| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
This article is a list of events in the year 2005 in Chad .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
This article is a list of events in the year 2005 in Chad .
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It borders Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west. Due to its distance from the sea and its largely desert climate, the country is sometimes referred to as the "Dead Heart of Africa".
The Chad National Army consists of the five Defence and Security Forces listed in Article 185 of the Chadian Constitution that came into effect on 4 May 2018. These are the National Army, the National Police, the National and Nomadic Guard (GNNT) and the Judicial Police.

Idriss Déby Itno was a Chadian politician and military officer who was the 6th president of Chad from 1991 until his death in 2021 during the Northern Chad offensive. His term of office of more than 30 years makes him Chad's longest-serving president.
Adré is the main town of the Assoungha department in the Ouaddaï Region of Chad. It is located very close to Chad's eastern border with Sudan, 400m away. The town is served by Adré Airport.

The Chadian Civil War of 2005–2010 began on December 18, 2005. Since its independence from France in 1960, Chad has been swamped by civil wars between the Arab-Muslims of the north and the Sub-Saharan-Christians of the south. As a result, leadership and presidency in Chad drifted back and forth between the Christian southerners and Muslim northerners. When one side was in power, the other side usually started a revolutionary war to counter it.
The Battle of N'Djamena took place between the forces of the revolutionary United Front for Democratic Change (UFCD) and the military of Chad that occurred on 13 April 2006 when rebel forces launched an assault on the capital of Chad in the pre-dawn hours, attempting to overthrow the government of President Idriss Déby Itno from their bases an estimated thousand miles east.

The War in Darfur, also nicknamed the Land Cruiser War, was a major armed conflict in the Darfur region of Sudan that began in February 2003 when the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM) and the Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) rebel groups began fighting against the government of Sudan, which they accused of oppressing Darfur's non-Arab population. The government responded to attacks by carrying out a campaign of ethnic cleansing against Darfur's non-Arabs. This resulted in the death of hundreds of thousands of civilians and the indictment of Sudan's president, Omar al-Bashir, for genocide, war crimes, and crimes against humanity by the International Criminal Court.
Tama are a non-Arab, African ethnic group of people who live in eastern Chad and western Sudan. They speak Tama, a Nilo-Saharan language. The population is 200,000–300,000 people and they practice Islam. Many Tama are subsistence farmers who live in permanent settlements and some raise livestock. In the civil war in Chad the Tama were involved in ethnic conflicts with the Zaghawa tribe.
Throughout its history, Darfur has been the home to several cultures and kingdoms, such as the Daju and Tunjur kingdoms. The recorded history of Darfur begins in the seventeenth century, with the foundation of the Fur Sultanate by the Keira dynasty. In 1875, the Anglo-Egyptian condominium in Khartoum ended the dynasty. The British allowed Darfur a measure of autonomy until formal annexation in 1916. However, the region remained underdeveloped through the period of colonial rule and after independence in 1956. The majority of national resources were directed toward the riverine Arabs clustered along the Nile near Khartoum. This pattern of structural inequality and overly underdevelopment resulted in increasing restiveness among Darfuris. The influence of regional geopolitics and war by proxy, coupled with economic hardship and environmental degradation, from soon after independence led to sporadic armed resistance from the mid-1980s. The continued violence culminated in an armed resistance movement around 2003.
Events from the year 2007 in Chad.
General Mahamat Nouri is a Chadian insurgent leader who currently commands the Union of Forces for Democracy and Development (UFDD). A Muslim from northern Chad, he began his career as a FROLINAT rebel, and when the group's Second Army split in 1976 he sided with his kinsman Hissène Habré. As Habré's associate he obtained in 1978 the first of the many ministerial positions in his career, becoming Interior Minister in a coalition government. When Habré reached the presidency in 1982, Nouri was by his side and played an important role in the regime.
The Battle of N'Djamena began on February 2, 2008, when Chadian rebel forces opposed to Chadian President Idriss Déby entered N'Djamena, the capital of Chad, after a three-day advance through the country. The rebels were initially successful, taking a large part of the city and attacking the heavily defended presidential palace. They did not capture the palace, and after two days of fighting they withdrew to outside the city. Around two days later they retreated east.
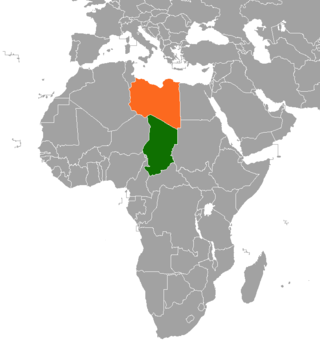
Chad–Libya relations have arisen out of centuries from ethnic, religious, and commercial ties.
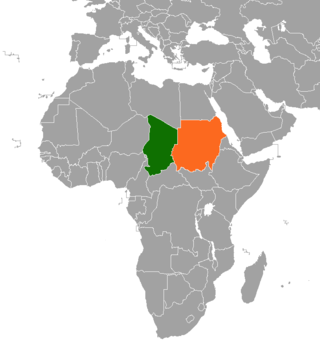
The populations of eastern Chad and western Sudan established social and religious ties long before either nation's independence, and these remained strong despite disputes between governments. In recent times, relations have been strained due to the conflict in Darfur and a civil war in Chad, which both governments accuse the other of supporting.
The following details notable events from the year 2008 in Chad. Chad is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west.

