In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4" due to the phonetic resemblance of its molecular formula to the word.

Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BaCl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other water-soluble barium salts, it is white, highly toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting first to the dihydrate BaCl2(H2O)2. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry.

Lead(II) chloride (PbCl2) is an inorganic compound which is a white solid under ambient conditions. It is poorly soluble in water. Lead(II) chloride is one of the most important lead-based reagents. It also occurs naturally in the form of the mineral cotunnite.
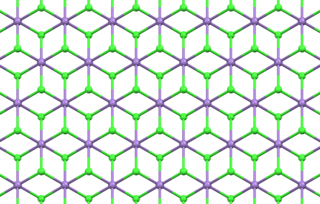
Manganese(II) chloride is the dichloride salt of manganese, MnCl2. This inorganic chemical exists in the anhydrous form, as well as the dihydrate (MnCl2·2H2O) and tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), with the tetrahydrate being the most common form. Like many Mn(II) species, these salts are pink, with the paleness of the color being characteristic of transition metal complexes with high spin d5 configurations.

Nickel(II) chloride (or just nickel chloride) is the chemical compound NiCl2. The anhydrous salt is yellow, but the more familiar hydrate NiCl2·6H2O is green. Nickel(II) chloride, in various forms, is the most important source of nickel for chemical synthesis. The nickel chlorides are deliquescent, absorbing moisture from the air to form a solution. Nickel salts have been shown to be carcinogenic to the lungs and nasal passages in cases of long-term inhalation exposure.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl2. It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.

Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moisture-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride.

Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures.

Tellurium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula TeCl4. The compound is volatile, subliming at 200 °C at 0.1 mmHg. Molten TeCl4 is ionic, dissociating into TeCl3+ and Te2Cl102−.

Tritellurium dichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Te3Cl2. It is one of the more stable lower chlorides of tellurium.

Selenium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound composed with the formula SeCl4. This compound exists as yellow to white volatile solid. It is one of two commonly available selenium chlorides, the other example being selenium monochloride, Se2Cl2. SeCl4 is used in the synthesis of other selenium compounds.

Germanium dichloride is a chemical compound of germanium and chlorine with the formula GeCl2. It is a yellow solid. Germanium dichloride is an example of a compound featuring germanium in the +2 oxidation state.

Diethylaluminium chloride, abbreviated DEAC, is an organoaluminium compound. Although usually given the chemical formula (C2H5)2AlCl, it exists as a dimer, [(C2H5)2AlCl]2 It is a precursor to Ziegler-Natta catalysts employed for the production of polyolefins. The compound is also a Lewis acid, useful in organic synthesis. The compound is a colorless waxy solid, but is usually handled as a solution in hydrocarbon solvents. It is highly reactive, even pyrophoric.
In chemistry, molecular oxohalides (oxyhalides) are a group of chemical compounds in which both oxygen and halogen atoms are attached to another chemical element A in a single molecule. They have the general formula AOmXn, where X = fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), and/or iodine (I). The element A may be a main group element, a transition element or an actinide. The term oxohalide, or oxyhalide, may also refer to minerals and other crystalline substances with the same overall chemical formula, but having an ionic structure.

Lead tetrachloride, also known as lead(IV) chloride, has the molecular formula PbCl4. It is a yellow, oily liquid which is stable below 0 °C, and decomposes at 50 °C. It has a tetrahedral configuration, with lead as the central atom. The Pb–Cl covalent bonds have been measured to be 247 pm and the bond energy is 243 kJ⋅mol−1.

Pentamethylantimony or pentamethylstiborane is an organometalllic compound containing five methyl groups bound to an antimony atom with formula Sb(CH3)5. It is an example of a hypervalent compound. The molecular shape is trigonal bipyramid. Some other antimony(V) organometallic compounds include pentapropynylantimony (Sb(CCCH3)5) and pentaphenyl antimony (Sb(C6H5)5). Other known pentamethyl-pnictides include pentamethylbismuth and pentamethylarsenic.

Europium dichloride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula EuCl2. When it is irradiated by ultraviolet light, it has bright blue fluorescence.


















