Related Research Articles

Riviera Beach is a city in Palm Beach County, Florida, United States, which was incorporated on September 29, 1922. Due to the location of its eastern boundary, it is also the easternmost municipality in the Miami metropolitan area. In the 2020 U.S. Census, the total population of Riviera Beach residents was 37,604 people.
The Albany Movement was a desegregation and voters' rights coalition formed in Albany, Georgia, in November 1961. This movement was founded by local black leaders and ministers, as well as members of the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) and the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP). The groups were assisted by Martin Luther King Jr. and the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). It was meant to draw attention to the brutally enforced racial segregation practices in Southwest Georgia. However, many leaders in SNCC were fundamentally opposed to King and the SCLC's involvement. They felt that a more democratic approach aimed at long-term solutions was preferable for the area other than King's tendency towards short-term, authoritatively-run organizing.
George Neves Leighton was an American judge who served as a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Northern District of Illinois. He was known for taking cases related to housing, voting, and jury service, especially if these cases were directly impacted by injustice, particularly racism.
The Cambridge riots of 1963 were race riots that occurred during the summer of 1963 in Cambridge, a small city on the Eastern Shore of Maryland. The riots emerged during the Civil Rights Movement, locally led by Gloria Richardson and the local chapter of the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee. They were opposed by segregationists including the police.
Diop Kamau is an American civil rights activist and former law enforcement officer. Kamau transitioned from law enforcement to activism after his father was beaten by police officers and he himself experienced racial harassment on the job. Kamau runs the Police Complaint Center to collect and investigate allegations of police abuse.
The Cambridge riot of 1967 was one of 159 race riots that swept cities in the United States during the "Long Hot Summer of 1967". This riot occurred on July 24, 1967 in Cambridge, Maryland, a county seat on the Eastern Shore. For years racial tension had been high in Cambridge, where black people had been limited to second-class status. Activists had conducted protests since 1961, and there was a riot in June 1963 after the governor imposed martial law. "The Treaty of Cambridge" was negotiated among federal, state, and local leaders in July 1963, initiating integration in the city prior to passage of federal civil rights laws.

The Biloxi wade-ins were three protests that were conducted by local African Americans on the beaches of Biloxi, Mississippi between 1959 and 1963, during the civil rights movement. The demonstrations were led by Dr. Gilbert R. Mason, Sr. in an effort to desegregate the city's 26 mi (42 km) of beaches on the Mississippi Gulf Coast. This was a local effort, without involvement from the state or national NAACP.
This is a timeline of the civil rights movement in the United States, a nonviolent mid-20th century freedom movement to gain legal equality and the enforcement of constitutional rights for people of color. The goals of the movement included securing equal protection under the law, ending legally institutionalized racial discrimination, and gaining equal access to public facilities, education reform, fair housing, and the ability to vote.
The 1967 Milwaukee riot was one of 159 race riots that swept cities in the United States during the "Long Hot Summer of 1967". In Milwaukee, Wisconsin, African American residents, outraged by the slow pace in ending housing discrimination and police brutality, began to riot on the evening of July 30, 1967. The inciting incident was a fight between teenagers, which escalated into full-fledged rioting with the arrival of police. Within minutes, arson, looting, and sniping were occurring in the north side of the city, primarily the 3rd Street Corridor.
Corey Jones was shot to death by police officer Nouman K. Raja, while waiting for a tow truck by his disabled car, in Palm Beach Gardens, Florida.
The Augusta Riot was a collective rebellion of Black citizens in Augusta, Georgia, and the largest urban uprising in the Deep South during the Civil Rights era. Fueled by long-simmering grievances about racial injustice, it was sparked by White officials’ stonewalling in the face of Black citizens’ demand for answers about the beating death of Black teenager Charles Oatman. At its height on the evening of May 11, 1970, 2,000 to 3,000 people participated, ransacking and set fire to White- and Chinese-American-owned businesses, damaging $1 million of property over a 130-block area. White police officers violently suppressed the riot, with the endorsement of Georgia governor Lester Maddox, shoot-to-kill orders from their captain, and reinforcements by the National Guard and State Patrol. Despite the suppression, the riot fundamentally shook the status quo, galvanizing a new wave of activism that opened economic and political doors for Augusta’s Black citizens.

