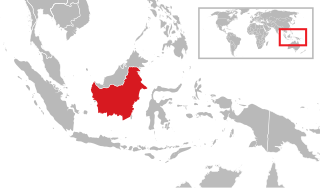
Kalimantan is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area, and consists of the provinces of Central Kalimantan, East Kalimantan, North Kalimantan, South Kalimantan, and West Kalimantan. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. Colloquially in Indonesia, the whole island of Borneo is also called "Kalimantan".

Batavia was the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The area corresponds to present-day Jakarta, Indonesia. Batavia can refer to the city proper or its suburbs and hinterland, the Ommelanden, which included the much larger area of the Residency of Batavia in the present-day Indonesian provinces of Jakarta, Banten and West Java.
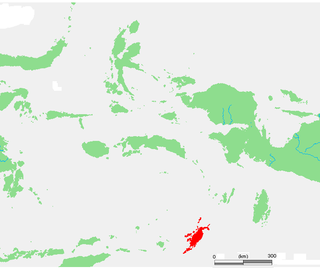
The Tanimbar Islands, also called Timur Laut, are a group of about 65 islands in the Maluku province of Indonesia. The largest and most central of the islands is Yamdena; others include Selaru to the southwest of Yamdena, Larat and Fordata to the northeast, Maru and Molu to the north, and Seira, Wuliaru, Selu, Wotap and Makasar to the west. The Indonesian phrase timur laut means "east of the sea" or "northeast".

Parepare is a city (kota) in South Sulawesi, Indonesia, located on the southwest coast of Sulawesi, about 155 km (96 mi) north of the provincial capital of Makassar. A port town, it is one of the major population centers of the Bugis people. The city had a population of 129,542 people at the 2010 Census and 151,454 at the 2020 Census; its official estimate as at mid-2023 was 160,309.

The Dutch Ethical Policy was the official policy of the colonial government of the Dutch East Indies during the four decades from 1901 until the Japanese occupation of 1942. In 1901, Dutch Queen Wilhelmina announced that the Netherlands accepted an ethical responsibility for the welfare of their colonial subjects. The announcement was a sharp contrast with the former official doctrine that Indonesia was a win-gewest and also marked the start of modern development policy. Other colonial powers talked of a civilising mission, which mainly involved spreading their culture to the colonised peoples.

Merauke is a large town (kelurahan) and an administrative district (distrik) in Merauke Regency of South Papua Province, Indonesia. It is also the administrative centre of Merauke Regency, and is considered to be the easternmost city in Indonesia, although it currently lacks city status. The town was originally called Ermasoe. It is next to the Maro River where the Port of Merauke is located. Merauke District covers a land area of 500.41 km2, and had a population of 87,634 at the 2010 Census. which at the 2020 Census had increased to 102,351; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 110,541.

The Indonesian National Awakening is a term for the period in the first half of the 20th century, during which people from many parts of the archipelago of Indonesia first began to develop a national consciousness as "Indonesians".

Company rule in the Dutch East Indies began when the Dutch East India Company appointed the first governor-general of the Dutch East Indies in 1610, and ended in 1800 when the bankrupt company was dissolved and its possessions were nationalized as the Dutch East Indies. By then it exerted territorial control over much of the archipelago, most notably on Java.

The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies, was a Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which declared independence on 17 August 1945. Following the Indonesian War of Independence, Indonesia and the Netherlands made peace in 1949. In the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, the Dutch ceded the governorate of Dutch Malacca to Britain, leading to its eventual incorporation into Malacca (state) of modern Malaysia.
Perserikatan was the national amateur football competitions in Indonesia held between 1931 and 1994 before the formation of Liga Indonesia, organized by the PSSI, the Indonesian football federation. The competition involved hundreds clubs in Indonesia and was divided into several levels.
The FIFA World Cup is an international association football competition contested by the men's national teams of the members of the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA), the sport's global governing body. It has been contested every four years since the first tournament in 1930, except in 1942 and 1946, due to World War II.

Arab Indonesians, or colloquially known as Jama'ah, are Indonesian citizens of mixed Arab, mainly Hadhrami, and Indonesian descent. The ethnic group generally also includes those of Arab descent from other Middle Eastern Arabic speaking nations. Restricted under Dutch East Indies law until 1919, the community elites later gained economic power through real estate investment and trading. Currently found mainly in Java, especially West Java and East Java, they are almost all Muslims.

The Indo people or Indos are Eurasian people living in or connected with Indonesia. In its narrowest sense, the term refers to people in the former Dutch East Indies who held European legal status but were of mixed Dutch and indigenous Indonesian descent as well as their descendants today.

The Javanese diaspora is the demographic group of descendants of ethnic Javanese who emigrated from the Indonesian island of Java to other parts of the world. The Javanese diaspora includes a significant population in Suriname, with over 13% of the country's population being of Javanese ancestry. Other major enclaves are found in French Guiana, Malaysia, the Netherlands, New Caledonia, Singapore, South Africa, and Sri Lanka.

Koedoes Residency was an administrative division (Residency) of Central Java province of the Dutch East Indies with its capital at Kudus, which existed between 1928 and 1931. It was significantly larger than the present-day Kudus Regency, as it also contained Demak Regency and Jepara Regency.

Blora Residency was an administrative division (Residency) of Central Java province of the Dutch East Indies with its capital at Blora, which existed between 1928 and 1931. It was significantly larger than the present-day Blora Regency, as it also contained Grobogan Regency and Purwodadi.

Buitenzorg Residency was an administrative division (Residency) of the Dutch East Indies located in western Java which existed from 1817 to 1867 and from 1925 to 1942. Its seat was at Buitenzorg which was also the seat of the colonial government of the Indies after 1905.
Censuses in Indonesia are censuses of Indonesia's population, agriculture, and economy conducted by Statistics Indonesia. The first census after independence was held in 1961.

The 1961 Indonesian census was the first census of Indonesia as a sovereign state. With a total population of 97,018,829, Indonesia was the world's fifth-most populous country at the time. The census covered all territories in the country, but no enumeration was done in Indonesian-claimed Western New Guinea because it was under Dutch occupation. Instead, an estimated population for the region was included in the final census numbers. During the 1961 census, its population density was 50.9 inhabitants/km2.
Censuses in the Dutch East Indies were censuses in the Dutch East Indies colony of the Netherlands. The last census was conducted in 1930.
















