
The 1989 Pacific typhoon season was the first of six consecutive years of above-average activity in the Western Pacific. It was an extremely active season spawning 32 tropical storms,20 typhoons and five super typhoons. It has no official bounds;it ran year-round in 1989,but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The first storm,Winona,formed on January 15,while the final storm,Jack,dissipated on December 27. This season was also quite a deadly season that were caused by a few notable storms such as Tropical Storm Cecil,which was the worst storm to impact Vietnam in over 50 years,and Typhoon Gay,which directly impacted the Malay Peninsula as the worst typhoon in 35 years. Both of these storms make up around half of the total fatalities of the entire season alone.

The 1966 Pacific typhoon season was an active season,with many tropical cyclones having severe impacts in China,Japan,and the Philippines. Overall,there were 49 tropical depressions declared officially or unofficially,of which 30 officially became named storms;of those,20 reached typhoon status,while 3 further became super typhoons by having winds of at least 240 km/h (150 mph). Throughout the year,storms were responsible for at least 997 fatalities and $377.6 million in damage;however,a complete record of their effects is unavailable.

The 1964 Pacific typhoon season was the most active tropical cyclone season recorded globally,with a total of 39 tropical storms forming. It had no official bounds;it ran year-round in 1964,but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1960 Pacific typhoon season had no official bounds;it ran year-round in 1960,but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

Typhoon Imbudo,known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Harurot,was a powerful typhoon that struck the Philippines and southern China in July 2003. The seventh named storm and fourth typhoon of the season,Imbudo formed on July 15 to the east of the Philippines. The storm moved generally west-northward for much of its duration due to a ridge to the north. Favorable conditions allowed Imbudo to intensify,gradually at first before undergoing rapid deepening on July 19. After reaching typhoon status,Imbudo strengthened further to peak 10–minute sustained winds of 165 km/h (103 mph) on July 20. The typhoon made landfall on northern Luzon near peak intensity on July 22,but quickly weakened over land. Once in the South China Sea,Imbudo re-intensified slightly before making its final landfall in southern China near Yangjiang on July 24,dissipating the next day.

Typhoon Babs,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Loleng,was a powerful typhoon that struck the Philippines days after Typhoon Zeb hit the same area. The seventh typhoon of the inactive 1998 Pacific typhoon season,Babs formed on October 14 between the Philippines and Guam. The storm moved westward initially,failing to intensify initially due to the outflow from Typhoon Zeb to the northwest. Babs slowed and briefly turned to the south before advancing to the northwest,whereupon it rapidly intensified into a strong typhoon. On October 20,the official Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) estimated peak 10‑minute winds of 155 km/h (96 mph),while the unofficial Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) estimated peak 1‑minute winds of 250 km/h (160 mph),making Babs an unofficial super typhoon. The storm struck the Philippine island of Catanduanes at that intensity and weakened slightly before hitting Luzon. Babs turned northward once in the South China Sea,later weakening due to unfavorable conditions and transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on October 27 in the Taiwan Strait.
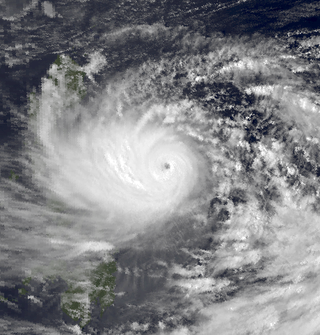
Typhoon Dot,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Saling,was the strongest storm of the 1985 season. Dot originated from a small area of thunderstorm activity in early to mid October. The system was first classified on October 11,and steadily intensified over the next few days. Dot attained typhoon strength on October 15,and subsequently entered a period of explosive deepening,which was not anticipated by forecasters. The next day the intensification rate slowed,but that evening,Dot attained its maximum intensify. A steady weakening trend began on October 17,though the system maintained typhoon intensity through the passage of the Philippines. After entering the South China Sea late on October 18,Dot briefly re-intensified,only to weaken as it approached Vietnam. On October 21,Dot struck Vietnam while still a typhoon,but dissipated the next day over the high terrain of the nation.

