An encyclopedia, or encyclopaedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on factual information concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.

The Encyclopædia Britannica is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various times through the centuries. The encyclopaedia is maintained by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 contributors. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2011, it is being published exclusively as an online encyclopaedia.
June 6 is the 157th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar; 208 days remain until the end of the year.

The Third Amendment to the United States Constitution places restrictions on the quartering of soldiers in private homes without the owner's consent, forbidding the practice in peacetime. The amendment is a response to the Quartering Acts passed by the British parliament during the buildup to the American Revolutionary War, which had allowed the British Army to lodge soldiers in public buildings.
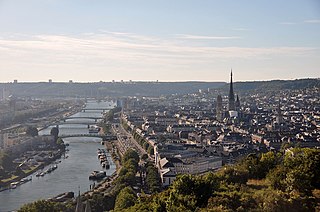
Rouen is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the region of Normandy and the department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population of the metropolitan area is 702,945 (2018). People from Rouen are known as Rouennais.

The Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition (1910–1911), is a 29-volume reference work, an edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica. It was developed during the encyclopaedia's transition from a British to an American publication. Some of its articles were written by the best-known scholars of the time. This edition of the encyclopaedia, containing 40,000 entries, is now in the public domain, and many of its articles have been used as a basis for articles in Wikipedia. However, the outdated nature of some of its content makes its use as a source for modern scholarship problematic. Some articles have special value and interest to modern scholars as cultural artefacts of the 19th and early 20th centuries.

This section of the Timeline of United States history concerns events from 1790 to 1819.

Charleville-Mézières is a commune of northern France, capital of the Ardennes department, Grand Est. Charleville-Mézières is located on the banks of the river Meuse.

Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. is a British-American company known for publishing the Encyclopædia Britannica, the world's oldest continuously published encyclopaedia, as well as extensive digital efforts—including text and audiovisual—that are aimed at educational tools for primary and secondary schools, and for everyday learners accessing information through online search.

The French Community was an association of former French colonies, most of which were in French Africa. In 1958 it replaced the French Union, which had itself succeeded the French colonial empire in 1946. While the Community remained formally in existence until 1995, when the French Parliament officially abolished it, it had effectively ceased to exist and function by the end of 1960, by which time all the African members had declared their independence and left it.

The Koro Sea or Sea of Koro is a sea in the Pacific Ocean between Viti Levu island, Fiji to the west and the Lau Islands to the east, surrounded by the islands of the Fijian archipelago.
James Browne LLD, Scottish advocate, scholar and man of letters.

A civil flag is a version of the national flag that is flown by civilians on nongovernmental installations or craft. The use of civil flags was more common in the past to denote buildings or ships not crewed by the military.
The Roundsman System, in the Elizabethan Poor Law (1601), was a form of organised labour exchange for the poorest labourers by which a parish vestry helped to pay local farmers, households and others to employ such applicants for relief at a rate of headline wages negotiated and set by the parish. It depended not on the services, but on the wants of the applicants: the employers being repaid out of the poor rate all they advanced in wages beyond a very low-wage amount. Variants of the Roundsman system operated and co-existed from parish-to-parish and sometimes depending on type of labour.
The Labour Rate was a system of poor relief, used in England from 1832 to 1834, where workers were paid at a given rate. If this was not met then the rest had to be made up by the parish's poor relief. It was authorised by the Agricultural Labourers Act 1832, and adopted in about 1 in 5 parishes until it was replaced by the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834.
Fujiwara no Fusasaki was a member of the Fujiwara clan and the founder of the Hokke branch of the Fujiwara.

The national symbols of England are things which are emblematic, representative or otherwise characteristic of England or English culture. Some are established, official symbols; for example, the Royal Arms of England, which has been codified in heraldry. Other symbols may not have official status, for one reason or another, but are likewise recognised at a national or international level.

This is a timeline of the presence of Eastern Orthodoxy in Greece from 1821 to 1924. The history of Greece traditionally encompasses the study of the Greek people, the areas they ruled historically, as well as the territory now composing the modern state of Greece.

Panna State was a princely state of colonial India, located in modern Panna district of Madhya Pradesh.

The Joachimsthal Gymnasium, was a princely high school for gifted boys, founded in 1607 in Joachimsthal, Brandenburg. In 1636, during the Thirty Years' War, the school’s buildings were destroyed, and the school migrated to Berlin. In 1912 it moved again, to Templin, where it was a boarding school.