The region now known as Guinea-Bissau, in West Africa, has been inhabited by humans for thousands of years. During the 13th century AD, it was a province of the Mali Empire which later became independent as the empire of Kaabu. Portugal claimed the region during the 1450s, but its control was limited to several forts along the coast during most of this period; it gained control of the mainland after the pacification campaigns from 1912 to 1915. The offshore Bijagos Islands were not colonized until 1936. Guinea-Bissau became independent in 1974, and the introduction of multi-party politics in 1991 led to the first multi-party elections in 1994. A civil war broke out in 1998, which lasted until the following year.

The islands of São Tomé and Príncipe were uninhabited at the time of the arrival of the Portuguese sometime between 1469 and 1471. After the islands were discovered by the explorers João de Santarém and Pêro Escobar, Portuguese navigators explored the islands and decided they would be a good location for bases to trade with the mainland.

Politics in Portugal operates as a unitary multi-party semi-presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Portugal is the head of government, and the President of Portugal is the non-executive head of state which, although it is a somewhat ceremonial figure, has some significant political powers they exercise often. Executive power is exercised by the Government, whose leader is the prime minister. Legislative power is primarily vested in the Assembly of the Republic, although the government is also able to legislate on certain matters. The Judiciary of Portugal is independent of the executive and the legislature. The President exerts a sort of "moderating power", not easily classified into any of the traditional three branches of government.

The Brazilian Democratic Movement is a Brazilian political party. It is considered a "big tent party" and it is one of the parties with the greatest representation throughout the national territory, with the most numbers of senators, mayors and city councillors, always having formed a large part of the National Congress since 1988, and also has the largest number of affiliates, with 2,043,709 members as of July 2023.

Bernardino Luís Machado Guimarães, GCTE, GCL, was a Portuguese political figure, the third and eighth president of Portugal.

The African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde is a political party in Guinea-Bissau. Originally formed to peacefully campaign for independence from Portugal, the party turned to armed conflict in the 1960s and was one of the belligerents in the Guinea-Bissau War of Independence. Towards the end of the war, the party established a socialist one-party state, which remained intact until multi-party democracy was introduced in the early 1990s. Although the party won the first multi-party elections in 1994, it was removed from power in the 1999–2000 elections. However, it returned to office after winning parliamentary elections in 2004 and presidential elections in 2005, since which it has remained the largest party in the National People's Assembly.

Arturo Fortunato Alessandri Palma was a Chilean political figure and reformer who served thrice as president of Chile, first from 1920 to 1924, then from March to October 1925, and finally from 1932 to 1938.

Presidential elections were held in Germany on 13 March 1932, with a runoff on 10 April. Independent incumbent Paul von Hindenburg won a second seven-year term against Adolf Hitler of the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Communist Party (KPD) leader Ernst Thälmann also ran and received more than ten percent of the vote in the runoff. Theodor Duesterberg, the deputy leader of the World War I veterans' organization Der Stahlhelm, ran in the first round but dropped out of the runoff. This was the second and final direct election to the office of President of the Reich, Germany's head of state under the Weimar Republic.

Geraldo José Rodrigues Alckmin Filho is a Brazilian physician and politician currently serving as 26th vice president of Brazil. He previously was the Governor of São Paulo for two nonconsecutive terms, the longest serving since democratization, 2001 to 2006 and 2011 to 2018.

Presidential elections were held in Portugal on 22 January 2006 to elect a successor to the incumbent President Jorge Sampaio, who was term-limited from running for a third consecutive term by the Constitution of Portugal. The result was a victory in the first round for Aníbal Cavaco Silva of the Social Democratic Party candidate, the former Prime Minister, won 50.54 percent of the vote in the first round, just over the majority required to avoid a runoff election. It was the first time in which a right-wing candidate was elected President of the Republic since the 1974 Carnation Revolution.

The presidential line of succession defines who may become or act as President of the Federative Republic of Brazil upon the death, resignation, incapacity or removal from office of the elected president, and also when the president is out of the country or is suspended due to impeachment proceedings.
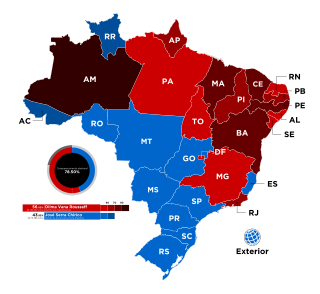
General elections were held in Brazil on 3 October 2010 to elect the president, National Congress and state governors. As no presidential candidate received more than 50% in the first round of voting, a second round was held on 31 October to choose a successor to Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva of the Workers' Party (PT), who was constitutionally ineligible to run for a third term as he has already served two terms after winning the elections in 2002 and being re-elected in 2006.

The 1924 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania took place on November 4, 1924 as part of the 1924 United States presidential election. Voters chose 38 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

General elections were held in Brazil on 5 October 2014 to elect the president, the National Congress, and state governorships. As no candidate in the presidential election received more than 50% of the vote in the first round on 5 October 2014, a second-round runoff was held on 26 October 2014.
First Lady of Portugal is the unofficial title attributed to the wife or Partner of the president of Portugal. To date, there has been no first gentleman of Portugal. The position is currently vacant since the first presidential inauguration of Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa in 2016.

Presidential elections were held in Portugal on 6 August 1923. The Congress of the Republic elected the president in Lisbon instead of the Portuguese people. However the new president Manuel Teixeira Gomes was elected In absentia, meaning that he wasn't present during the election.

General elections were held in Brazil on 7 October 2018 to elect the president, National Congress and state governors. As no candidate in the presidential election received more than 50% of the vote in the first round, a runoff round was held on 28 October.

Presidential elections were held in Portugal on 24 January. The incumbent President, Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa, was reelected for a second term.

General elections were held in Brazil on 2 October 2022 to elect the president, vice president, the National Congress, the governors, vice governors, and legislative assemblies of all federative units, and the district council of Fernando de Noronha. As no candidate for president—or for governor in some states—received more than half of the valid votes in the first round, a runoff election for these offices was held on 30 October. Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva received the majority of the votes in the second round and became president-elect of Brazil.


















