
Carbon dioxide is a colorless gas with a density about 53% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gas. The current concentration is about 0.04% (412 ppm) by volume, having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Natural sources include volcanoes, hot springs and geysers, and it is freed from carbonate rocks by dissolution in water and acids. Because carbon dioxide is soluble in water, it occurs naturally in groundwater, rivers and lakes, ice caps, glaciers and seawater. It is present in deposits of petroleum and natural gas. Carbon dioxide has a sharp and acidic odor and generates the taste of soda water in the mouth. However, at normally encountered concentrations it is odorless.

In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn, form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
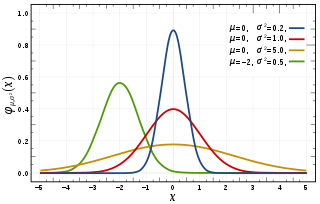
In probability theory, a normaldistribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
The number π is a mathematical constant. It is defined as the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, and it also has various equivalent definitions. It appears in many formulas in all areas of mathematics and physics. The earliest known use of the Greek letter π to represent the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter was by Welsh mathematician William Jones in 1706. It is approximately equal to 3.14159. It has been represented by the Greek letter "π" since the mid-18th century, and is spelled out as "pi". It is also referred to as Archimedes' constant.
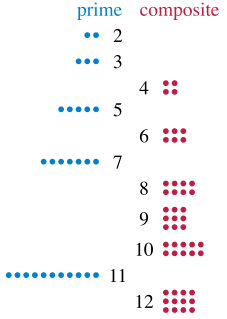
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order.
Python is an interpreted high-level general-purpose programming language. Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant indentation. Its language constructs as well as its object-oriented approach aim to help programmers write clear, logical code for small and large-scale projects.
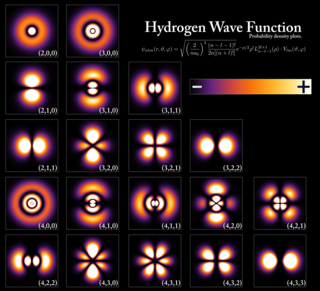
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.
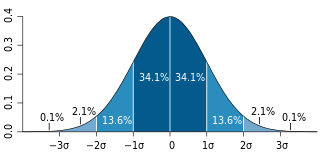
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range.

U2 are an Irish rock band from Dublin, formed in 1976. The group consists of Bono, the Edge, Adam Clayton, and Larry Mullen Jr.. Initially rooted in post-punk, U2's musical style has evolved throughout their career, yet has maintained an anthemic quality built on Bono's expressive vocals and the Edge's chiming, effects-based guitar sounds. Their lyrics, often embellished with spiritual imagery, focus on personal and sociopolitical themes. Popular for their live performances, the group have staged several ambitious and elaborate tours over their career.
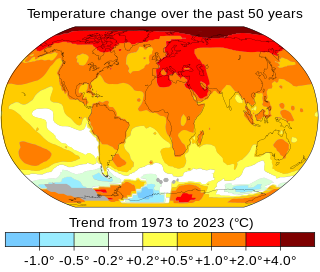
Climate change includes both global warming driven by human emissions of greenhouse gases and the resulting large-scale shifts in weather patterns. Though there have been previous periods of climatic change, since the mid-20th century humans have had an unprecedented impact on Earth's climate system and caused change on a global scale.

Levomoramide is the inactive isomer of the opioid analgesic dextromoramide, invented by the chemist Paul Janssen in 1956. Unlike dextromoramide, which is a potent analgesic with high abuse potential, levomoramide is virtually without activity.

Trimethyldiphenylpropylamine (N,N,1-Trimethyl-3,3-diphenylpropylamine) is a drug used for functional gastrointestinal disorders. Its tradename is Recipavrin.

The Academy Award for Best Actor is an award presented annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS). It is given in honor of an actor who has delivered an outstanding performance in a leading role while working within the film industry. The award is traditionally presented by the previous year's Best Actress winner.
The molecular formula C18H23N (molar mass: 253.382 g/mol) may refer to:
Diphenylpropylamine is a propylamine derivative and may refer to:

3,3-Diphenylpropylamine is a form of diphenylpropylamine.

2,3-Diphenylpropylamine is a form of diphenylpropylamine.
The molecular formula C15H17N (molar mass: 211.30 g/mol, exact mass: 211.1361 u) may refer to:

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Colloquially known as simply the coronavirus, it was previously referred to by its provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called human coronavirus 2019. The World Health Organization declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January 2020, and a pandemic on 11 March 2020.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.