Typhoon Rose,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Uring,was the most violent and intense tropical cyclone to strike Hong Kong since Typhoon Wanda in 1962. The 21st named storm of the 1971 Pacific typhoon season,Rose developed from an area of disturbed weather while west of Guam on August 9. Moving west-northwestward,the storm briefly became a typhoon on the following day. After weakening to a tropical storm on August 11,Rose re-intensified into a typhoon several hours later. The system then curved westward and reached a primary peak intensity with winds of 205 km/h (127 mph) on August 13. Later that day,the typhoon made landfall near Palanan,Isabela in the Philippines. Rose weakened significantly while crossing the island of Luzon and was a minimal typhoon upon reaching the South China Sea on August 14.

Typhoon Joan,known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Sening,was the first of two super typhoons to strike the Philippines within a week in October 1970,the second being Super Typhoon Kate. Typhoon Joan is the fourth strongest typhoon ever to affect the Philippines,just after typhoons Haiyan in 2013,Meranti in 2016,and Goni in 2020.

The Philippines has five types of climates:tropical rainforest,tropical monsoon,tropical savanna,humid subtropical and oceanic. The country overall is characterized by relatively high temperature,oppressive humidity and plenty of rainfall. There are two seasons in the country:the wet season and the dry season,based upon the amount of rainfall. This is also dependent on location in the country as some areas experience rain all throughout the year. The warm months of the year are March through October;the winter monsoon brings cooler air from November to February. May is the warmest month,and January,the coolest.

Typhoon Angela,known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Rosing,was an extremely powerful and catastrophic tropical cyclone that impacted the Philippines in November 1995,and the most intense tropical cyclone worldwide in 1995. Typhoon Angela was the third storm in a row that struck the Philippines,following Yvette and Zack. Typhoon Angela was the twenty-ninth tropical cyclone,and the fifth super typhoon of the moderately active 1995 Pacific typhoon season.
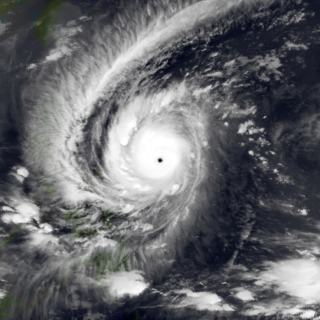
Typhoon Ivan,known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Narsing,was an extremely intense tropical cyclone that existed simultaneously with another storm of the same intensity,Typhoon Joan,in October 1997. Forming out of an area of disturbed weather on October 13,Ivan gradually intensified into a typhoon as it tracked steadily to the west-northwest. On October 15,the storm underwent rapid intensification and reached an intensity corresponding to Category 5 status on the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale. Late on October 17,Ivan reached its peak strength with winds of 295 km/h (183 mph) and a barometric pressure of 905 hPa (mbar). Shortly thereafter,the typhoon began to weaken as it approached the Philippines. Ivan eventually made landfall in northern Luzon with winds of 220 km/h (140 mph) on October 20 before weakening to a tropical storm the next day. The storm then curved northeastward and became extratropical on October 25 and dissipating the following day.

Typhoon Roy,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Asiang,was the second-most intense January tropical cyclone on record in the Western Pacific basin. Forming out of an area of disturbed weather on January 7,1988,Roy quickly intensified as it moved through the Marshall Islands. By January 9,the storm intensified into a typhoon and attained its peak intensity the following day. At its peak,sustained winds reached 215 km/h (135 mph). Slight weakening took place before the storm moved through the Mariana Islands. Continuing westward,the system eventually struck the Philippines as a minimal typhoon before dissipating over the South China Sea on January 19.

Typhoon Amy,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Gening,was a very destructive typhoon which was the second typhoon to strike China in a week during mid-July 1991. An area of convection was first observed on July 13 within the vicinity of Yap. A tropical depression developed the next day. While initially tracking westward,the system slowly deepened,becoming Tropical Storm Amy on July 16. After briefly turning northwestward,Amy intensified into a typhoon on July 17. Continuing to intensify as it tracked through the Luzon Strait,Amy reached its peak intensity of 175 km/h (110 mph) on July 18. That evening,the typhoon began to show signs of weakening,although it was still believed to have been a typhoon when it made landfall in the province of Guangdong on July 19,becoming the strongest tropical cyclone to hit the province in 22 years. Once inland,the storm rapidly weakened,and by late on July 20,had dissipated completely.

