Related Research Articles

The Ashmolean Museum of Art and Archaeology on Beaumont Street in Oxford, England, is Britain's first public museum. Its first building was erected in 1678–1683 to house the cabinet of curiosities that Elias Ashmole gave to the University of Oxford in 1677. It is also the world's second university museum, after the establishment of the Kunstmuseum Basel in 1661 by the University of Basel.

Edward Lhuyd, also known as Edward Lhwyd and by other spellings, was a Welsh naturalist, botanist, herbalist, alchemist, scientist, linguist, geographer, and antiquary. He was the second Keeper of the University of Oxford's Ashmolean Museum, and published the first catalogue of fossils, the Lithophylacii Britannici Ichnographia.

The Alfred Jewel is a piece of Anglo-Saxon goldsmithing work made of enamel and quartz enclosed in gold. It was discovered in 1693, in North Petherton, Somerset, England and is now one of the most popular exhibits at the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford. It has been dated to the late 9th century, in the reign of Alfred the Great, and is inscribed "AELFRED MEC HEHT GEWYRCAN", meaning "Alfred ordered me made". The jewel was once attached to a rod, probably of wood, at its base. After decades of scholarly discussion, it is now "generally accepted" that the jewel's function was to be the handle for a pointer stick for following words when reading a book. It is an exceptional and unusual example of Anglo-Saxon jewellery.

The Red Book of Hergest, Oxford, Jesus College, MS 111, is a large vellum manuscript written shortly after 1382, which ranks as one of the most important medieval manuscripts written in the Welsh language. It preserves a collection of Welsh prose and poetry, notably the tales of the Mabinogion and Gogynfeirdd poetry. The manuscript derives its name from the colour of its leather binding and from its association with Hergest Court between the late 15th and early 17th century.

Ballyshannon is a town in County Donegal, Ireland. It is located at the southern end of the county where the N3 from Dublin ends and the N15 crosses the River Erne. Incorporated in 1613, it is one of the oldest towns in Ireland.
VavasorPowell was a Welsh Puritan and Fifth Monarchist, imprisoned for his role in a plot to depose King Charles II.
William Fuller (1608–1675) was an English churchman.
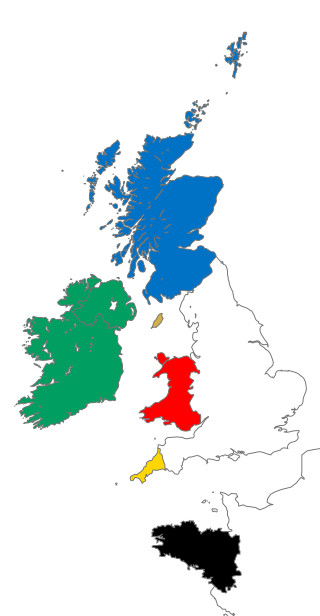
The Celtic nations or Celtic countries are a cultural area and collection of geographical regions in Northwestern Europe where the Celtic languages and cultural traits have survived. The term nation is used in its original sense to mean a people who share a common identity and culture and are identified with a traditional territory.

John Tradescant the Elder, father of John Tradescant the Younger, was an English naturalist, gardener, collector and traveller.
Events from the year 1699 in England.
The decade of the 1700s in archaeology involved some significant events.

Richard Ellis was a Welsh librarian and bibliographer, whose main work was to collect materials on the life and work of Edward Lhuyd.
David Parry was a Welsh scholar and assistant to the naturalist Edward Lhuyd. He was Keeper of the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford from 1709 until his death in 1714.
William Huddesford (1732–1772) was curator of the Ashmolean Museum from 1755 to 1772. Huddesford is credited with reinventing the museum's reputation.
Events from the year 1669 in Ireland.

Sir William Le Neve (1600?–1661) was an English herald and genealogist.
This article is about the particular significance of the year 1709 to Wales and its people.

Archæologia Britannica, the first volume of which was published in 1707, is a pioneering study of the Celtic languages written by Edward Lhuyd.
References
- ↑ Theodore Ayrault Dodge (1896). Hannibal: A History of the Art of War Among the Carthaginians and Romans Down to the Battle of Pydna, 168 B.C., with a Detailed Account of the Second Punic War. Houghton, Mifflin and Company.
- ↑ Camden's Britannia. 1695 edn.
- ↑ "Ballyshannon 'Sun Disc'". Oxford: Ashmolean Museum . Retrieved 2022-10-29.
- ↑ "The Discovery Service". discovery.nationalarchives.gov.uk. Retrieved 4 June 2017.
- ↑ "Lhuyd, Edward". Dictionary of Welsh Biography . National Library of Wales . Retrieved 20 June 2017.