| 1991 World Championships in Fencing | |
|---|---|
| Host city | |
| Date(s) | June 13–23 |
The 1991 World Fencing Championships were held in Budapest, Hungary. The event took place from June 13 to June 23, 1991.[ citation needed ]
| 1991 World Championships in Fencing | |
|---|---|
| Host city | |
| Date(s) | June 13–23 |
The 1991 World Fencing Championships were held in Budapest, Hungary. The event took place from June 13 to June 23, 1991.[ citation needed ]
* Host nation (Hungary)
| Rank | Nation | Gold | Silver | Bronze | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 10 | |
| 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | |
| 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 9 | |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 6 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Totals (7 entries) | 10 | 10 | 15 | 35 | |

Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire or the Dual Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consisted of two sovereign states with a single monarch who was titled both emperor of Austria and King of Hungary. Austria-Hungary constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy: it was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after Hungary terminated the union with Austria on 31 October 1918.

Czechoslovakia was a landlocked state in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland became part of Nazi Germany, while the country lost further territories to Hungary and Poland. Between 1939 and 1945, the state ceased to exist, as Slovakia proclaimed its independence and Carpathian Ruthenia became part of Hungary, while the German Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia was proclaimed in the remainder of the Czech Lands. In 1939, after the outbreak of World War II, former Czechoslovak President Edvard Beneš formed a government-in-exile and sought recognition from the Allies.

Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning 93,030 square kilometres (35,920 sq mi) of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of 9.5 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian, a language belonging to the Ugric branch of the Uralic language family, is the official language, and Budapest is the country's capital and largest city.

Jadwiga, also known as Hedwig, was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Great, King of Hungary and Poland, and his wife, Elizabeth of Bosnia. Jadwiga was a member of the Capetian House of Anjou, but she had more close forebears among the Polish Piasts than among the Angevins.

Mary, also known as Maria of Anjou, reigned as Queen of Hungary and Croatia between 1382 and 1385, and from 1386 until her death. She was the daughter of Louis the Great, King of Hungary and Poland, and his wife, Elizabeth of Bosnia. Mary's marriage to Sigismund of Luxembourg, a member of the imperial Luxembourg dynasty, was already decided before her first birthday. A delegation of Polish prelates and lords confirmed her right to succeed her father in Poland in 1379.

Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate, and an area of 238,397 km2 (92,046 sq mi) with a population of 19 million people (2023). Romania is the twelfth-largest country in Europe and the sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Its capital and largest city is Bucharest, followed by Cluj-Napoca, Iași, Timișoara, Constanța, Craiova, Brașov, and Galați.
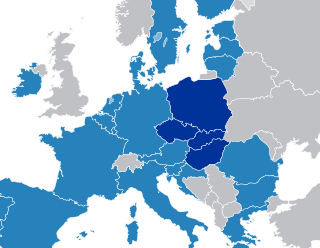
The Visegrád Group is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, economic, cultural and energy affairs, and to further their integration with the EU. All four states are also members of the European Union (EU), the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), and the Bucharest Nine (B9).

The forint is the currency of Hungary. It was formerly divided into 100 fillér, but fillér coins are no longer in circulation. The introduction of the forint on 1 August 1946 was a crucial step in the post-World War II stabilisation of the Hungarian economy, and the currency remained relatively stable until the 1980s. Transition to a market economy in the early 1990s adversely affected the value of the forint; inflation peaked at 35% in 1991. Between 2001 and 2022, inflation was in single digits, and the forint has been declared fully convertible. In May 2022, inflation reached 10.7% amid the Russian invasion of Ukraine and economic uncertainty. As a member of the European Union, the long-term aim of the Hungarian government may be to replace the forint with the euro, although under the current government there is no target date for adopting the euro.

Vlad III, commonly known as Vlad the Impaler or Vlad Dracula, was Voivode of Wallachia three times between 1448 and his death in 1476/77. He is often considered one of the most important rulers in Wallachian history and a national hero of Romania.
The Alliance of Free Democrats – Hungarian Liberal Party was a liberal political party in Hungary.
Tibor Benedek was a Hungarian professional water polo player and coach, widely regarded as one of the greatest players of all time. He played on the gold medal squads at the 2000 Summer Olympics, 2004 Summer Olympics and 2008 Summer Olympics. Benedek also competed at the 1992 and 1996 Summer Olympics, where the Hungarian team placed 6th and 4th, respectively.
George Martin Lott was an American tennis player and tennis coach who was born in Springfield, Illinois. Lott is mostly remembered as being one of the great doubles players of all time. He won the U.S. title five times with three different partners: John Hennessey in 1928; John Doeg in 1929 and 1930; and Les Stoefen in 1933 and 1934.
The Nemzeti Bajnokság, also known as NB I, is the top flight of Hungarian football league system. The league is officially named OTP Bank Liga after its title sponsor, OTP Bank.
Pál Csernai was a Hungarian football player and manager.

The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, were a revolutionary wave of liberal democracy movements that resulted in the collapse of most Marxist–Leninist governments in the Eastern Bloc and other parts of the world. This revolutionary wave is sometimes referred to as the Autumn of Nations, a play on the term Spring of Nations that is sometimes used to describe the Revolutions of 1848 in Europe. The Revolutions of 1989 contributed to the dissolution of the Soviet Union—one of the two global superpowers—and the abandonment of communist regimes in many parts of the world, some of which were violently overthrown. These events drastically altered the world's balance of power, marking the end of the Cold War and the beginning of the post-Cold War era.

Vác FC is a Hungarian football club based in Vác, north of Budapest. The club of the fourth division of the Hungarian football league was established in June 1899 as Váci Városi SE plays its home matches at the Stadion Városi Vác. Before 2009, the club was known by a variety of other names.

Tatabányai Sport Club is a Hungarian football club based in Tatabánya, Komárom-Esztergom, Hungary. The team set to play in Nemzeti Bajnokság II from 2024–25, the second tier of Hungarian football after promotion from Nemzeti Bajnokság III in 2023–24. They play their home games at Stadion Gyula Grosics.

Tibor Nyilasi is a retired Hungarian football player and manager. A midfielder, he signed with Ferencváros in 1972 and played there until transferring to Austria Wien in 1983. He made 70 appearances for the Hungary national team from 1975 to 1985, scoring 32 goals. He played in the 1978 FIFA World Cup and the 1982 FIFA World Cup. After he retired as a player he was manager of Ferencváros. He has more recently also worked for the Hungarian Football Federation and is regularly appearing as a pundit on the Hungarian sports channel 'Sport TV'.

Hungarian–Soviet relations were characterized by political, economic, and cultural interventions by the Soviet Union in internal Hungarian politics for 45 years, the length of the Cold War. Hungary became a member of the Warsaw Pact in 1955; since the end of World War II, Soviet troops were stationed in the country, intervening at the time of the Hungarian Revolution of 1956. Starting in March 1990, the Soviet Army began leaving Hungary, with the last troops being withdrawn on June 19, 1991.
The Hungary women's national basketball team is the team representing Hungary in international women's basketball competitions, organized and run by the Magyar Kosárlabdázók Országos Szövetsége, the governing body of basketball in the country.