
Konqueror is a free and open-source web browser and file manager that provides web access and file-viewer functionality for file systems. It forms a core part of the KDE Software Compilation. Developed by volunteers, Konqueror can run on most Unix-like operating systems. The KDE community licenses and distributes Konqueror under GNU GPL-2.0-or-later.
Gecko is a browser engine developed by Mozilla. It is used in the Firefox browser, the Thunderbird email client, and many other projects.

Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. In November 2017, Firefox began incorporating new technology under the code name "Quantum" to promote parallelism and a more intuitive user interface. Firefox is available for Windows 7 and later versions, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, illumos, and Solaris Unix. It is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser.

GNOME Web, called Epiphany until 2012 and still known by that code name, is a free and open-source web browser based on the GTK port of Apple's WebKit rendering engine, called WebKitGTK. It is developed by the GNOME project for Unix-like systems. It is the default and official web browser of GNOME, and part of the GNOME Core Applications.
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is a communications protocol providing security to datagram-based applications by allowing them to communicate in a way designed to prevent eavesdropping, tampering, or message forgery. The DTLS protocol is based on the stream-oriented Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol and is intended to provide similar security guarantees. The DTLS protocol datagram preserves the semantics of the underlying transport—the application does not suffer from the delays associated with stream protocols, but because it uses UDP or SCTP, the application has to deal with packet reordering, loss of datagram and data larger than the size of a datagram network packet. Because DTLS uses UDP or SCTP rather than TCP, it avoids the "TCP meltdown problem", when being used to create a VPN tunnel.
The following tables compare general and technical information between a number of notable IRC client programs which have been discussed in independent, reliable prior published sources.
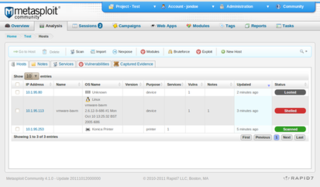
The Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development. It is owned by Boston, Massachusetts-based security company Rapid7.

Zotero is a free and open-source reference management software to manage bibliographic data and related research materials, such as PDF files. Features include web browser integration, online syncing, generation of in-text citations, footnotes, and bibliographies, an integrated PDF reader and note editor, as well as integration with the word processors Microsoft Word, LibreOffice Writer, and Google Docs. It was originally created at the Center for History and New Media at George Mason University and, as of 2021, is developed by the non-profit Corporation for Digital Scholarship.

DownThemAll! (DTA) is a free software download manager browser extension. DTA can download all or some linked files, images, or embedded objects associated with a webpage. It can pause, resume, or restart downloads.
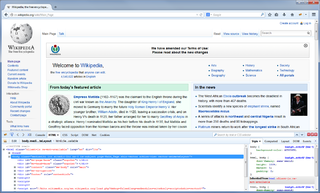
Firebug is a discontinued free and open-source web browser extension for Mozilla Firefox that facilitated the live debugging, editing, and monitoring of any website's CSS, HTML, DOM, XHR, and JavaScript.

Uzbl is a discontinued free and open-source minimalist web browser designed for simplicity and adherence to the Unix philosophy. Development began in early 2009 and is still considered in alpha software by the developers. The core component of Uzbl is written in C, but other languages are also used, most notably Python. All parts of the Uzbl project are released as free software under GNU GPL-3.0-only.

Arora is a discontinued free and open-source web browser developed by Benjamin C. Meyer. It was available for Linux, Mac OS X, Windows, FreeBSD, OS/2, Haiku, Genode, and any other operating system supported by the Qt toolkit. The browser's features included tabbed browsing, bookmarks, browsing history, smart location bar, OpenSearch, session management, privacy mode, a download manager, WebInspector, and AdBlock.
A lightweight web browser is a web browser that sacrifices some of the features of a mainstream web browser in order to reduce the consumption of system resources, and especially to minimize the memory footprint.
Content Security Policy (CSP) is a computer security standard introduced to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS), clickjacking and other code injection attacks resulting from execution of malicious content in the trusted web page context. It is a Candidate Recommendation of the W3C working group on Web Application Security, widely supported by modern web browsers. CSP provides a standard method for website owners to declare approved origins of content that browsers should be allowed to load on that website—covered types are JavaScript, CSS, HTML frames, web workers, fonts, images, embeddable objects such as Java applets, ActiveX, audio and video files, and other HTML5 features.
HTML5 Audio is a subject of the HTML5 specification, incorporating audio input, playback, and synthesis, as well as speech to text, in the browser.

Falkon is a free and open-source web browser developed by KDE. It is built on the QtWebEngine, which is a wrapper for the Chromium browser core.
A headless browser is a web browser without a graphical user interface.

PhantomJS is a discontinued headless browser used for automating web page interaction. PhantomJS provides a JavaScript API enabling automated navigation, screenshots, user behavior and assertions making it a common tool used to run browser-based unit tests in a headless system like a continuous integration environment. PhantomJS is based on WebKit making it a similar browsing environment to Safari and Google Chrome. It is open-source software released under the BSD License.
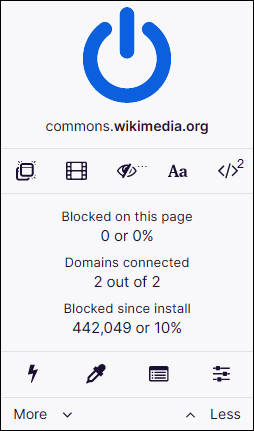
uBlock Origin is a free and open-source browser extension for content filtering, including ad blocking. The extension is available for Chrome, Chromium, Edge, Firefox, Opera, Pale Moon, as well as versions of Safari prior to 13. uBlock Origin has received praise from technology websites and is reported to be much less memory-intensive than other extensions with similar functionality. uBlock Origin's stated purpose is to give users the means to enforce their own (content-filtering) choices.
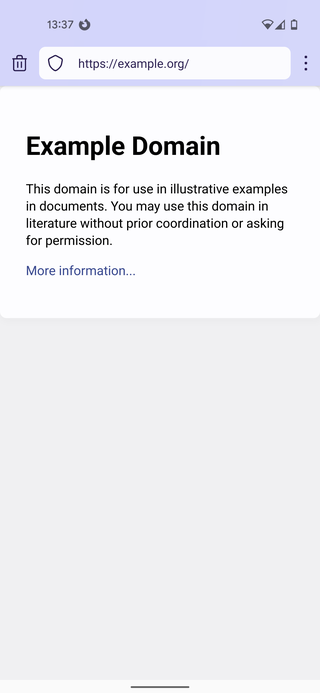
Firefox Focus is a free and open-source privacy-focused mobile browser based on Firefox from Mozilla, available for Android and iOS smartphones and tablets. Firefox Focus was initially a tracker-blocking application for mobile iOS devices, released in December 2015. It was developed into a minimalistic web browser shortly afterwards. However, it can still work solely as a tracking-blocker in the background of the Safari browser on Apple devices.












