Contents
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1933 History of Bolivia • Years | ||||
This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2024) |
Events in the year 1933 in Bolivia .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1933 History of Bolivia • Years | ||||
This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2024) |
Events in the year 1933 in Bolivia .
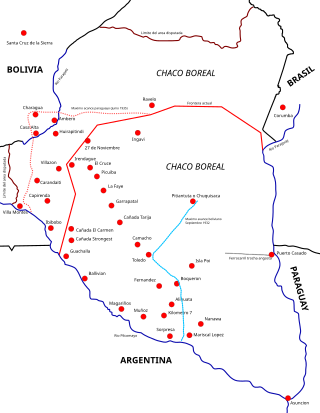
The Chaco War was fought from 1932 to 1935 between Bolivia and Paraguay, over the control of the northern part of the Gran Chaco region of South America, which was thought to be rich in oil. The war is also referred to as La Guerra de la Sed in literary circles since it was fought in the semi-arid Chaco. The bloodiest interstate military conflict fought in South America in the 20th century, it was fought between two of its poorest countries, both of which had lost territory to neighbours in 19th-century wars.

Presidente Hayes is a department in Paraguay. The capital is the city of Villa Hayes. The department was named after U.S. President Rutherford B. Hayes, who awarded the territory to Paraguay while arbitrating a boundary dispute between Paraguay and Argentina after the Paraguayan War.

Ismael Montes Gamboa was a Bolivian general and political figure who served as the 26th president of Bolivia twice nonconsecutively from 1904 to 1909 and from 1913 to 1917. During his first term, the Treaty of Peace and Friendship with Chile was signed on 20 October 1904.
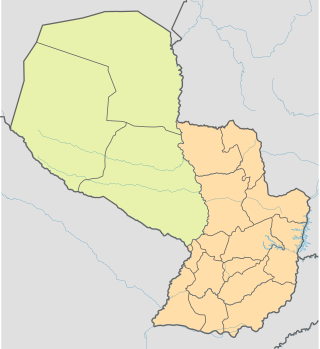
The Paraguayan Chaco or Región Occidental is a semi-arid region in Paraguay, with a very low population density. The area is being rapidly deforested. Consisting of more than 60% of Paraguay's land area, but with less than 3% of the population, the Chaco is one of the most sparsely inhabited areas in South America.
Jhasmani Campos Dávalos is a Bolivian professional footballer who plays as a Attacking midfielder or winger for Independiente Petrolero and the Bolivia national team.
The Colonel Luis Irrazábal Barboza was born in Encarnación, in Itapúa Department, Paraguay, on August 8, 1891, and died on March 16, 1958, in Asunción, capital of Paraguay.

Hans Anton Wilhelm Friedrich Kundt was a German military officer. He was the primary military figure of Bolivia during the two decades preceding the Chaco War.
The Chaco War was the first major Latin American conflict in which aircraft were used. This aerial war carried a large human and materiel cost. At that time, Bolivia possessed one of the greatest aerial forces in the region, however this fact did not prevent its final defeat. Bolivia lacked the expertise to utilise its aerial forces, and was thus unable to maximise its use of military aviation. Paraguay had a small number of pilots and technicians, all veterans of the revolution of 1922. The 1922 revolution was a brief civil war in which the government and the rebels used aircraft in the operations, and José Félix Estigarribia could be considered an innovator in the military use of aircraft on the continent.
The Chaco War (1932–35), between Bolivia and Paraguay, was the first South American conflict in which tanks were employed. They originated exclusively from Bolivia, but Paraguay operated tanks captured from Bolivia during the war.
The battle of the Campo Vía pocket was a decisive engagement of the Chaco War between Paraguay and Bolivia which took place in December 1933. It was one of the most prominent battles of the Chaco War. Lt Col José Félix Estigarribia, with a massive force of several divisions of the Paraguayan Army, was able to surround two Bolivian divisions around the outpost of Alihuatá. The encircled troops were forced to capitulate due to lack of supplies on 11 December. Up to 2,000 Bolivian soldiers were killed and 7,000 captured. Barely 900 Bolivian troops escaped, led by Colonel Germán Bush. Subsequently, the Paraguayan troops expelled the Bolivian army from the eastern region of Chaco by the end of 1933, forcing the resignation of German General Hans Kundt from the Bolivian High Command.
The Battle of Gondra occurred during the Chaco War between the Bolivian 4th Division, "The Brave Fourth", and the Paraguayan 1st Division, "The Iron Division", stationed around Fort Gondra, from 11 to 15 July 1933, in the aftermath of the Second Battle of Nanawa. The 1st Division enveloped the Bolivian 4th after a series of assaults through the dense woods southwest of Gondra. The Bolivian 34th infantry and the "Lanza" cavalry regiment, led by captain German Busch, fought a rearguard action which allowed the encircled troops to withdraw northward, toward Campo 31, an open field leading to Alihuatá. Meanwhile, the 3rd "Pérez" infantry regiment built up a new blocking position in the eastern part of Campo Vía, a dried bed six kilometers west of Gondra, which prevented any further Paraguayan advance. On 15 July, the Bolivian troops retreated unmolested from the pocket, carrying out all their heavy equipment with them.

