| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
This article lists events from the year 1999 in The Bahamas .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
This article lists events from the year 1999 in The Bahamas .

The Bahamas, known officially as the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is a country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 700 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the US state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.

Nassau is the capital and largest city of The Bahamas. With a population of 274,400 as of 2016, or just over 70% of the entire population of the Bahamas (≈391,000), Nassau is commonly defined as a primate city, dwarfing all other towns in the country. It is the centre of commerce, education, law, administration and media of the country.

Andros Island is an archipelago within the Bahamas, the largest of the Bahamian Islands. Politically considered a single island, Andros in total has an area greater than all the other 700 Bahamian islands combined. The land area of Andros consists of hundreds of small islets and cays connected by mangrove estuaries and tidal swamplands, together with three major islands: North Andros, Mangrove Cay, and South Andros. The three main islands are separated by "bights", estuaries that trifurcate the island, connecting the island's east and west coasts. It is 167 kilometres (104 mi) long by 64 km (40 mi) wide at the widest point.

Local government in the Bahamas exists in two forms, namely second-schedule and third-schedule district councils. There are a total of 32 local government districts: 13 second-schedule districts, which are further sub-divided into town areas, and 19 third-schedule districts, which are all unitary authorities. The second and third schedules together make up the first schedule. Local government policy is formulated and administered by the Department of Lands and Local Government through the Office of the Prime Minister. The day-to-day policy handling of the portfolio falls to the Minister of Local Government who also is empowered to create new local government areas from time to time based on demographics. The administrative and financial management is overseen by the ministry’s permanent secretary.
Tonique Williams-Darling is a Bahamian sprint athlete. She won the gold medal in the 400 meters at the 2004 Summer Olympics in Athens, Greece. She graduated from St. John's College Bahamas.
Savatheda Fynes is a track and field sprint athlete, competing internationally for Bahamas. She is an Olympic gold medalist in the 4 x 100 meter relay race. Some sources spell her first name "Sevatheda."

The Bahamas Football Association (BFA) is the official football federation in The Bahamas. It was founded in 1967 for men, women, and children to learn more about football. It affiliated with FIFA in 1968. The headquarters are in Nassau. The federation is also in charge of its football clubs and the Bahamanian national team. They control the New Providence Football League's divisions 1 and 2. They are also in charge of the Grand Bahama Football League for both men and women. The BFA is led by (President) Mr. Anton Sealey and the board of executives, Jason McDowall, Kevin Davis, Stanley Darville, Antoine Dias and Bruce LeFleur. The headquarters is managed by Mr. Frederick Lunn, with the Technical Department being directed by Mr. Garry Markham.

The Bahamas competed at the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney, Australia.

The Barbados national rugby union team represents Barbados at the sport of rugby union. Barbados has been playing international rugby union since the mid-1990s. They have thus far not qualified for a Rugby World Cup. Barbados has also hosted the Caribbean Championship.
Stephanie Jutta Schwabe is a geomicrobiologist. She completed a Ph.D. in the biogeochemical investigation of caves within the Bahamian carbonate platforms, commonly referred to as blue holes. She is an expert geologic diver mostly in Bahamian blues holes, though her experience extends to expeditions in U.S. waters. Diver International named her one of the top 40 divers in the world. She earned a degree in law with a focus on international environmental law.
The Bahamas national rugby union team represent the Bahamas in the sport of rugby union. The team have thus far not qualified for a Rugby World Cup, but have participated in qualifying tournament. The nation is classified as tier three by the International Rugby Board (IRB).
The Cayman Islands national rugby union team represents the Cayman Islands in the sport of rugby union. They have thus far not qualified for a Rugby World Cup, but have participated in qualifying tournaments. The sport in the Cayman Islands is governed by the Cayman Rugby Union. The Cayman Islands have players throughout the squad playing through the UK, Ireland, South Africa, Canada and the USA.

Association Internationale pour le Développement de l'Apnée (AIDA) is a worldwide rule- and record-keeping body for competitive breath holding events, also known as freediving. It sets standards for safety, comparability of Official World Record attempts and freedive education. AIDA International is the parent organization for national clubs of the same name.
The Bahamas President's Cup is the top knockout tournament of the Bahamas football. The cup was created in 1999.
Religion in the Bahamas is dominated by various Christian denominations and reflects the country's diversity. Since the English colonization, most Bahamians adhere to diverse Protestant denominations with Anglicanism, Baptist churches, Pentecostalism, Adventism and Methodism being at the forefront. There is no state religion in the Bahamas, and there is generally free practice of religious beliefs.

The Catholic Church in the Bahamas is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome. Columbus landed on one of the islands of the Bahamas in 1492 which he named San Salvador.
The High Commissioner of the United Kingdom to the Bahamas is the United Kingdom's foremost diplomatic representative to the Commonwealth of The Bahamas.
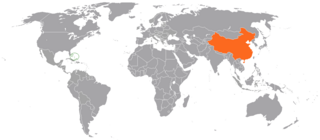
Bahamas–China relations refers to bilateral relations between the People's Republic of China and the Bahamas. Diplomatic relations were established on May 23, 1997. Less than two months later, the Chinese government opened up an embassy in Nassau, on the island of New Providence. The government of The Bahamas has not established an embassy in Beijing, although in 1999 Dr. Arthur Foulkes was appointed the first non-resident ambassador. Prime Minister Hubert Ingraham became the first Bahamian head of government to visit China in 1997.

Bahamas–Mexico relations refers to the diplomatic relations between the Commonwealth of the Bahamas and the United Mexican States. Both nations are members of the Association of Caribbean States, Organization of American States and the United Nations.

The COVID-19 pandemic in the Bahamas is part of the COVID-19 pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The outbreak was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, declared to be a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January 2020, and recognised as a pandemic by the World Health Organization on 11 March 2020. It was confirmed to have reached the Bahamas on 15 March 2020 with the announcement of the first case.
![]() Media related to 1999 in the Bahamas at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 1999 in the Bahamas at Wikimedia Commons