Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides relief from nasal congestion, sneezing, or hives caused by pollen, dust mites, or animal allergy with few side effects. Antihistamines are usually for short-term treatment. Chronic allergies increase the risk of health problems which antihistamines might not treat, including asthma, sinusitis, and lower respiratory tract infection. Consultation of a medical professional is recommended for those who intend to take antihistamines for longer-term use.

Vilazodone, sold under the brand name Viibryd among others, is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder. It is classified as a serotonin modulator and is taken by mouth.

Buprenorphine/naloxone, sold under the brand name Suboxone among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication that includes buprenorphine and naloxone. It is used to treat opioid use disorder, and reduces the mortality of opioid use disorder by 50%. It relieves cravings to use and withdrawal symptoms. Buprenorphine/naloxone is available for use in two different forms, under the tongue or in the cheek.

Somnifacient, also known as sedatives or sleeping pills, is a class of medications that induces sleep. It is mainly used for treatment of insomnia. Examples of somnifacients include benzodiazepines, barbiturates and antihistamines.
