The Battle of Campo Grande was a major engagement during the Chaco War, in the southern region of the Chaco Boreal. During this battle, the Paraguayan Army successfully encircled two Bolivian regiments defending two of the three flanks of Fort Alihuatá, forcing them to surrender.

The Battle of Kilometer 7 was a series of clashes during the Chaco War between Bolivian and Paraguayan forces from 7 November 1932 to February 1933, and ended with a Paraguayan retreat to the northeast towards Gondra, later to be the site of the Battle of Campo Jordán. The Paraguayan initiative, which had belonged to the Paraguayans since the beginning of the siege of Boquerón passed to the Bolivian army until the Second Battle of Nanawa in July.

The Second Battle of Nanawa was fought from the 4 to 9 July 1933, between the Bolivian and Paraguayan armies during the Chaco War. It was one of the bloodiest battles fought in South America in the 20th century, coming to be labeled as the "South American Verdun" by comparison with the Battle of Verdun of World War I.
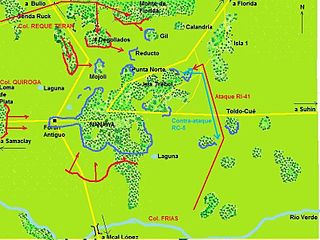
The First Battle of Nanawa was fought from 20 to 26 January 1933 between the Bolivian and Paraguayan armies during the Chaco War. Nanawa, established by the Paraguayans in 1928, was considered the strongest Paraguayan outpost after it was heavily fortified by the end of 1932 under directives of Ivan Belaieff and Nicolas Ern, two White Russian former officers who joined the Paraguayan army in the 1920s. Zig-zag trenches, barbed wire and machine gun nests were built by the garrison around a horseshoe-shaped defence. Nanawa's commander, Col. Luis Irrazábal, summoned under his command four regiments and several minor units which made up the Paraguayan fifth division. The commander-in-chief of the Bolivian army, German World War I veteran Hans Kundt, commanded the Bolivian assault personally in place. The Bolivian army launched three attacks that stalled after seizing some parts of the stronghold. After this failure, the Bolivian troops attempted to dig a trench around the Nanawa complex to isolate it but were met by Paraguayan reinforcements. Heavy rains forced the Bolivians to abandon what they had captured of the complex and the Paraguayans soon recovered these positions.
Below is the timeline of Paraguayan history.
The following lists events that happened during 1933 in the Republic of Paraguay.
Achim von Kries was a German military officer who served in the 1932-1935 Chaco War between Paraguay and Bolivia, commanding Bolivian armored fighting vehicles. He was wounded in action during the second battle of Nanawa. Von Kries later founded the Landesgruppe-Bolivie, the Bolivia branch of the German Nazi Party's Auslands-Organisation.

The Salaverry-Santa Cruz War, sometimes called the Peruvian Civil War of 1835–1836, was an internal conflict in Peru with the involvement of the Bolivian army of Andres de Santa Cruz. It ended with the defeat and execution of Felipe Santiago Salaverry and the creation of the Peru-Bolivian Confederation.
The First Battle of Alihuatá was a battle of the Chaco War between Bolivia and Paraguay, it took place between March 10 to 13 of 1933 and culminated in the occupation of the Alihuatá fort by the Bolivian army and the withdrawal of the small Paraguayan unit that defended it, allowing the Bolivian 9th Division to cut the supply route from Arce to the Paraguayan 1st Division that was fighting in the area of "Kilometer 7" and Campo Jordán south of Alihuatá.