Related Research Articles

The Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, often shortened to Rio Grande, D&RG or D&RGW, formerly the Denver & Rio Grande Railroad, was an American Class I railroad company. The railroad started as a 3 ft narrow-gauge line running south from Denver, Colorado, in 1870. It served mainly as a transcontinental bridge line between Denver and Salt Lake City, Utah. The Rio Grande was also a major origin of coal and mineral traffic.

The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States.

The California State Railroad Museum is a museum in the California State Parks system that interprets the role of railroads in the West. It is located in Old Sacramento State Historic Park at 111 I Street, Sacramento, California.

A dome car is a type of railway passenger car that has a glass dome on the top of the car where passengers can ride and see in all directions around the train. It also can include features of a coach, lounge car, dining car, sleeping car or observation. Beginning in 1945, dome cars were primarily used in the United States and Canada, though a small number were constructed in Europe for Trans Europ Express service.

The Colorado Railroad Museum is a non-profit railroad museum. The museum is located on 15 acres (6.1 ha) at a point where Clear Creek flows between North and South Table Mountains in Golden, Colorado.

Railroad Wars were business rivalries between railroad companies, which occurred frequently in American history. Although they were usually little more than legal disputes inside a courtroom, they sometimes turned into armed conflicts. There has been competition between railroad companies since the beginning of railroading in the United States, but violent confrontations were most common in the final quarter of the 19th century, particularly in the Old West.
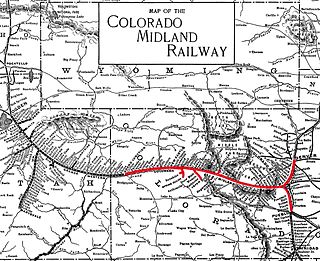
The Colorado Midland Railway, incorporated in 1883, was the first standard gauge railroad built over the Continental Divide in Colorado. It ran from Colorado Springs to Leadville and through the divide at Hagerman Pass to Glenwood Springs and Grand Junction.

The Royal Gorge Route Railroad is a heritage railroad based in Cañon City, Colorado. A 1950s-era train makes daily 2-hour excursion runs from the Santa Fe Depot through the Royal Gorge along a famous section of the former Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad.

Pueblo Union Depot is the historic railroad station in Pueblo, Colorado. It was built in the Richardsonian Romanesque style in 1889–1890 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1975. It is located within the Union Avenue Historic Commercial District.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.

The Fort Worth and Rio Grande Railway, chartered under the laws of Texas on June 1, 1885, was part of a plan conceived by Buckley Burton Paddock and other Fort Worth civic leaders to create a transcontinental route linking New York, Fort Worth, and the Pacific port of Topolobampo, which they believed would stimulate the growth and development of southwest Texas in general, and the economy of Fort Worth in particular.
Southern California Railway was formed on November 7, 1889. it was formed by consolidation of California Southern Railroad Company, the California Central Railway Company, and the Redondo Beach Railway Company.

The Alamosa–Durango line or San Juan extension was a railroad line built by the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, following the border between the U.S. states of Colorado and New Mexico, in the Rocky Mountains. The line was originally built as a 3 ft narrow-gauge line between Alamosa, Colorado, and Durango, Colorado. Portions of the route survive: the now standard-gauged segment from Alamosa to Antonito, Colorado, and a narrow-gauge portion from Antonito to Chama, New Mexico.
References
- Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad . Retrieved July 18, 2005.
- Railroad History Timeline 1880 . Retrieved March 23, 2005.
- Reitwiesner, William Addams, The Ancestors of Julia Stimson Thorne . Retrieved October 11, 2005.
- Santa Fe Railroad (1945), Along Your Way, Rand McNally, Chicago, Illinois.
- ↑ MichiganRailroads.com Railroad History Timeline: 1880 Archived 2005-04-19 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved February 12, 2006.
- ↑ Rivanna Chapter National Railway Historical Society. "This Month in Railroad History: March". Archived from the original on 17 April 2006. Retrieved March 27, 2006.
- ↑ Blaszak, Michael W. "Santa Fe: A Chronology". ATSF Internet Resource Center. Retrieved March 27, 2011.
- ↑ Griffin, James R. (2003). Rio Grande Railroad. Voyageur Press. pp. 27–28. Retrieved March 27, 2011.
- ↑ Hilton, George W. (1990). American Narrow Gauge Railroads. Stanford University Press. p. 346. Retrieved March 27, 2011.
- ↑ Ross, Delmer G. (1977). "The construction of the Interoceanic Railroad of Guatemala". The Americas. 33 (3): 430–56. doi:10.2307/980947. JSTOR 980947. S2CID 147590795.
- 1 2 Serpico, Philip C. (1988). Santa Fé Route to the Pacific. Palmdale, California: Omni Publications. ISBN 0-88418-000-X.
- ↑ Spradling, David. "The Del Monte Passenger Train". Monterey Public Library. Retrieved 9 November 2019.
- ↑ "Sir Josiah Charles Stamp (later Lord Stamp of Shortlands)". steamindex.com. Retrieved August 22, 2007.