
The population of Indonesia was 270.20 million according to the 2020 national census, an increase from 237.64 in 2010. Indonesia is the fourth most populous country in the world. Approximately 55% of Indonesia's population resides on Java, which is the most populous island in the world.
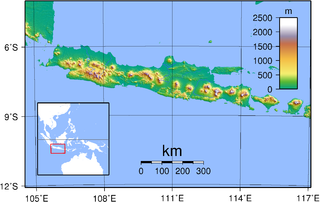
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's most populous island, home to approximately 56% of the Indonesian population.

Alor is the largest island in the Alor Archipelago and is one of the 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indonesia. It is located at the eastern Lesser Sunda Islands that runs through southeastern Indonesia, which from the west include such islands as Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Komodo, and Flores.

Bandar Lampung is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Lampung. Located on the southern tip of Sumatra, Bandar Lampung was originally called Tanjungkarang–Telukbetung, since it was a unification of two major settlements in Lampung, before being renamed in 1983.

The Surabaya metropolitan area, or known locally as Gerbangkertosusila, is a metropolitan area in East Java, Indonesia. It is the country's second-largest metropolitan area, after Jakarta metropolitan area.

Indonesians are citizens or people who are identified with the country of Indonesia, regardless of their ethnic or religious background. There are more than 1,300 ethnicities in Indonesia, making it a multicultural archipelagic country with a diversity of languages, culture and religious beliefs. The population of Indonesia according to the 2020 national census was 270.2 million. 56% live on the island of Java, the world's most populous island. Around 95% of Indonesians are Native Indonesians, with 40% Javanese and 15% Sundanese forming the majority, while the other 5% are Indonesians with ancestry from foreign origin, such as Arab Indonesians, Chinese Indonesians, Indian Indonesians, and Indos.

Merauke Regency is a regency in the far south of the Indonesian province of South Papua. It covers an area of 46,791.63 km2, and had a population of 195,716 at the 2010 Census and 230,932 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 231,696, comprising 121,078 males and 110,618 female inhabitants. The administrative centre is the town of Merauke; this was projected since 2013 to become an independent city (kota) separate from Merauke Regency, but the alteration has been deferred. It is also the provincial capital of South Papua since 2022. It is the largest regency in Indonesia, with an area of 46,791 km2, slightly larger than Estonia.

Ponorogo Regency is a regency (kabupaten) of East Java, Indonesia. It is considered the birthplace of Reog Ponorogo, a traditional Indonesian dance form. The regency covers an area of 1,371.78 km2 (529.65 sq mi), and it had a population of 855,281 at the 2010 census and 949,318 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 955,839. The capital of the kabupaten is the local town of Ponorogo located around 30 km (19 mi) south of the main East Java city of Madiun and 65 km (40 mi) south Ngawi

Statistics Indonesia, is a non-departmental government institute of Indonesia that is responsible for conducting statistical surveys. Its main customer is the government, but statistical data is also available to the public. Annual surveys include national and provincial socio-economics, manufacturing establishments, population and the labour force.

Demak is a regency located in the Indonesian province of Central Java, on northern coast of the island. It is bordered by Jepara regency and the Java Sea to the north, Kudus and Grobogan regencies to the east, Grobogan and Semarang regencies to the south, while to the west are Semarang Regency and the city of Semarang, to which the districts of Mranggen and Sayung are essentially suburban. The regency covers an area of 897.43 km2 (346.50 sq mi) and had a population of 1,055,579 at the 2010 Census and 1,203,956 at the 2020 Census. It was originally the centre of the Demak Sultanate, once a dominant power in the region. Due to its strong relation with the spread of Islam in Java and the Wali Sanga, it is sometimes referred to with the nickname Kota Wali.

Bandung metropolitan area, officially Bandung Basin or Greater Bandung, is a metropolitan area surrounding the city of Bandung, West Java, Indonesia. It was home to 8.873 million people in mid 2021 and is composed of regencies and cities previously part of the Dutch East Indies era "Central Priangan Residency" administration.
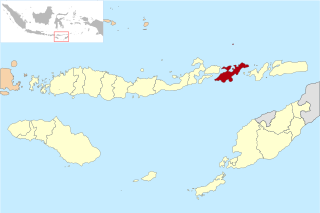
Lembata Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Established on 4 October 1999 from part of East Flores Regency, the regency covers the island of Lembata, together with three small offshore islands together forming the eastern part of the Solor Archipelago, and has its administrative seat (capital) in Lewoleba. The population of the Regency was 117,829 at the 2010 decennial census and at the 2020 census was 135,930; the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 137,630.

Sabu Raijua Regency is one of the regencies in the province of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. It comprises the three Savu Islands, lying between Sumba and Rote Island in the Savu Sea. The regency was established by Indonesia's Minister of Home Affairs, Mardiyanto, on 29 October 2008, partitioned from Kupang Regency. The population was 72,960 at the 2010 census, and 89,327 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 90,837.

Bone Regency is a regency of South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Originally the seat of the Bone state, it joined Indonesia in 1950. The regency covers an area of 4,559.00 km2 and had a population of 717,682 at the 2010 Census and 801,775 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 806,750. Its main products are seaweed, rice, and fish. The principal town is Watampone, which comprises the three districts of Tanete Riattang Barat, Tanete Riattang and Tanete Riattang Timur within the regency.

North Minahasa Regency is a regency in North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Its capital is Airmadidi. It was originally part of the Minahasa Regency until it was established as a separate regency on 20 November 2003. It covers an area of 1,059.24 km2, and had a population of 188,904 at the 2010 Census; this had risen to 224,993 at the 2020 Census. The Regency includes the offshore islands of Bangka and Talisei to the north of Sulawesi, and Mantenang and Naeng Besar to the northwest.

Sungai Durian, or "Durian River", is a district of Kotabaru Regency in the province of South Kalimantan, Indonesia. The population is entirely rural.

Banua Lawas is a district in Tabalong Regency, South Kalimantan Province, Indonesia. The majority of population in this district is Banjar people whose belief is Islam.

The 1961 Indonesian census was the first census of Indonesia as a sovereign state. With a total population of 97,018,829, Indonesia was the world's fifth-most populous country at the time. The census covered all territories in the country, but no enumeration was done in Indonesian-claimed Western New Guinea because it was under Dutch occupation. Instead, an estimated population for the region was included in the final census numbers.

















