
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule.

Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, inability to urinate, or loss of bladder control. Complications can include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and chronic kidney problems.
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement, and angioplasty of narrowed structures.
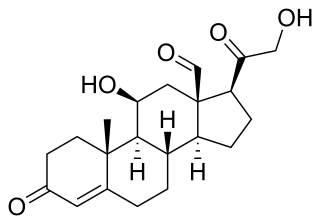
Primary aldosteronism (PA), also known as primary hyperaldosteronism or Conn's syndrome, refers to the excess production of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands, resulting in low renin levels and high blood pressure. This abnormality is caused by hyperplasia or tumors. Many experience fatigue, potassium deficiency and high blood pressure which may cause poor vision, confusion or headaches. Symptoms may also include: muscular aches and weakness, muscle spasms, low back and flank pain from the kidneys, trembling, tingling sensations, dizziness/vertigo, nocturia and excessive urination. Complications include cardiovascular disease such as stroke, myocardial infarction, kidney failure and abnormal heart rhythms.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency (CAH) is a genetic disorder characterized by impaired production of cortisol in the adrenal glands.

Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas. Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasms and the estimated prevalence rate in the general population is approximately 17%.

Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonymous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula.

Primary hyperparathyroidism is a medical condition where the parathyroid gland produce excess amounts of parathyroid hormone (PTH). The symptoms of the condition relate to the resulting elevated serum calcium (hypercalcemia), which can cause digestive symptoms, kidney stones, psychiatric abnormalities, and bone disease.
Thyroid disease is a medical condition that affects the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and produces thyroid hormones that travel through the blood to help regulate many other organs, meaning that it is an endocrine organ. These hormones normally act in the body to regulate energy use, infant development, and childhood development.

Tertiary hyperparathyroidism is a condition involving the overproduction of the hormone, parathyroid hormone, produced by the parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands are involved in monitoring and regulating blood calcium levels and respond by either producing or ceasing to produce parathyroid hormone. Anatomically, these glands are located in the neck, para-lateral to the thyroid gland, which does not have any influence in the production of parathyroid hormone. Parathyroid hormone is released by the parathyroid glands in response to low blood calcium circulation. Persistent low levels of circulating calcium are thought to be the catalyst in the progressive development of adenoma, in the parathyroid glands resulting in primary hyperparathyroidism. While primary hyperparathyroidism is the most common form of this condition, secondary and tertiary are thought to result due to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Estimates of CKD prevalence in the global community range from 11 to 13% which translate to a large portion of the global population at risk of developing tertiary hyperparathyroidism. Tertiary hyperparathyroidism was first described in the late 1960s and had been misdiagnosed as primary prior to this. Unlike primary hyperparathyroidism, the tertiary form presents as a progressive stage of resolved secondary hyperparathyroidism with biochemical hallmarks that include elevated calcium ion levels in the blood, hypercalcemia, along with autonomous production of parathyroid hormone and adenoma in all four parathyroid glands. Upon diagnosis treatment of tertiary hyperparathyroidism usually leads to a surgical intervention.
Prostatic congestion is a medical condition of the prostate gland that happens when the prostate becomes swollen by excess fluid and can be caused by prostatosis. The condition often results in a person with prostatic congestion feeling the urge to urinate frequently. Prostatic congestion has been associated with prostate disease, which can progress due to age. Oftentimes, the prostate will grow in size which can lead to further problems, such as prostatitis, enlarged prostate, or prostate cancer.

Nezelof syndrome is an autosomal recessive congenital immunodeficiency condition due to underdevelopment of the thymus. The defect is a type of purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency with inactive phosphorylase, this results in an accumulation of deoxy-GTP which inhibits ribonucleotide reductase. Ribonucleotide reductase catalyzes the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides, thus, DNA replication is inhibited.

Gingival enlargement is an increase in the size of the gingiva (gums). It is a common feature of gingival disease. Gingival enlargement can be caused by a number of factors, including inflammatory conditions and the side effects of certain medications. The treatment is based on the cause. A closely related term is epulis, denoting a localized tumor on the gingiva.
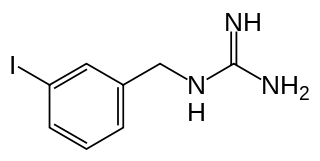
Iobenguane, or MIBG, is an aralkylguanidine analog of the adrenergic neurotransmitter norepinephrine (noradrenaline), typically used as a radiopharmaceutical. It acts as a blocking agent for adrenergic neurons. When radiolabeled, it can be used in nuclear medicinal diagnostic and therapy techniques as well as in neuroendocrine chemotherapy treatments.

Acromegaly is a disorder that results in excess growth of certain parts of the human body. It is caused by excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure.
Ectopic thymus is a condition where thymus tissue is found in an abnormal location. It usually does not cause symptoms, but may leads to a mass in the neck that may compress the trachea and the esophagus. It is thought to be the result of either a failure of descent or a failure of involution of normal thymus tissue. It may be diagnosed with radiology, such as an ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. If it causes illness, surgery can be used to remove it. Recurrence after surgery is very unlikely.
Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis is a chronic (long-lasting) inflammatory condition affecting the salivary gland. Relatively rare in occurrence, this condition is benign, but presents as hard, indurated and enlarged masses that are clinically indistinguishable from salivary gland neoplasms or tumors. It is now regarded as a manifestation of IgG4-related disease.

Pneumatosis is the abnormal presence of air or other gas within tissues.
A cervical thymic cyst, also called thymopharyngeal duct cyst, is a fluid-filled mass that occurs when the thymopharyngeal duct, an embryonic structure connecting the nascent thymus with the embryonic pharynx, fails to close and disappear. A thymic cyst is typically a solitary mass on one side of the neck, and is usually found near the carotid sheath. Some cervical thymic cysts may extend into the mediastinum. It is usually asymptomatic. The diagnostic process includes differentiating between other causes of neck masses in infants and children, including branchial cleft cysts and cystic hygromas. The treatment is surgical excision. On histologic examination, the wall of the cyst includes thymic tissue, and may include parathyroid gland tissue because of the parathyroid gland's common embryonic origin with the thymus gland in the third pharyngeal pouch. Fewer than 100 cases of cervical thymic cysts have been reported in the medical literature.
Adrenal hemorrhage (AH) is acute blood loss from a ruptured vessel of the adrenal glands above the kidneys.













