
The Royal Marines, also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, and officially as the Corps of Royal Marines, are the United Kingdom's amphibious special operations capable commando force, one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy, and provide a company strength unit to the Special Forces Support Group (SFSG). The Royal Marines trace their origins back to the formation of the "Duke of York and Albany's maritime regiment of Foot" on 28 October 1664, and the first Royal Marines Commando unit was formed at Deal in Kent on 14 February 1942 and designated "The Royal Marine Commando".

Naval gunfire support (NGFS), also known as naval surface fire support (NSFS), or shore bombardment, is the use of naval artillery to provide fire support for amphibious assault and other troops operating within their range. NGFS is one of several disciplines encompassed by the term naval fires. Modern naval gunfire support is one of the three main components of amphibious warfare assault operations support, along with aircraft and ship-launched land-attack missiles. Shipborne guns have been used against shore defences since medieval naval warfare.

The Commandos Marine, nicknamed Bérets Verts, are the special operation forces (SOF) of the French Navy, headquartered in Lorient, Brittany in western France. They operate under the Special Operations Command (COS), FORFUSCO, one of the four main forces of the French Navy or any operational command designated by the French Army staff. They specialize in offshore operations; operations from sea to land and special operations on land. One of the major characteristics of marine commando units is to be perfectly interoperable with all the resources and units of the navy.
This is a list of British ground forces in the Falklands War. For a list of ground forces from Argentina, see Argentine ground forces in the Falklands War

An artillery observer, artillery spotter, or forward observer (FO) is a soldier responsible for directing artillery and mortar fire support onto a target. An artillery observer usually accompanies a tank or infantry unit. Spotters ensure that indirect fire hits targets which those at a fire support base cannot see.
100th (Yeomanry) Regiment Royal Artillery is a reserve unit of the British Army that provides tactical air control parties, naval gunnery liaison officers, specialist staff officers and gunnery instructors.

Marines are military personnel who primarily operate in littoral zones, both on land and at sea. Historically, the main tasks undertaken by marines have included raiding ashore in support of naval objectives, and the boarding of vessels during combat or capture of prize ships. Marines also help maintain discipline and order aboard the ship. In most countries, marines are an integral part of that state's navy; in some countries their marine forces can also instead be part of the land army, such as the French Troupes de Marine, or an autonomous branch such as the United States Marine Corps.

Air Naval Gunfire Liaison Company (ANGLICO) is an airborne fire support and liaison unit of the United States Marine Corps. The mission of ANGLICO is "To provide Marine Air-Ground Task Force (MAGTF) Commanders a liaison capability to plan, coordinate, and conduct terminal control of fires in support of joint, allied, and coalition forces. Per this mission statement, ANGLICOs are not designed to support U.S. Marine Corps maneuver elements. Instead, the doctrinal purpose of ANGLICO is to provide fire support and coordination in support of units adjacent to the MAGTF.

29 Commando Regiment, Royal Artillery is the Commando-trained unit of the British Army's Royal Artillery, based in Plymouth. The regiment is under the operational control of the UK Commando Force, to which it provides artillery support and gunnery observation.
The role of the Commando Logistic Regiment (CLR), Royal Marines is to provide second line Combat Service Support to UK Commando Force.

The naval gunfire liaison officer (NGLO) is a U.S. Navy officer or non-commissioned officer who assists infantry personnel requiring naval gunfire support. The mission was defined during World War II amphibious warfare, and these personnel remain an important coordination point for effective utilization of naval guns by troops ashore.
The history of the Royal Marines began on 28 October 1664 with the formation of the Duke of York and Albany's Maritime Regiment of Foot soon becoming known as the Admiral's Regiment. During the War of the Spanish Succession the most historic achievement of the Marines was the capture of the mole during the assault on Gibraltar in 1704. On 5 April 1755, His Majesty's Marine Forces, fifty Companies in three Divisions, headquartered at Portsmouth, Chatham and Plymouth, were formed by Order of Council under Admiralty control.

Special reconnaissance (SR) is conducted by small units, such as a recon team, made up of highly trained military personnel, usually from special forces units and/or military intelligence organizations. Special reconnaissance teams operate behind enemy lines, avoiding direct combat and detection by the enemy. As a role, SR is distinct from commando operations, but both are often carried out by the same units. The SR role frequently includes covert direction of airstrikes and indirect fire, in areas deep behind enemy lines, placement of remotely monitored sensors, and preparations for other special forces. Like other special forces, SR units may also carry out direct action and unconventional warfare, including guerrilla operations.

The 202nd Coastal Ranger Company is a marine commando unit within the Swedish Amphibious Corps, which is the infantry component of the Swedish Navy.

South Africa currently does not have a marine corps, though in the past it did. It was originally set up as a sub-branch of the South African Navy during the apartheid era, with the primary purpose of protecting the country's harbours (1951-1955). Then it was recreated in 1979 during the South African Border War as 1 Marine Brigade with the aim of serving as marine infantry (1979-1990). Today, the SAN Maritime Reaction Squadron is the closest analogue to a marine corps South Africa has.
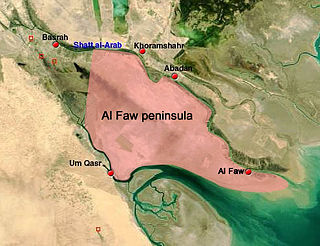
The Battle of Al Faw began on 20 March 2003 and continued for four days, as part of the 2003 invasion of Iraq.

Camp Dwyer was a military camp formerly of the United States Marine Corps located within the Helmand River Valley southwest of Garmsir in Garmsir District, Helmand Province, Afghanistan.
Forward observers in the U.S. military are artillery observers who carry the Military Occupational Specialty designator of 13F in the United States Army and 0861 in the United States Marine Corps. They are officially called "joint fire support specialists" in the U.S. Army and "fire support marines" in the U.S. Marine Corps. They are colloquially known as "FiSTers", regardless of whether they are members of a FiST. A battalion fire support officer (FSO) is the officer in charge of a battalion fire support element.
In 1989 the Royal Navy was under the direction of the Navy Department in the UK Ministry of Defence. It had two main commands, CINCFLEET and Naval Home Command.











