Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
The Hofmann rearrangement is the organic reaction of a primary amide to a primary amine with one less carbon atom. The reaction involves oxidation of the nitrogen followed by rearrangement of the carbonyl and nitrogen to give an isocyanate intermediate. The reaction can form a wide range of products, including alkyl and aryl amines.
In organic chemistry, an electrophilic aromatic halogenation is a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution. This organic reaction is typical of aromatic compounds and a very useful method for adding substituents to an aromatic system.

Biphenyl is an organic compound that forms colorless crystals. Particularly in older literature, compounds containing the functional group consisting of biphenyl less one hydrogen may use the prefixes xenyl or diphenylyl.
In chemistry the descriptor vicinal, abbreviated vic, is a descriptor that identifies two functional groups as bonded to two adjacent carbon atoms.
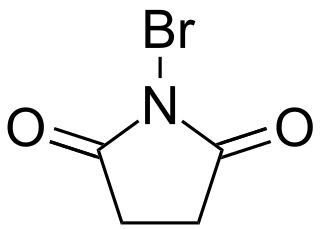
N-Bromosuccinimide or NBS is a chemical reagent used in radical substitution, electrophilic addition, and electrophilic substitution reactions in organic chemistry. NBS can be a convenient source of Br•, the bromine radical.
Aromatization is a chemical reaction in which an aromatic system is formed from a single nonaromatic precursor. Typically aromatization is achieved by dehydrogenation of existing cyclic compounds, illustrated by the conversion of cyclohexane into benzene. Aromatization includes the formation of heterocyclic systems.

Azobisisobutyronitrile (abbreviated AIBN) is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3)2C(CN)]2N2. This white powder is soluble in alcohols and common organic solvents but is insoluble in water. It is often used as a foamer in plastics and rubber and as a radical initiator.

o-Xylene (ortho-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon with the formula C6H4(CH3)2, with two methyl substituents bonded to adjacent carbon atoms of a benzene ring (the ortho configuration). It is a constitutional isomer of m-xylene and p-xylene, the mixture being called xylene or xylenes. o-Xylene is a colourless slightly oily flammable liquid.
The Hunsdiecker reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry whereby silver salts of carboxylic acids react with a halogen to produce an organic halide. It is an example of both a decarboxylation and a halogenation reaction as the product has one fewer carbon atoms than the starting material and a halogen atom is introduced its place. A catalytic approach has been developed.

The Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction is a chemical transformation that involves the halogenation of a carboxylic acid at the α carbon. For this reaction to occur the α carbon must bear at least one proton. The reaction is named after the German chemists Carl Magnus von Hell (1849–1926) and Jacob Volhard (1834–1910) and the Russian chemist Nikolay Zelinsky (1861–1953).
Barrelene is a bicyclic organic compound with chemical formula C8H8 and systematic name bicyclo[2.2.2]octa-2,5,7-triene. First synthesized and described by Howard Zimmerman in 1960, the name derives from the resemblance to a barrel, with the staves being three ethylene units attached to two methine groups. It is the formal Diels–Alder adduct of benzene and acetylene. Due to its unusual molecular geometry, the compound is of considerable interest to theoretical chemists.
Antimony tribromide (SbBr3) is a chemical compound containing antimony in its +3 oxidation state.
Diphenylmethane is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CH2 (often abbreviated CH
2Ph
2). The compound consists of methane wherein two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two phenyl groups. It is a white solid.

Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH), C
6H
6Cl
6, is any of several polyhalogenated organic compounds consisting of a six-carbon ring with one chlorine and one hydrogen attached to each carbon. This structure has nine stereoisomers, which differ by the stereochemistry of the individual chlorine substituents on the cyclohexane. It is sometimes erroneously called "benzene hexachloride" (BHC). They have been used as models for analyzing the effects of different geometric positions of the large atoms with dipolar bonds on the stability of the cyclohexane conformation. The isomers are poisonous, pesticidal, and persistent organic pollutants, to varying degrees.
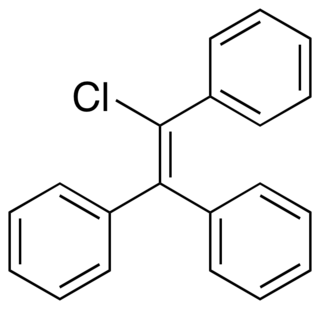
Triphenylchloroethylene, or triphenylchlorethylene, also known as chlorotriphenylethylene or as phenylstilbene chloride, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the triphenylethylene group that was marketed in the 1940s for the treatment of menopausal symptoms, vaginal atrophy, lactation suppression, and all other estrogen-indicated conditions.
Bromotoluene is a group of three isomeric methyl aryl halides. They consist of a disubstituted benzene ring with one bromine atom and one methyl group.

Terephthalaldehyde (TA) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CHO)2. It is one of three isomers of benzene dicarboxaldehyde, in which the aldehyde moieties are positioned in the para conformation on the benzene ring. Terephthalaldehyde appears as a white to beige solid, typically in the form of a powder. It is soluble in many organic solvents, such as alcohols (e.g., methanol or ethanol) and ethers (e.g., tetrahydrofuran or diethylether).