
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.

Samuel Leroy Jackson is an American actor and producer. One of the most widely recognized actors of his generation, the films in which he has appeared have collectively grossed over $27 billion worldwide, making him the second highest-grossing actor of all time. The Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences gave him an Academy Honorary Award in 2022 as "A cultural icon whose dynamic work has resonated across genres and generations and audiences worldwide".

Indapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used in the treatment of hypertension, as well as decompensated heart failure. Combination preparations with perindopril are available. The thiazide-like diuretics reduce risk of major cardiovascular events and heart failure in hypertensive patients compared with hydrochlorothiazide with a comparable incidence of adverse events. Both thiazide diuretics and thiazide-like diuretics are effective in reducing risk of stroke. Both drug classes appear to have comparable rates of adverse effects as other antihypertensives such as angiotensin II receptor blockers and dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers and lesser prevalence of side-effects when compared to ACE-inhibitors and non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers.

Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesize hundreds of chemical compounds for various functions, including defense and protection against insects, fungi, diseases, and herbivorous mammals.
ATC code C04Peripheral vasodilators is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup C04 is part of the anatomical group C Cardiovascular system.

Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human and plant biology, and the biosynthesis of these compounds. Plants synthesize phytochemicals for many reasons, including to protect themselves against insect attacks and plant diseases. The compounds found in plants are of many kinds, but most can be grouped into four major biosynthetic classes: alkaloids, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, and terpenoids.

Vinca is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, native to Europe, northwest Africa and southwest Asia. The English name periwinkle is shared with the related genus Catharanthus.

L, or l, is the twelfth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is el, plural els.
Vinca alkaloids are a set of anti-mitotic and anti-microtubule alkaloid agents originally derived from the periwinkle plant Catharanthus roseus and other vinca plants. They block beta-tubulin polymerization in a dividing cell.
Vincamine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid found in the leaves of Vinca minor, comprising about 25-65% of its indole alkaloids by weight. It can also be synthesized from related alkaloids.

Quebec is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the largest province by area and the second-largest by population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York in the United States.

Vinconate is a synthetic vincamine analog used as a nootropic.

Tabernaemontana corymbosa is a species of plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is found in Brunei, China, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. Glossy green leaves and faintly sweet scented flower. Flowers continuously all year. Frost tolerant. Grows to about 2metres. Likes full sun to part shade. A number of cultivars are available.
The molecular formula C21H26N2O3 may refer to:
The molecular formula C22H26N2O2 (molar mass: 350.45 g/mol) may refer to:

Voacamine, also known under the older names voacanginine and vocamine, is a naturally occurring dimeric indole alkaloid of the secologanin type, found in a number of plants, including Voacanga africana and Tabernaemontana divaricata. It is approved for use as an antimalarial drug in several African countries. Voacamine exhibits cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonistic activity.

Vincaminol (C20H26N2O2) is a chemical that is a part of the Vinca alkaloid group, which were discovered in the 1950s by a Canadian scientist and are derived from Vinca minor (periwinkle). Vincaminol is not as well known as some of the other Vinca alkaloids such as vinblastine, vinorelbine, vincristine, and vindesine, which are the four main, medically useful Vinca alkaloids.

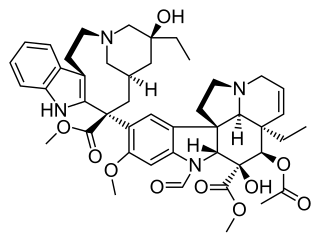
Tabernamine is a bisindole isolate of Tabernaemontana with anticancer activity.

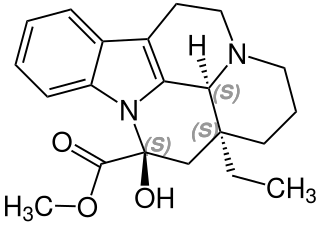
Dregamine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Ervatamia hirta and Tabernaemontana divaricata.
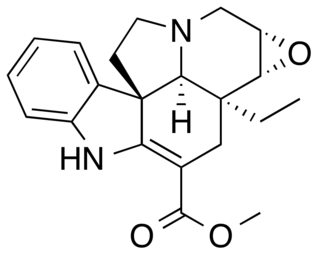
Lochnericine is a major monoterpene indole alkaloid present in the roots of Catharanthus roseus. It is also present in Tabernaemontana divaricata.

