The Newberry Six lynchings took place in Newberry, Alachua County, Florida, on August 18, 1916.
Lozman v. City of Riviera Beach, 585 U.S. ___ (2018), is a case in which the United States Supreme Court decided that the mere existence of probable cause for an arrest did not bar the plaintiff's First Amendment retaliatory arrest claim, but deferred consideration of the broader question of when it might. The case concerned a 42 U.S.C. § 1983 lawsuit filed against Riviera Beach by Fane Lozman, who had been arrested while criticizing local politicians during the public comments section of a City Council meeting. The city argued that under Hartman v. Moore he could not sue for retaliation, as they had probable cause to arrest him for the offense of disturbing a lawful assembly. Lozman conceded that they had probable cause, but argued that Hartman, a case about retaliatory prosecutions, did not extend to retaliatory arrests, and that instead Mt. Healthy City School District Board of Education v. Doyle allowed his suit.
The Chester school protests were a series of demonstrations that occurred from November 1963 through April 1964 in Chester, Pennsylvania. The demonstrations aimed to end the de facto segregation of Chester public schools that persisted after the 1954 Supreme Court case Brown v. The Board of Education of Topeka. The racial unrest and civil rights protests were led by Stanley Branche of the Committee for Freedom Now (CFFN) and George Raymond of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored Persons (NAACP).
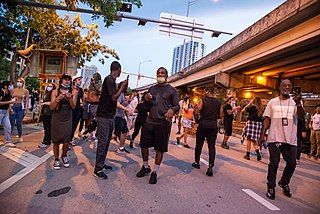
This is a list of protests in Florida in response to the murder of George Floyd. On May 31, 2020, Florida Governor Ron DeSantis activated the Florida National Guard, and deployed 700 soldiers to assist law enforcement agencies across the state. Additionally, DeSantis instructed the Florida Highway Patrol to mobilize 1,300 troopers to assist in policing actions.

This is a list of protests that took place in Los Angeles County, California following the murder of George Floyd on May 25, 2020, in Minneapolis, Minnesota, while in police custody.
The 1967 Tampa riots were a series of race riots during June 1967 in Tampa, Florida, as one of 159 such riots in the United States that summer.
The 1968 Tallahassee riots were one of many riots that broke out after Martin Luther King Jr. was assassinated in Tallahassee, Florida lasting from April 5–7, 1968. It was originally a student protest but later escalated into a riot. The riot happened at Florida A & M University but unrest would be seen to a lesser extent in the Frenchtown neighborhood.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Marshall, Barbara (July 28, 2017). "Mobs, fires fueled summer of riots in Riviera Beach, West Palm Beach". The Palm Beach Post . Archived from the original on June 24, 2021. Retrieved June 20, 2021.
- ↑ Levy, Peter B. (2011). "The Dream Deferred: The Assassination of Martin Luther King Jr., and the Holy Week Uprisings of 1968". In Jessica I. Elfenbein; Thomas L. Hollowak; Elizabeth M. Nix (eds.). Baltimore '68 : riots and rebirth in an American city. Philadelphia: Temple University Press. ISBN 978-1-4399-0662-0.
- ↑ Friedland, Michael B. (1998). Lift Up Your Voice Like a Trumpet: White Clergy and the Civil Rights and Antiwar Movements, 1954–1973. University of North Carolina Press. p. 189. ISBN 9780807846469.
- ↑ Pinnix, Aaron (2020-06-24). "The Long Hot Summer of 1967". Aaron Pinnix. Retrieved 2023-03-16.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Skinner, Sara (May 22, 2014). "This week in history: Race riots in Riviera Beach and West Palm Beach". Palm Beach Daily News . Retrieved June 20, 2021.
- ↑ "Riveria Beach Rioting Results in 45 Arrests". St. Petersburg Times . August 1, 1967. p. 19. Retrieved June 3, 2022– via Google News Archive.
- ↑ "Race Troubles: 109 U.S. Cities Faced Violence in 1967". U.S. News & World Report (published August 14, 1967). July 12, 2017. Archived from the original on 2017-07-14.
- 1 2 Lands, LeeAnn (1995). BELT OF BLIGHT: PUBLIC POLICY AND HOUSING SEGREGATION IN PALM BEACH COUNTY, 1960–1986 (PDF).
- ↑ "School Desegregation". Palm Beach County History Online. Archived from the original on 2014-10-18. Retrieved 2021-06-30.