Typhoon Gordon,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Goring,was a powerful tropical cyclone that caused widespread damage and loss of life in the Philippines and Southern China in July 1989. Gordon developed into a tropical depression near the Northern Mariana Islands on July 9 and quickly intensified as it tracked west-southwestward. On July 13,the storm attained typhoon status and subsequently underwent a period of rapid intensification. By July 15,the storm attained its peak strength as a Category 5 equivalent super typhoon with winds estimated at 260 km/h (160 mph). After striking the northern Philippines,Gordon moved through the South China Sea and slowly weakened. On July 18,the storm made landfall in southern China and was last noted the following day as it dissipated over land.

Typhoon Nora,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Luming,is tied for the fourth-most intense tropical cyclone on record. Originating from an area of low pressure over the western Pacific,Nora was first identified as a tropical depression on October 2,1973. Tracking generally westward,the system gradually intensified,attaining typhoon status the following evening. After turning northwestward,the typhoon underwent a period of rapid intensification,during which its central pressure decreased by 77 mb in 24 hours. At the end of this phase,Nora peaked with winds of 295 km/h (185 mph) and a pressure of 875 mb,making it the most-intense tropical cyclone on record at the time;however,this pressure has since been surpassed by Typhoon June,Typhoon Tip and Hurricane Patricia. The typhoon subsequently weakened and turned northwestward as it approached the Philippines. After brushing Luzon on October 7,the system passed south of Taiwan and ultimately made landfall in China on October 10. Once onshore,Nora quickly weakened and dissipated the following day.
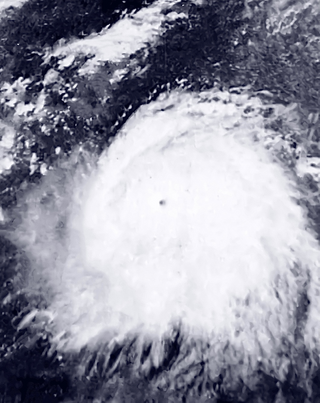
Typhoon Rita,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Kading,was the most powerful tropical cyclone during the 1978 Pacific typhoon season and one of the most intense tropical cyclones on record. A long-lived and destructive tropical cyclone,Rita began its journey east of the Marshall Islands and rapidly moved westwards,becoming a typhoon on October 20. Rita continued rapid intensification and attained super typhoon status and later an atmospheric pressure of 878 mbar (25.9 inHg) on October 25. Rita struck the Philippines overnight on October 26 and entered the South China Sea as a minimal typhoon. Rita caused extreme damage and more than 300 deaths.

Typhoon Vera,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Bebeng,brought significant flooding to the Philippines in July 1983. The monsoon trough spawned a tropical depression on July 12 east of the Philippines. Although the depression was initially slow to organize,the system headed west-northwestward,strengthening to a tropical storm the following day and a typhoon on the July 14. Vera moved onshore early the next day as a minimal typhoon in the Philippines before weakening slightly over the islands. However,Vera managed to restrengthen over the South China Sea while accelerating,later attaining winds of 85 mph (135 km/h). After crossing Hainan while still at peak intensity and moving into the northern portion of the Gulf of Tonkin,Vera gradually weakened before moving ashore in northern Vietnam on July 18. By July 19,Vera had dissipated inland.

Typhoon Sally,known in the Philippines as Typhoon Aring,was a powerful tropical cyclone that brought widespread impacts during its week-long trek across the western Pacific in September 1964. The strongest tropical cyclone of the 1964 Pacific typhoon season and one of the most intense tropical cyclones on record,and among the strongest typhoons ever recorded,with one-minute maximum sustained winds of 315 km/h (196 mph) as estimated by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Sally first became a tropical cyclone near the Marshall Islands on September 3,organizing into a tropical depression and then a tropical storm later that day. On September 4,Sally intensified into a typhoon and struck southern Guam the next day. Widespread agricultural damage occurred in the island's southern regions,with the banana crop suffering the costliest losses;the damage toll from crops and property exceeded $115,000. Sally continued to intensify on its west-northwestward trek,and reached its peak strength on September 7 over the Philippine Sea.



