Acheikh Ibn-Oumar is a Chadian politician and military leader. In the 1980s he led the Democratic Revolutionary Council, a military-political group opposing the government of President Hissène Habré. He studied mathematics in France, and then, in the late 70's, joined the historical Chadian revolutionary mouvement FROLINAT . He held several cabinet positions within the GUNT, led by Goukouni Weddeye . In November 1984, Acheikh Ibn-Oumar was arrested in Tripoli and then transferred to Tibesti where he remained in detention until December 1985, because of serious divergences with both late Colonel Gaddafi and Goukouni. After a short-lived reconciliation with Goukouni, in 1986, Acheikh Ibn-Oumar and the CDR withdrew support for Goukouni Oueddei, leaving Goukouni isolated. Libya switched support from Goukouni to Ibn-Oumar, backing Ibn-Oumar's forces as they took Ennedi in northern Chad, and sending aircraft and tanks to help Ibn-Oumar defend against a counter-attack by Toubou forces loyal to Goukouni. In mid-November 1986, supported by Libya, Ibn-Oumar became president of a newly constituted GUNT, consisting of seven of the original eleven factions. In 1987 Ibn-Oumar's militia was driven into Darfur by French and Chadian forces, fighting the Fur people there. In defeat Acheikh Ibn Oumar distributed 1,500 automatic weapons to his Arab allies in Chad and "across the international boundary in Darfur."
Events in the year 2013 in Chad.

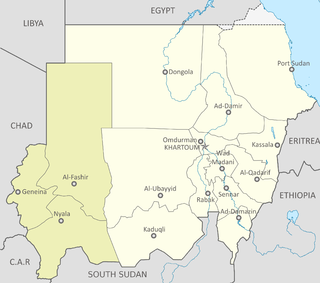
The Geneina massacre, also the Battle of Geneina, was a series of major battles for control of Geneina, the capital of West Darfur in Sudan, between the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) and allied militias against Masalit self-defense militias and the Sudanese Alliance. The battles primarily lasted between April 24 and June 14, 2023, with major attacks and massacres by the RSF and allied militias on Masalit civilians in the city. After the killing of West Darfur governor Khamis Abakar on June 14, thousands of Masalit civilians were slaughtered in the city between June 14 and June 22 by the RSF and allied militias.
On April 10, 2023, clashes broke out between Masalit and Arab civilians in Foro Baranga, West Darfur, Sudan, killing at least 25 people. Four days later the clashes ceased but a wider national conflict broke out.
Between April 3 and 8, 2021, clashes broke out between Arabs and Masalit in El Geneina, Sudan following the killing on April 3 of two Masalit men on a road separating Arab and Masalit neighborhoods in Krinding. At least 144 people were killed and 233 injured in the clashes. The clashes were the second major conflict in Krinding in 2021, with ethnic clashes occurring in January as well that killed 163 people.