
The Cyrix 6x86 is a line of sixth-generation, 32-bit x86 microprocessors designed and released by Cyrix in 1995. Cyrix, being a fabless company, had the chips manufactured by IBM and SGS-Thomson. The 6x86 was made as a direct competitor to Intel's Pentium microprocessor line, and was pin compatible. During the 6x86's development, the majority of applications performed almost entirely integer operations. The designers foresaw that future applications would most likely maintain this instruction focus. So, to optimize the chip's performance for what they believed to be the most likely application of the CPU, the integer execution resources received most of the transistor budget. This would later prove to be a strategic mistake, as the popularity of the P5 Pentium caused many software developers to hand-optimize code in assembly language, to take advantage of the P5 Pentium's tightly pipelined and lower latency FPU. For example, the highly anticipated first-person shooter Quake used highly optimized assembly code designed almost entirely around the P5 Pentium's FPU. As a result, the P5 Pentium significantly outperformed other CPUs in the game.

The Intel 386, originally released as 80386 and later renamed i386, is a 32-bit microprocessor designed by Intel. The first pre-production samples of the 386 were released to select developers in 1985, while mass production commenced in 1986. The processor was a significant evolution in the x86 architecture, extending a long line of processors that stretched back to the Intel 8008. The 386 was the central processing unit (CPU) of many workstations and high-end personal computers of the time. The 386 began to fall out of public use starting with the release of the i486 processor in 1989, while in embedded systems the 386 remained in widespread use until Intel finally discontinued it in 2007.

The Intel 486, officially named i486 and also known as 80486, is a microprocessor. It is a higher-performance follow-up to the Intel 386. The i486 was introduced in 1989. It represents the fourth generation of binary compatible CPUs following the 8086 of 1978, the Intel 80286 of 1982, and 1985's i386.

The Pentium is a x86 microprocessor introduced by Intel on March 22, 1993. It is the first CPU using the Pentium brand. Considered the fifth generation in the 8086 compatible line of processors, its implementation and microarchitecture was internally called P5.

Cyrix Corporation was a microprocessor developer that was founded in 1988 in Richardson, Texas, as a specialist supplier of floating point units for 286 and 386 microprocessors. The company was founded by Tom Brightman and Jerry Rogers.

The Pentium III brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile CPUs based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 28, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded processors. The most notable differences were the addition of the Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) instruction set, and the introduction of a controversial serial number embedded in the chip during manufacturing. The Pentium III is also a single-core processor.

The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications. Later, it was reduced to a more narrow role as a server and high-end desktop processor. The Pentium Pro was also used in supercomputers, most notably ASCI Red, which used two Pentium Pro CPUs on each computing nodes and was the first computer to reach over one teraFLOPS in 1996, holding the number one spot in the TOP500 list from 1997 to 2000.

The Cyrix 5x86 was a line of x86 microprocessors designed by Cyrix and released on June 5 of 1995. Cyrix, being a fabless company, had the chips manufactured by IBM. The line came out about 5 months before the more famous Cyrix 6x86. The Cyrix 5x86 was one of the fastest CPUs ever produced for Socket 3 computer systems. With better performance in most applications than an Intel Pentium processor at 75 MHz, the Cyrix Cx5x86 filled a gap by providing a medium-performance processor option for 486 Socket 3 motherboards.

VIA Technologies, Inc. is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory. It was the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets. As a fabless semiconductor company, VIA conducts research and development of its chipsets in-house, then subcontracts the actual (silicon) manufacturing to third-party merchant foundries such as TSMC.

The WinChip series was a low-power Socket 7-based x86 processor designed by Centaur Technology and marketed by its parent company IDT.

The VIA C7 is an x86 central processing unit designed by Centaur Technology and sold by VIA Technologies.

Geode was a series of x86-compatible system-on-a-chip (SoC) microprocessors and I/O companions produced by AMD, targeted at the embedded computing market.
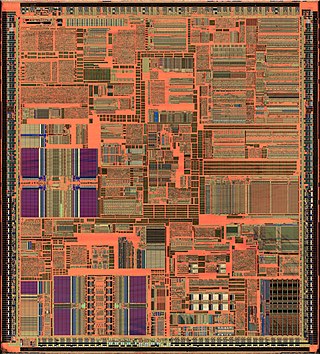
The P6 microarchitecture is the sixth-generation Intel x86 microarchitecture, implemented by the Pentium Pro microprocessor that was introduced in November 1995. It is frequently referred to as i686. It was planned to be succeeded by the NetBurst microarchitecture used by the Pentium 4 in 2000, but was revived for the Pentium M line of microprocessors. The successor to the Pentium M variant of the P6 microarchitecture is the Core microarchitecture which in turn is also derived from P6.
x87 is a floating-point-related subset of the x86 architecture instruction set. It originated as an extension of the 8086 instruction set in the form of optional floating-point coprocessors that work in tandem with corresponding x86 CPUs. These microchips have names ending in "87". This is also known as the NPX. Like other extensions to the basic instruction set, x87 instructions are not strictly needed to construct working programs, but provide hardware and microcode implementations of common numerical tasks, allowing these tasks to be performed much faster than corresponding machine code routines can. The x87 instruction set includes instructions for basic floating-point operations such as addition, subtraction and comparison, but also for more complex numerical operations, such as the computation of the tangent function and its inverse, for example.

Centaur Technology was an x86 CPU design company started in 1995 and subsequently a wholly owned subsidiary of VIA Technologies. In 2015, the documentary Rise of the Centaur covered the early history of the company. The company was broken up in 2021.

Cyrix III is an x86-compatible Socket 370 CPU. VIA Technologies launched the processor in February 2000. VIA had purchased both Centaur Technology and Cyrix. Cyrix III was to be based upon a core from one of the two companies.

The VIA Nano is a 64-bit CPU for personal computers. The VIA Nano was released by VIA Technologies in 2008 after five years of development by its CPU division, Centaur Technology. This new Isaiah 64-bit architecture was designed from scratch, unveiled on 24 January 2008, and launched on 29 May, including low-voltage variants and the Nano brand name. The processor supports a number of VIA-specific x86 extensions designed to boost efficiency in low-power appliances.
The Alternate Instruction Set (AIS) is a second 32-bit instruction set architecture found in some x86 CPUs made by VIA Technologies. On these VIA C3 processors, the second hidden processor mode is accessed by executing the x86 instruction JMPAI. If AIS mode has been enabled, the processor will perform a JMP EAX and begin executing AIS instructions at the address of the EAX register. Using AIS allows native access to the Centaur Technology-designed RISC core inside the processor.

















